fresnelc
Fresnel cosine integral function
Syntax
Description
fresnelc( returns the Fresnel cosine integral of
z)z.
Examples
Fresnel Cosine Integral Function for Numeric and Symbolic Input Arguments
Find the Fresnel cosine integral function for these numbers. Since these are not symbolic objects, you receive floating-point results.
fresnelc([-2 0.001 1.22+0.31i])
ans = -0.4883 + 0.0000i 0.0010 + 0.0000i 0.8617 - 0.2524i
Find the Fresnel cosine integral function symbolically by converting the numbers to symbolic objects:
y = fresnelc(sym([-2 0.001 1.22+0.31i]))
y = [ -fresnelc(2), fresnelc(1/1000), fresnelc(61/50 + 31i/100)]
Use vpa to approximate results:
vpa(y)
ans = [ -0.48825340607534075450022350335726, 0.00099999999999975325988997279422003,... 0.86166573430841730950055370401908 - 0.25236540291386150167658349493972i]
Fresnel Cosine Integral Function for Special Values
Find the Fresnel cosine integral function for special values:
fresnelc([0 Inf -Inf i*Inf -i*Inf])
ans = 0.0000 + 0.0000i 0.5000 + 0.0000i -0.5000 + 0.0000i... 0.0000 + 0.5000i 0.0000 - 0.5000i
Fresnel Cosine Integral for Symbolic Functions
Find the Fresnel cosine integral for the function exp(x)
+ 2*x:
syms f(x) f = exp(x)+2*x; fresnelc(f)
ans = fresnelc(2*x + exp(x))
Fresnel Cosine Integral for Symbolic Vectors and Arrays
Find the Fresnel cosine integral for elements of vector
V and matrix M:
syms x V = [sin(x) 2i -7]; M = [0 2; i exp(x)]; fresnelc(V) fresnelc(M)
ans = [ fresnelc(sin(x)), fresnelc(2i), -fresnelc(7)] ans = [ 0, fresnelc(2)] [ fresnelc(1i), fresnelc(exp(x))]
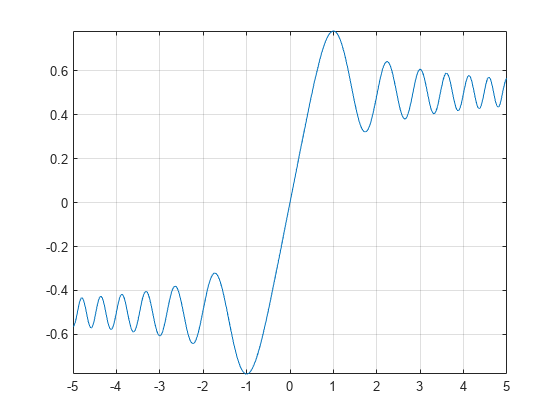
Plot Fresnel Cosine Integral Function
Plot the Fresnel cosine integral function from x = -5 to x = 5.
syms x fplot(fresnelc(x),[-5 5]) grid on
Differentiate and Find Limits of Fresnel Cosine Integral
The functions diff and
limit handle expressions containing
fresnelc.
Find the third derivative of the Fresnel cosine integral function:
syms x diff(fresnelc(x),x,3)
ans = - pi*sin((pi*x^2)/2) - x^2*pi^2*cos((pi*x^2)/2)
Find the limit of the Fresnel cosine integral function as x tends to infinity:
syms x limit(fresnelc(x),Inf)
ans = 1/2
Taylor Series Expansion of Fresnel Cosine Integral
Use taylor to expand the Fresnel cosine
integral in terms of the Taylor series:
syms x taylor(fresnelc(x))
ans = x - (x^5*pi^2)/40
Simplify Expressions Containing fresnelc
Use simplify to simplify expressions:
syms x simplify(3*fresnelc(x)+2*fresnelc(-x))
ans = fresnelc(x)
Input Arguments
More About
Algorithms
fresnelc is analytic throughout the complex plane. It satisfies fresnelc(-z) =
-fresnelc(z), conj(fresnelc(z)) =
fresnelc(conj(z)), and fresnelc(i*z) =
i*fresnelc(z) for all complex values of z.
fresnelc returns special values for z = 0, z = ±∞, and z = ±i∞ which are 0, ±5, and ±0.5i. fresnelc(z) returns symbolic function calls for all
other symbolic values of z.
Version History
Introduced in R2014a