Product, Matrix Multiply
Multiply and divide scalars and nonscalars or multiply and invert matrices
Libraries:
Simulink /
Commonly Used Blocks
Simulink /
Math Operations
Simulink /
Matrix Operations
HDL Coder /
Commonly Used Blocks
HDL Coder /
HDL Floating Point Operations
HDL Coder /
Math Operations
Description
The Product block outputs the result of multiplying two inputs: two scalars, a scalar and a nonscalar, or two nonscalars that have the same dimensions. The default parameter values that specify this behavior are:
Multiplication:
Element-wise(.*)Number of inputs:
2
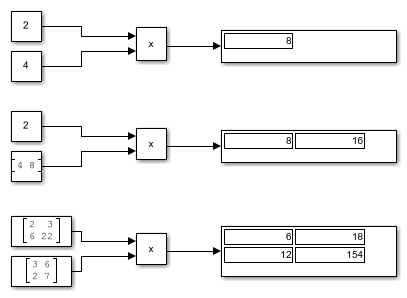
This table shows the output of the Product block for Multiply Inputs of Different Dimensions with the Product Block using default block parameter values.
| Inputs and Behavior | Example |
|---|---|
Scalar X Scalar Output the product of the two inputs. |
|
Scalar X Nonscalar Output a nonscalar having the same dimensions as the input nonscalar. Each element of the output nonscalar is the product of the input scalar and the corresponding element of the input nonscalar. |
|
Nonscalar X Nonscalar Output a nonscalar having the same dimensions as the inputs. Each element of the output is the product of corresponding elements of the inputs. |
|
The Divide and Product of Elements blocks are variants of the Product block.
For information on the Divide block, see Divide.
For information on the Product of Elements block, see Product of Elements.
The Product block (or the Divide block or Product of Elements block, if appropriately configured) can:
Numerically multiply and divide any number of scalar, vector, or matrix inputs
Perform matrix multiplication and division on any number of matrix inputs
The Product block performs scalar or matrix multiplication, depending on the value of the Multiplication parameter. The block accepts one or more inputs, depending on the Number of inputs parameter. The Number of inputs parameter also specifies the operation to perform on each input.
The Product block can input any combination of scalars, vectors, and matrices for which the operation to perform has a mathematically defined result. The block performs the specified operations on the inputs, then outputs the result.
The Product block has two modes: Element-wise mode, which processes nonscalar inputs element by element, and Matrix mode, which processes nonscalar inputs as matrices.
Element-Wise Mode
When you set Multiplication to
Element-wise(.*), the Product block is in
Element-wise mode, in which it operates on the individual
numeric elements of any nonscalar inputs. The MATLAB® equivalent is the .* operator. In element-wise
mode, the Product block can perform a variety of multiplication,
division, and arithmetic inversion operations.
The value of the Number of inputs parameter controls both how many inputs exist and whether each is multiplied or divided to form the output. When the Product block is in element-wise mode and has only one input, it is functionally equivalent to a Product of Elements block. When the block has multiple inputs, any nonscalar inputs must have identical dimensions, and the block outputs a nonscalar with those dimensions. To calculate the output, the block first expands any scalar input to a nonscalar that has the same dimensions as the nonscalar inputs.
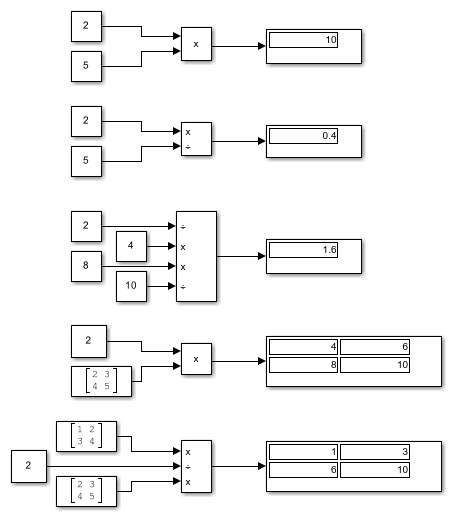
This table shows the output of the Product block for Multiply Inputs of Different Dimensions with the Product Block, using the indicated values for the Number of inputs parameter.
| Parameter Values | Examples |
|---|---|
Number of inputs:
|
|
Number of inputs:
|
|
Number of inputs:
|
|
Number of
inputs: |
|
Number of inputs:
|
|
Matrix Mode
When the value of the Multiplication parameter is
Matrix(*), the Product block is in
Matrix mode, in which it processes nonscalar inputs as
matrices. The MATLAB equivalent is the * operator. In Matrix mode, the
Product block can invert a single square matrix, or multiply and
divide any number of matrices that have dimensions for which the result is
mathematically defined.
The value of the Number of inputs parameter controls both how many inputs exist and whether each input matrix is multiplied or divided to form the output. The syntax of Number of inputs is the same as in element-wise mode. The difference between the modes is in the type of multiplication and division that occur.
Interactions Between Block Inputs and Modes
The interactions between the Product block inputs and its Multiplication modes are:
1or*or/The block has one input port. In element-wise mode, the block processes the input as described for the Product of Elements block. In matrix mode, if the parameter value is
1or*, the block outputs the input value. If the value is/, the input must be a square matrix (including a scalar as a degenerate case) and the block outputs the matrix inverse. See Element-Wise Mode and Matrix Mode for more information.Integer value > 1
The block has the number of inputs given by the integer value. The inputs are multiplied together in element-wise mode or matrix mode, as specified by the Multiplication parameter. See Element-Wise Mode and Matrix Mode for more information.
Unquoted string of two or more
*and/charactersThe block has the number of inputs given by the length of the character vector. Each input that corresponds to a
*character is multiplied into the output. Each input that corresponds to a/character is divided into the output. The operations occur in element-wise mode or matrix mode, as specified by the Multiplication parameter. See Element-Wise Mode and Matrix Mode for more information.
Expected Differences Between Simulation and Code Generation
For element-wise operations on complex floating-point inputs, simulation and code generation results might differ in near-overflow cases. Although complex numbers is selected and non-finite numbers is not selected on the Code Generation > Interface pane of the Configuration Parameters dialog box, the code generator does not emit special case code for intermediate overflows. This method improves the efficiency of embedded operations for the general case that does not include extreme values. If the inputs could include extreme values, you must manage these cases explicitly.
The generated code might not produce the same pattern of NaN
and inf values as simulation when these values are mathematically
meaningless. For example, if the simulation output contains a
NaN, output from the generated code also contains a
NaN, but not necessarily in the same place.
Examples
Ports
Input
Output
Parameters
Block Characteristics
Data Types |
|
Direct Feedthrough |
|
Multidimensional Signals |
|
Variable-Size Signals |
|
Zero-Crossing Detection |
|








![2D matrix with Constant block value [1 2 3;7 6 4] as input to Product block configured for all dimensions](prod_alldim.png)
![2D matrix with Constant block value [1 2 3;7 6 4] as input to Product block configured for dimension 2](prod_2dim.png)