signalLabelDefinition
Create signal label definition
Description
Use signalLabelDefinition to create signal label definitions for
data sets. The labels can correspond to attributes, regions, or points of interest. Use a
vector of signalLabelDefinition objects to create a labeledSignalSet.
Creation
Description
sld = signalLabelDefinition(name,PropertyName=Value)
Input Arguments
Label name, specified as a character vector or string scalar.
Data Types: char | string
Properties
Name of label, specified as a character vector or string scalar.
Data Types: char | string
Type of label, specified as one of these:
"attribute"— Define signal characteristics."roi"— Define signal characteristics over regions of interest in the time domain."point"— Define signal characteristics over points of interest in the time domain."attributeFeature"— Define signal characteristics that correspond to features."roiFeature"— Define signal characteristics over regions of interest that correspond to features."roiTimeFrequency"— Define signal characteristics over regions of interest in the time-frequency domain.
Data Types: char | string
Data type of label, specified as "logical",
"categorical", "numeric",
"string", "table", or
"timetable". When you set this property to
"categorical", use the Categories property to specify the array
of categories. The object does not support timetable and table data types for
attributeFeature and roiFeature labels.
Data Types: char | string
Label category names, specified as a string array or a cell array of character
vectors. The array must have unique elements. This property applies only when the
LabelDataType property is set to "categorical".
Example: LabelDataType="categorical",Categories=["apple","orange"]
Data Types: char | string
Data type of point locations, specified as either "double" or
"duration". This property applies only when LabelType
is set to "point".
Data Types: char | string
Validation function, specified as a function handle. Use this property when setting
label values in a labeledSignalSet object. The specified function must
return true when given a valid input value and
false when given an invalid input value. This property applies only
when LabelDataType is set to "logical",
"numeric", "table", or
"timetable".
If you do not specify a validation function:
If
LabelDataTypeis set to"categorical", thesignalLabelDefinitionobject checks that each input value belongs to one of the categories specified using Categories.Otherwise, the
signalLabelDefinitionobject checks only that each input value is of the correct data type.
Example: LabelDataType="numeric",DefaultValue=1,ValidationFunction=@(x)x<2
Data Types: function_handle
Default value of label, specified as a value of the type specified using LabelDataType. If LabelDataType is set to "categorical", then DefaultValue must be one of the values specified using Categories.
Example: LabelDataType="categorical",Categories=["apple","orange"],DefaultValue="apple"
Data Types: char | double | logical | string | table
Label description, specified as a character vector or string scalar.
Example: Description="Patient is asleep"
Data Types: char | string
Label tag identifier, specified as a character vector or string scalar. Use this property to identify the same label in a larger labeling scheme or public labeling set.
Example: Tag="Peak1"
Data Types: char | string
Array of sublabels, specified as a signal label definition object. To specify more
than one sublabel, set this property to a vector of signal label definition objects. Use
this property to create a relationship between a parent label and its children. If
LabelType
is set to "attributeFeature" or "roiFeature", then
this property does not apply.
Note
Sublabels cannot have sublabels.
Example: Sublabels=[signalLabelDefinition("negative"),signalLabelDefinition("positive")]
Frame size, specified as a numeric scalar. You must specify
FrameSize if LabelType
is set to "roiFeature".
Example: FrameSize=50
Data Types: double
Overlap length of adjacent frames, specified as a numeric scalar. To enable this
property, set LabelType
to "roiFeature". You cannot specify
FrameOverlapLength and FrameRate
simultaneously. If you do not specify FramerOverlapLength, then the
object assumes the overlap length to be zero.
Example: FrameSize=50,FrameOverlapLength=5
Data Types: double
Frame rate, specified as a numeric scalar. To enable this property, set LabelType
to "roiFeature". You cannot specify FrameRate
and FrameOverlapLength simultaneously. If you do not specify
FrameRate, then the object assumes no overlap between
frames.
