ndgrid
Rectangular grid in N-D space
Description
[
replicates the grid vectors X1,X2,...,Xn]
= ndgrid(x1,x2,...,xn)x1,x2,...,xn to produce an
n-dimensional full grid.
[ specifies a single grid vector
X1,X2,...,Xn]
= ndgrid(xg)xg to use for all dimensions. The number of output arguments
you specify determines the dimensionality n of the output.
Examples
Create a 2-D grid from the vectors [1 3 5 7 9 11 13 15 17 19] and [2 4 6 8 10 12].
[X,Y] = ndgrid(1:2:19,2:2:12)
X = 10×6
1 1 1 1 1 1
3 3 3 3 3 3
5 5 5 5 5 5
7 7 7 7 7 7
9 9 9 9 9 9
11 11 11 11 11 11
13 13 13 13 13 13
15 15 15 15 15 15
17 17 17 17 17 17
19 19 19 19 19 19
Y = 10×6
2 4 6 8 10 12
2 4 6 8 10 12
2 4 6 8 10 12
2 4 6 8 10 12
2 4 6 8 10 12
2 4 6 8 10 12
2 4 6 8 10 12
2 4 6 8 10 12
2 4 6 8 10 12
2 4 6 8 10 12
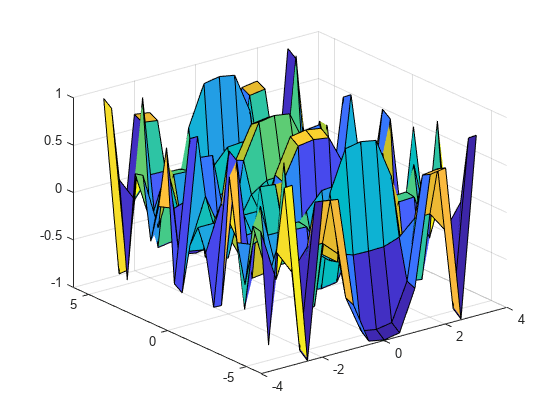
Create a rectangular grid and calculate function values on the grid. Interpolate between the assigned values to refine the grid.
Create a coarse grid for , where the range of is and the range of is .
[X,Y] = ndgrid(-6:0.5:6,-3:0.5:3);
Evaluate the function at the locations defined in the grid. Then, visualize the function using a surface plot. Alternatively, since R2016b, you can use implicit expansion for this task.
f = sin(X.^2) .* cos(Y.^2); surf(Y,X,f)
Interpolate between the points on a more refined grid (Xq,Yq). Then, visualize the interpolated values using a surface plot.
[Xq,Yq] = ndgrid(-6:0.125:6,-3:0.125:3);
F = interpn(X,Y,f,Xq,Yq,"spline");
surf(Yq,Xq,F)
Input Arguments
Grid vectors, specified as vectors containing grid coordinates for each dimension. The grid vectors implicitly define the grid. For example, in 2-D:

Data Types: single | double | int8 | int16 | int32 | int64 | uint8 | uint16 | uint32 | uint64
Complex Number Support: Yes
Grid vector for all dimensions, specified as a vector containing grid
coordinates. ndgrid uses xg as the
grid vector for each dimension.
Data Types: single | double | int8 | int16 | int32 | int64 | uint8 | uint16 | uint32 | uint64
Complex Number Support: Yes
Output Arguments
Full grid representation, returned as separate arrays. For each output
array Xi, the ith dimension contains
copies of the grid vector xi.
More About
meshgrid and ndgrid create grids
using different output formats. Specifically, the first two dimensions of a grid created using
one of these functions are swapped when compared to the other grid format. Some MATLAB® functions use grids in meshgrid format, while others use
ndgrid format, so it is common to convert grids between the two
formats.
You can convert between these grid formats using pagetranspose (as of R2020b) or permute to swap the first two dimensions of the grid arrays. For example, create a 3-D grid with meshgrid.
[X,Y,Z] = meshgrid(1:4,1:3,1:2);
Now transpose the first two dimensions of each grid array to convert the grid to ndgrid format, and compare the results against the outputs from ndgrid.
Xt = pagetranspose(X); Yt = pagetranspose(Y); Zt = pagetranspose(Z); [Xn,Yn,Zn] = ndgrid(1:4,1:3,1:2); isequal(Xt,Xn) & isequal(Yt,Yn) & isequal(Zt,Zn)
ans = logical 1
Using pagetranspose is equivalent to permuting the first two dimensions while leaving other dimensions the same. You can also perform this operation using permute(X,[2 1 3:ndims(X)]).
Extended Capabilities
C/C++ Code Generation
Generate C and C++ code using MATLAB® Coder™.
This function fully supports thread-based environments. For more information, see Run MATLAB Functions in Thread-Based Environment.
The ndgrid function
supports GPU array input with these usage notes and limitations:
The 1-D syntax,
X = ndgrid(x), returns agpuArraycolumn vectorXthat contains the elements of the inputgpuArrayxfor use as a one-dimensional grid.The inputs must be floating-point double or single.
For more information, see Run MATLAB Functions on a GPU (Parallel Computing Toolbox).
Usage notes and limitations:
The 1-D syntax,
X = ndgrid(x), returns a distributed array column vectorXthat contains the elements of the input distributed arrayxfor use as a one-dimensional grid.The inputs must be floating-point double or single.
For more information, see Run MATLAB Functions with Distributed Arrays (Parallel Computing Toolbox).
Version History
Introduced before R2006a
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.
Website auswählen
Wählen Sie eine Website aus, um übersetzte Inhalte (sofern verfügbar) sowie lokale Veranstaltungen und Angebote anzuzeigen. Auf der Grundlage Ihres Standorts empfehlen wir Ihnen die folgende Auswahl: .
Sie können auch eine Website aus der folgenden Liste auswählen:
So erhalten Sie die bestmögliche Leistung auf der Website
Wählen Sie für die bestmögliche Website-Leistung die Website für China (auf Chinesisch oder Englisch). Andere landesspezifische Websites von MathWorks sind für Besuche von Ihrem Standort aus nicht optimiert.
Amerika
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
Europa
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)