countlabels
Description
Use this function when you are working on a machine or deep learning classification problem and you want to look at the proportions of label values in your dataset.
cnt = countlabels(lblsrc,Name,Value)'TableVariable','Color' reads the labels corresponding to
'Color'.
Examples
Categorical Arrays
Generate a categorical array with the categories A, B, C, and D. The array contains samples of each category.
lbls = categorical(["B" "C" "A" "D" "B" "A" "A" "B" "C" "A"]', ... ["A" "B" "C" "D"])
lbls = 10×1 categorical
B
C
A
D
B
A
A
B
C
A
Count the number of unique label category values in the array.
cnt = countlabels(lbls)
cnt=4×3 table
Label Count Percent
_____ _____ _______
A 4 40
B 3 30
C 2 20
D 1 10
Generate a second categorical array with the same categories. The array contains samples of each category and one sample with a missing value.
mlbls = categorical(["B" "C" "A" "D" "B" "A" missing "B" "C" "A"]', ... ["A" "B" "C" "D"])
mlbls = 10×1 categorical
B
C
A
D
B
A
<undefined>
B
C
A
Count the number of unique label category values in the array. The sample with a missing value is included in the count as <undefined>.
mcnt = countlabels(mlbls)
mcnt=5×3 table
Label Count Percent
___________ _____ _______
A 3 30
B 3 30
C 2 20
D 1 10
<undefined> 1 10
Character Arrays
Read William Shakespeare's sonnets with the fileread function. Remove all nonalphabetic characters from the text and convert to lowercase.
sonnets = fileread("sonnets.txt"); letters = lower(sonnets(regexp(sonnets,"[A-z]")))';
Count how many times each letter appears in the sonnets. List the letters that appear most often.
cnt = countlabels(letters); cnt = sortrows(cnt,"Count","descend"); head(cnt)
Label Count Percent
_____ _____ _______
e 9028 12.298
t 7210 9.8216
o 5710 7.7782
h 5064 6.8982
s 4994 6.8029
a 4940 6.7293
i 4895 6.668
n 4522 6.1599
Numeric Arrays
Use the poisrand function to generate an array of 1000 random integers from the Poisson distribution with rate parameter 3. Plot a histogram of the results.
N = 1000; lam = 3; nums = zeros(N,1); for jk = 1:N nums(jk) = poisrand(lam); end histogram(nums)
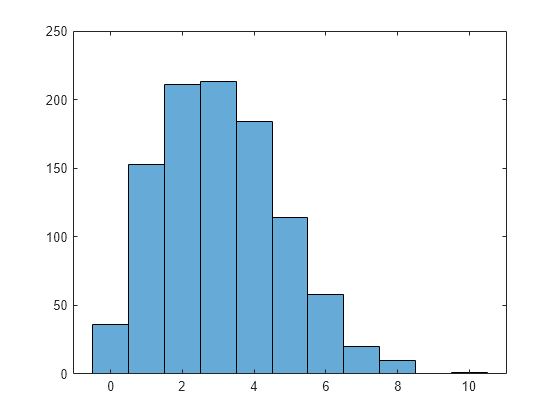
Count the frequencies of the integers represented in the array.
mm = countlabels(nums)
mm=10×3 table
Label Count Percent
_____ _____ _______
0 36 3.6
1 153 15.3
10 1 0.1
2 211 21.1
3 213 21.3
4 184 18.4
5 114 11.4
6 58 5.8
7 20 2
8 10 1
function num = poisrand(lam) % Poisson random integer using rejection method p = 0; num = -1; while p <= lam p = p - log(rand); num = num + 1; end end
Create a table of characters with two variables. The first variable Type1 contains instances of the letters P, Q, and R. The second variable Type2 contains instances of the letters A, B, and D.
tbl = table(["P" "R" "P" "Q" "Q" "Q" "R" "P"]', ... ["A" "B" "B" "A" "D" "D" "A" "A"]',... 'VariableNames',["Type1","Type2"]);
Count how many times each letter appears in each of the table variables.