Example: FrameSize=50,FrameRate=45
Data Types: double
Since R2025a
Time-frequency options, specified as a labelSpectrogramOptions object. Use a
labelSpectrogramOptions object to store spectrogram options for
signal labeling in the time-frequency domain.
Data Types: labelSpectrogramOptions
Since R2025a
Member channel, specified as a positive integer. Specify which channel of the member to use when computing the time-frequency map for time-frequency labeling.
To specify this argument, you must set LabelType to
"roiTimeFrequency".
Data Types: double
Object Functions
labelDefinitionsHierarchy | Get hierarchical list of label and sublabel names |
labelDefinitionsSummary | Get summary table of signal label definitions |
Examples
Consider a set of whale sound recordings. The recorded whale sounds consist of trills and moans. Trills sound like series of clicks. Moans are low-frequency cries similar to the sound made by a ship's horn. You want to look at each signal and label it to identify the whale type, the trill regions, and the moan regions. For each trill region, you also want to label the signal peaks higher than a certain threshold.
Signal Label Definitions
Define an attribute label to store whale types. The possible categories are blue whale, humpback whale, and white whale.
dWhaleType = signalLabelDefinition("WhaleType", ... LabelType="attribute", ... LabelDataType="categorical", ... Categories=["blue" "humpback" "white"], ... Description="Whale type");
Define a region-of-interest (ROI) label to capture moan regions. Define another ROI label to capture trill regions.
dMoans = signalLabelDefinition("MoanRegions", ... LabelType="roi", ... LabelDataType="logical", ... Description="Regions where moans occur"); dTrills = signalLabelDefinition("TrillRegions", ... LabelType="roi", ... LabelDataType="logical", ... Description="Regions where trills occur");
Finally, define a point label to capture the trill peaks. Set this label as a sublabel of the dTrills definition.
dTrillPeaks = signalLabelDefinition("TrillPeaks", ... LabelType="point", ... LabelDataType="numeric", ... Description="Trill peaks"); dTrills.Sublabels = dTrillPeaks;
Labeled Signal Set
Create a labeledSignalSet with the whale signals and the label definitions. Add label values to identify the whale type, the moan and trill regions, and the peaks of the trills.
load labelwhalesignals lbldefs = [dWhaleType dMoans dTrills]; lss = labeledSignalSet({whale1 whale2},lbldefs, ... MemberNames=["Whale1" "Whale2"], ... SampleRate=Fs,Description="Characterize whale song regions");
Visualize the label hierarchy and label properties using labelDefinitionsHierarchy and labelDefinitionsSummary.
labelDefinitionsHierarchy(lss)
ans =
'WhaleType
Sublabels: []
MoanRegions
Sublabels: []
TrillRegions
Sublabels: TrillPeaks
'
labelDefinitionsSummary(lss)
ans=3×9 table
LabelName LabelType LabelDataType Categories ValidationFunction DefaultValue Sublabels Tag Description
______________ ___________ _____________ ____________ __________________ ____________ ___________________________ ___ ____________________________
"WhaleType" "attribute" "categorical" {3×1 string} {["N/A" ]} {0×0 double} {0×0 double } "" "Whale type"
"MoanRegions" "roi" "logical" {["N/A" ]} {0×0 double} {0×0 double} {0×0 double } "" "Regions where moans occur"
"TrillRegions" "roi" "logical" {["N/A" ]} {0×0 double} {0×0 double} {1×1 signalLabelDefinition} "" "Regions where trills occur"
The signals in the loaded data correspond to songs of two blue whales. Set the "WhaleType" values for both signals.
setLabelValue(lss,1,"WhaleType","blue"); setLabelValue(lss,2,"WhaleType","blue");
Visualize the Labels property. The table has the newly added "WhaleType" values for both signals.
lss.Labels
ans=2×3 table
WhaleType MoanRegions TrillRegions
_________ ___________ ____________
Whale1 blue {0×2 table} {0×3 table}
Whale2 blue {0×2 table} {0×3 table}
Visualize Region Labels
Visualize the whale songs to identify the trill and moan regions.
subplot(2,1,1) plot((0:length(whale1)-1)/Fs,whale1) ylabel("Whale 1") subplot(2,1,2) plot((0:length(whale2)-1)/Fs,whale2) ylabel("Whale 2")

Moan regions are sustained low-frequency wails.
whale1has moans centered at about 7 seconds, 12 seconds, and 17 seconds.whale2has moans centered at about 3 seconds, 7 seconds, and 16 seconds.
