Integrate Custom Structures in Stateflow Charts
This example shows how to use structures from custom code in a Stateflow® chart. You can define structure typed data in C code and integrate it with Stateflow structures and Simulink® buses. By sharing data with custom code, you can augment the capabilities supported by Stateflow and take advantage of your preexisting code. For more information, see Reuse Custom Code in Stateflow Charts.
In this example, a Stateflow chart processes data from one Simulink bus and outputs the result to another Simulink bus. Both the input and output buses are defined by the Simulink.Bus (Simulink)COUNTERBUS. In the chart, the Simulink buses interface with the Stateflow structures inbus and outbus. The chart calls a custom C function to write to the output structure outbus.
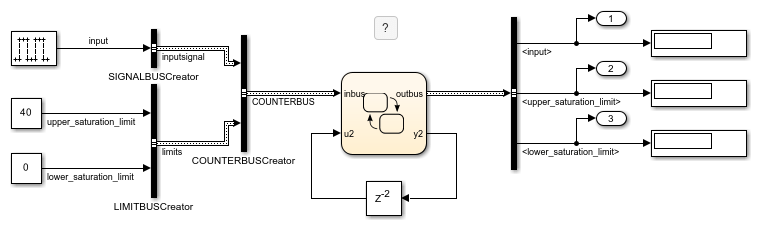
Define Custom Structures in C Code
1. In your C code, define a structure by creating a custom header file. The header file contains typedef declarations that define the properties of the custom structure. For example, in this model, the header file counterbus.h declares three custom structures:
...
typedef struct {
int input;
} SIGNALBUS;typedef struct {
int upper_saturation_limit;
int lower_saturation_limit;
} LIMITBUS;typedef struct {
SIGNALBUS inputsignal;
LIMITBUS limits;
} COUNTERBUS;
...2. In the Type Editor, define a Simulink.Bus object that matches each custom structure typedef declaration. In the Header file field of each Simulink.Bus object, enter the name of the header file that contains the matching typedef declaration.

3. Configure the Stateflow chart to include custom C code, as described in Configure Custom Code.
4. Build and run your model.
Pass Stateflow Structures to Custom Code
When you call custom code functions that take structure pointers as arguments, pass the Stateflow structures by address. To pass the address of a Stateflow structure or one of its fields to a custom function, use the & operator and dot notation:
&outbusprovides the address of the Stateflow structureoutbus.&outbus.inputsignalprovides the address of the substructureinputsignalof the structureoutbus.&outbus.inputsignal.inputprovides the address of the fieldinputof the substructureoutbus.inputsignal.
For more information, see Index and Assign Values to Stateflow Structures.
For instance, this example contains a custom C function counterbusFcn that takes structure pointers as arguments. The custom header file counterbus.h contains this function declaration:
extern void counterbusFcn(COUNTERBUS *u1, int u2, COUNTERBUS *y1, int *y2);
The chart passes the addresses to the Stateflow structures counterbus_struct and outbus by using this function call:
counterbusFcn(&counterbus_struct, u2, &outbus, &y2);

The function reads the value of the chart input u2 and the local structure counterbus_struct. It writes to the chart output y2 and the output structure outbus.

Bus Limitations for Custom Code
You cannot import a bus defined in custom code if that bus contains multidimensional arrays.
To use buses containing multidimensional arrays in custom code, define the bus in Stateflow and pass the bus to your custom code.
See Also
Simulink.Bus (Simulink)