cnt = countlabels(tbl,'TableVariable','Type1')
cnt=3×3 table
Type1 Count Percent
_____ _____ _______
P 3 37.5
Q 3 37.5
R 2 25
cnt = countlabels(tbl,'TableVariable','Type2')
cnt=3×3 table
Type2 Count Percent
_____ _____ _______
A 4 50
B 2 25
D 2 25
Create an ArrayDatastore object containing the table.
ads = arrayDatastore(tbl,'OutputType','same');
Count how many times each letter appears in each of the table variables.
cnt = countlabels(ads,'TableVariable','Type1')
cnt=3×3 table
Type1 Count Percent
_____ _____ _______
P 3 37.5
Q 3 37.5
R 2 25
cnt = countlabels(ads,'TableVariable','Type2')
cnt=3×3 table
Type2 Count Percent
_____ _____ _______
A 4 50
B 2 25
D 2 25
Input Arguments
Input label source, specified as one of these:
A categorical vector.
A string vector or a cell array of character vectors.
A numeric vector or a cell array of numeric scalars.
A logical vector or a cell array of logical scalars.
A table with variables containing any of the previous data types.
A datastore whose
readallfunction returns any of the previous data types.A
CombinedDatastoreobject containing an underlying datastore whosereadallfunction returns any of the previous data types. In this case, you must specify the index of the underlying datastore that has the label values.
lblsrc must contain labels that can be converted to a vector with a discrete set of categories.
Example: lblsrc = categorical(["B" "C" "A" "E" "B" "A" "A" "B" "C" "A"],["A" "B" "C"
"D"]) creates the label source as a ten-sample categorical vector with
four categories: A, B, C, and
D.
Example: lblsrc = [0 7 2 5 11 17 15 7 7 11] creates the label source
as a ten-sample numeric vector.
Data Types: single | double | int8 | int16 | int32 | int64 | uint8 | uint16 | uint32 | uint64 | logical | char | string | table | cell | categorical
Name-Value Arguments
Specify optional pairs of arguments as
Name1=Value1,...,NameN=ValueN, where Name is
the argument name and Value is the corresponding value.
Name-value arguments must appear after other arguments, but the order of the
pairs does not matter.
Before R2021a, use commas to separate each name and value, and enclose
Name in quotes.
Example: 'TableVariable','Sex','UnderlyingDatastoreIndex',5 reads the
labels corresponding to 'Sex' only in the fifth underlying datastore of a
combined datastore.
Table variable to read, specified as a character vector or string scalar. If this argument is
not specified, then countlabels uses the first table
variable.
Underlying datastore index, specified as an integer scalar. This argument applies when
lblsrc is a CombinedDatastore
object. countlabels counts the labels in the datastore obtained
using the UnderlyingDatastores property of
lblsrc.
Output Arguments
Unique label counts, returned as a table with these variables:
Label— Unique label category values. If'TableVariable'is specified, then theLabelname is replaced with the table variable name.Count— Number of instances of each label value.Percent— Proportion of each label value, expressed as a percentage.
Version History
Introduced in R2021a
See Also
Signal
Labeler | labeledSignalSet | signalLabelDefinition | filenames2labels | folders2labels | splitlabels
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.
Website auswählen
Wählen Sie eine Website aus, um übersetzte Inhalte (sofern verfügbar) sowie lokale Veranstaltungen und Angebote anzuzeigen. Auf der Grundlage Ihres Standorts empfehlen wir Ihnen die folgende Auswahl: .
Sie können auch eine Website aus der folgenden Liste auswählen:
So erhalten Sie die bestmögliche Leistung auf der Website
Wählen Sie für die bestmögliche Website-Leistung die Website für China (auf Chinesisch oder Englisch). Andere landesspezifische Websites von MathWorks sind für Besuche von Ihrem Standort aus nicht optimiert.
Amerika
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
Europa
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)