Add the moan regions to the labeled set. Specify the ROI limits in seconds and the label values.
moanRegionsWhale1 = [6.1 7.7; 11.4 13.1; 16.5 18.1]; mrsz1 = [size(moanRegionsWhale1,1) 1]; setLabelValue(lss,1,"MoanRegions",moanRegionsWhale1,true(mrsz1)); moanRegionsWhale2 = [2.5 3.5; 5.8 8; 15.4 16.7]; mrsz2 = [size(moanRegionsWhale2,1) 1]; setLabelValue(lss,2,"MoanRegions",moanRegionsWhale2,true(mrsz2));
Trill regions have distinct bursts of sound punctuated by silence.
whale1has a trill centered at about 2 seconds.whale2has a trill centered at about 12 seconds.
Add the trill regions to the labeled set.
trillRegionWhale1 = [1.4 3.1]; trsz1 = [size(trillRegionWhale1,1) 1]; setLabelValue(lss,1,"TrillRegions",trillRegionWhale1,true(trsz1)); trillRegionWhale2 = [11.1 13]; trsz2 = [size(trillRegionWhale1,1) 1]; setLabelValue(lss,2,"TrillRegions",trillRegionWhale2,true(trsz2));
Create a signalMask object for each whale song and use it to visualize and label the different regions. For better visualization, change the label values from logical to categorical.
mr1 = getLabelValues(lss,1,"MoanRegions"); mr1.Value = categorical(repmat("moan",mrsz1)); tr1 = getLabelValues(lss,1,"TrillRegions"); tr1.Value = categorical(repmat("trill",trsz1)); msk1 = signalMask([mr1;tr1],"SampleRate",Fs); subplot(2,1,1) plotsigroi(msk1,whale1) ylabel("Whale 1") hold on mr2 = getLabelValues(lss,2,"MoanRegions"); mr2.Value = categorical(repmat("moan",mrsz2)); tr2 = getLabelValues(lss,2,"TrillRegions"); tr2.Value = categorical(repmat("trill",trsz2)); msk2 = signalMask([mr2;tr2],"SampleRate",Fs); subplot(2,1,2) plotsigroi(msk2,whale2) ylabel("Whale 2") hold on

Visualize Point Labels
Label three peaks for each trill region. For point labels, you specify the point locations and the label values. In this example, the point locations are in seconds.
peakLocsWhale1 = [1.553 1.626 1.7]; peakValsWhale1 = [0.211 0.254 0.211]; setLabelValue(lss,1,["TrillRegions" "TrillPeaks"], ... peakLocsWhale1,peakValsWhale1,LabelRowIndex=1); subplot(2,1,1) plot(peakLocsWhale1,peakValsWhale1,"v") hold off peakLocsWhale2 = [11.214 11.288 11.437]; peakValsWhale2 = [0.119 0.14 0.15]; setLabelValue(lss,2,["TrillRegions" "TrillPeaks"], ... peakLocsWhale2,peakValsWhale2,LabelRowIndex=1); subplot(2,1,2) plot(peakLocsWhale2,peakValsWhale2,"v") hold off

Explore Label Values
Explore the label values using getLabelValues.
getLabelValues(lss)
ans=2×3 table
WhaleType MoanRegions TrillRegions
_________ ___________ ____________
Whale1 blue {3×2 table} {1×3 table}
Whale2 blue {3×2 table} {1×3 table}
Retrieve the moan regions for the first member of the labeled set.
getLabelValues(lss,1,"MoanRegions")ans=3×2 table
ROILimits Value
____________ _____
6.1 7.7 {[1]}
11.4 13.1 {[1]}
16.5 18.1 {[1]}
Use a second output argument to list the sublabels of a label.
[value,valueWithSublabel] = getLabelValues(lss,1,"TrillRegions")value=1×2 table
ROILimits Value
__________ _____
1.4 3.1 {[1]}
valueWithSublabel=1×3 table
ROILimits Value Sublabels
__________ _____ ___________
TrillPeaks
___________
1.4 3.1 {[1]} {3×2 table}
To retrieve the values in a sublabel, express the label name as a two-element array.
getLabelValues(lss,1,["TrillRegions","TrillPeaks"])
ans=3×2 table
Location Value
________ __________
1.553 {[0.2110]}
1.626 {[0.2540]}
1.7 {[0.2110]}
Find the value of the third trill peak corresponding to the second member of the set.
getLabelValues(lss,2,["TrillRegions" "TrillPeaks"], ... LabelRowIndex=1,SublabelRowIndex=3)
ans=1×2 table
Location Value
________ __________
11.437 {[0.1500]}
Specify the path to a set of audio signals included as MAT files with MATLAB®. Each file contains a signal variable and a sample rate. List the names of the files.
folder = fullfile(matlabroot,"toolbox","matlab","audiovideo"); lst = dir(append(folder,"/*.mat")); nms = {lst(:).name}'
nms = 7×1 cell
{'chirp.mat' }
{'gong.mat' }
{'handel.mat' }
{'laughter.mat'}
{'mtlb.mat' }
{'splat.mat' }
{'train.mat' }
Create a signal datastore that points to the specified folder. Set the sample rate variable name to Fs, which is common to all files. Generate a subset of the datastore that excludes the file mtlb.mat. Use the subset datastore as the source for a labeledSignalSet object.
sds = signalDatastore(folder,SampleRateVariableName="Fs"); sds = subset(sds,~strcmp(nms,"mtlb.mat")); lss = labeledSignalSet(sds);
Create three label definitions to label the signals:
Define a logical attribute label that is true for signals that contain human voices.
Define a numeric point label that marks the location and amplitude of the maximum of each signal.
Define a categorical region-of-interest (ROI) label to pick out nonoverlapping, uniform-length random regions of each signal.
Add the signal label definitions to the labeled signal set.
vc = signalLabelDefinition("Voice",LabelType="attribute", ... LabelDataType="logical",DefaultValue=false); mx = signalLabelDefinition("Maximum",LabelType="point", ... LabelDataType="numeric"); rs = signalLabelDefinition("RanROI",LabelType="ROI", ... LabelDataType="categorical",Categories=["ROI" "other"]); addLabelDefinitions(lss,[vc mx rs])
Label the signals:
Label
'handel.mat'and'laughter.mat'as having human voices.Use the
islocalmaxfunction to find the maximum of each signal. Label its location and value.Use the
randROIfunction to generate as many regions of length N/10 samples as can fit in a signal of length N given a minimum separation of N/6 samples between regions. Label their locations and assign them to theROIcategory.
When labeling points and regions, convert sample values to time values. Subtract 1 to account for MATLAB array indexing and divide by the sample rate.
kj = 1; while hasdata(sds) [sig,info] = read(sds); fs = info.SampleRate; [~,fn] = fileparts(info.FileName); if fn=="handel" || fn=="laughter" setLabelValue(lss,kj,"Voice",true) end xm = find(islocalmax(sig,MaxNumExtrema=1)); setLabelValue(lss,kj,"Maximum",(xm-1)/fs,sig(xm)) N = length(sig); rois = randROI(N,round(N/10),round(N/6)); setLabelValue(lss,kj,"RanROI",(rois-1)/fs, ... repelem("ROI",size(rois,1))) kj = kj+1; end
Verify that only two signals contain voices.
countLabelValues(lss,"Voice")ans=2×3 table
Voice Count Percent
_____ _____ _______
false 4 66.667
true 2 33.333
Verify that two signals have a maximum amplitude of 1.
countLabelValues(lss,"Maximum")ans=5×4 table
Maximum Count Percent MemberCount
______________________ _____ _______ ___________
0.80000000000000004441 1 16.667 1
0.89113331915798421612 1 16.667 1
0.94730769230769229505 1 16.667 1
1 2 33.333 2
1.0575668990330560071 1 16.667 1
Verify that each signal has four nonoverlapping random regions of interest.
countLabelValues(lss,"RanROI")ans=2×4 table
RanROI Count Percent MemberCount
______ _____ _______ ___________
ROI 24 100 6
other 0 0 0
Create two datastores with the data in the labeled signal set:
The
signalDatastoreobjectsdcontains the signal data.The
arrayDatastoreobjectldcontains the labeling information. Specify that you want to include the information corresponding to all the labels you created.
[sd,ld] = createDatastores(lss,["Voice" "RanROI" "Maximum"]);
Use the information in the datastores to plot the signals and display their labels.
Use a
signalMaskobject to highlight the regions of interest in blue.Plot yellow lines to mark the locations of the maxima.
Add a red axis label to the signals that contain human voices.
tiledlayout flow while hasdata(sd) [sg,nf] = read(sd); lbls = read(ld); nexttile msk = signalMask(lbls{:}.RanROI{:},SampleRate=nf.SampleRate); plotsigroi(msk,sg) colorbar off xlabel('') xline(lbls{:}.Maximum{:}.Location, ... LineWidth=2,Color="#EDB120") if lbls{:}.Voice{:} ylabel("VOICED",Color="#D95319") end end

function roilims = randROI(N,wid,sep) num = floor((N+sep)/(wid+sep)); hq = histcounts(randi(num+1,1,N-num*wid-(num-1)*sep),(1:num+2)-1/2); roilims = (1 + (0:num-1)*(wid+sep) + cumsum(hq(1:num)))' + [0 wid-1]; end
Since R2025a
Label Gaussian atoms in the time-frequency domain using a time-frequency region-of-interest (ROI) label definition and spectrogram options.
Generate Signal and Visualize Spectrogram
Generate a signal that consists of a voltage-controlled oscillator and four Gaussian atoms. The signal is sampled at 14 kHz for two seconds. Plot the spectrogram of the signal.
Fs = 14000; t = (0:1/Fs:2)'; st = 0.01; gaussFun = @(A,x,mu,f) exp(-(x-mu).^2/(2*st^2)).*sin(2*pi*f.*x)*A'; atomTimeCenters = [0.2 0.5 1 1.75]; atomFreqCenters = [2 6 2 5]*1000; s = gaussFun([1 1 1 1]/10,t,atomTimeCenters,atomFreqCenters); x = vco(chirp(t+.1,0,t(end),3).*exp(-2*(t-1).^2),[0.1 0.4]*Fs,Fs); s = s/10+x; bt = 0.2; tr = 0.05; op = 99; pspectrum(s,Fs,"spectrogram", ... Leakage=bt,TimeResolution=tr,OverlapPercent=op)
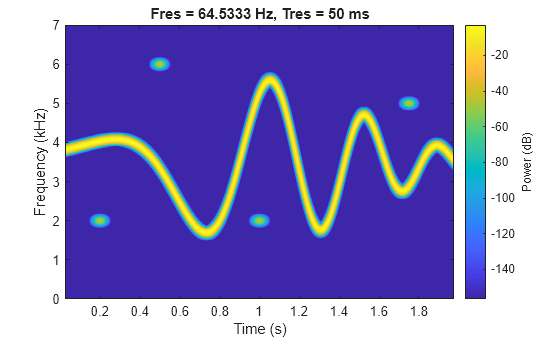
The spectrogram shows four patches in time-frequency domain that correspond with the Gaussian atoms. Define the times and frequencies for all the atoms.
atomTimes = atomTimeCenters'+[-st st]*5.5; atomFreqs = atomFreqCenters'+[-1 1]*200;
Label Signal in Time-Frequency Domain
Create a logical time-frequency ROI label definition to label the Gaussian atoms. Specify spectrogram options with leakage properties.
opts = labelSpectrogramOptions("leakage", ... Leakage=40*(1-bt),Overlap=op, ... TimeResolutionMode="specify",TimeResolution=tr); lblDef = signalLabelDefinition("Atom", ... LabelDataType="logical", ... LabelType="roiTimeFrequency",TimeFrequencyOptions=opts);
Create a labeled signal set from the signal and time-frequency ROI label definition.
lss = labeledSignalSet(s,lblDef,SampleRate=Fs);
Label the four atoms in time-frequency domain. Set the label values to true.
setLabelValue(lss,1,"Atom",atomTimes,atomFreqs,true(1,4))Visualize Time-Frequency Image and Label Mask
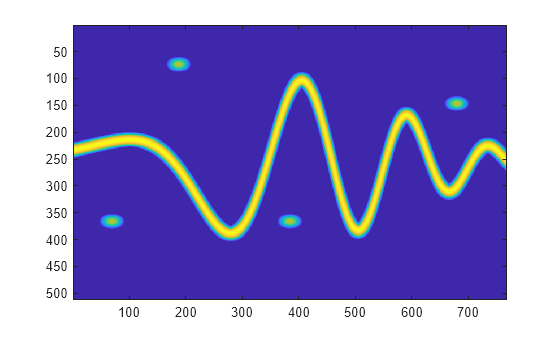
Create datastores from the labeled signal set for the time-frequency ROI label.
imSize = [512 768]; [sds,ads] = createDatastores(lss,"Atom", ... TimeFrequencyMapFormat="image", ... TimeFrequencyImageSize=imSize, ... TimeFrequencyLabelFormat="mask", ... TimeFrequencyMaskPriority=true);
Read and show the time-frequency image.
imagesc(read(sds))
Read the label mask and display it above the time-frequency image.
lbl = read(ads);
im = zeros([imSize 3]);
im(:,:,1) = lbl{1};
hold on
imagesc(im,AlphaData=0.5*lbl{1})
hold off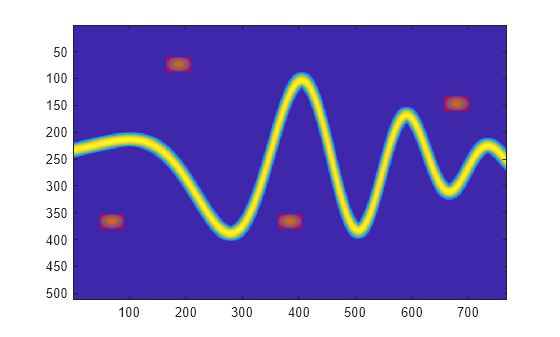
Version History
Introduced in R2018bThe signalLabelDefinition object includes these enhancements:
Set the
LabelTypeproperty to"roiTimeFrequency"to indicate an ROI time-frequency label definition.The
TimeFrequencyOptionsandMemberChannelname-value arguments enable you to specify options and a member channel to compute the time-frequency map.
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.
Website auswählen
Wählen Sie eine Website aus, um übersetzte Inhalte (sofern verfügbar) sowie lokale Veranstaltungen und Angebote anzuzeigen. Auf der Grundlage Ihres Standorts empfehlen wir Ihnen die folgende Auswahl: .
Sie können auch eine Website aus der folgenden Liste auswählen:
So erhalten Sie die bestmögliche Leistung auf der Website
Wählen Sie für die bestmögliche Website-Leistung die Website für China (auf Chinesisch oder Englisch). Andere landesspezifische Websites von MathWorks sind für Besuche von Ihrem Standort aus nicht optimiert.
Amerika
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
Europa
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)