setBlock
(To be removed) Put data in specific block of bigimage
object
The setBlock function of the bigimage object will be
removed in a future release. Use the setBlock function
associated with the blockedImage object
instead. For more information, see Version History.
Description
setBlock(
sets the pixel data in the block of big image bigimg,level,locationWorld,data)bigimg that contains
coordinate locationWorld at the specified resolution level.
Examples
Create a bigimage using a modified version of image "tumor_091.tif" from the CAMELYON16 data set. The original image is a training image of a lymph node containing tumor tissue. The original image has eight resolution levels, and the finest level has resolution 53760-by-61440. The modified image has only three coarse resolution levels. The spatial referencing of the modified image has been adjusted to enforce a consistent aspect ratio and to register features at each level.
bim = bigimage('tumor_091R.tif');
Display the bigimage, then create a circle ROI over the displayed image.
h = bigimageshow(bim); hROI = drawcircle(gca,'Radius',470,'Position',[1477 2284]);
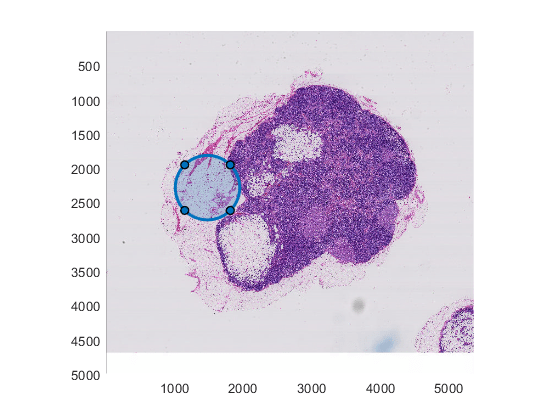
Choose the level at which to create a writeable bigimage. Level 3 is the coarsest resolution level.
maskLevel = 3;
Get the spatial referencing and pixel extents from the specified level.
ref = bim.SpatialReferencing(maskLevel); pixelExtent = [ref.PixelExtentInWorldX,ref.PixelExtentInWorldY];
Create a writeable bigimage by specifying the spatial referencing instead of image data. This big image has one channel and is of data type logical.
bmask = bigimage(ref,1,'logical');
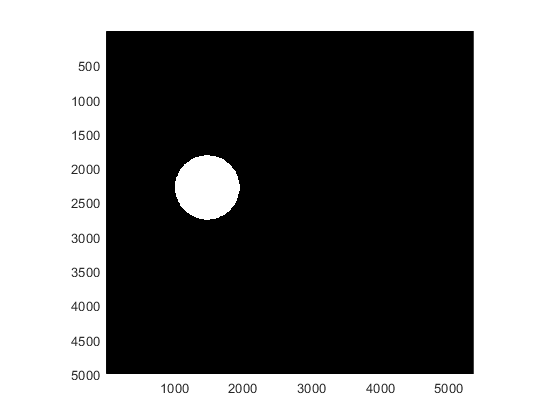
Loop through all blocks in the writeable big image to create a mask image. For each block, set the pixel values as 1 (true) for pixels inside the ROI and 0 (false) for pixels outside the ROI.
for cStart = 1:bmask.BlockSize(2):ref.ImageSize(2) for rStart = 1:bmask.BlockSize(1):ref.ImageSize(1) % Get the center of top left pixel of this block in world units. xyStart = [cStart,rStart].*pixelExtent; % Get the block size. The |'BlockSize'| property represents the % size as a 2-element vector of the form [row,column]. Switch the % order of the elements so that the block size is represented as % [x,y]. bsize = bmask.BlockSize; numRows = bsize(1); numCols = bsize(2); % Determine which pixels have coordinates inside the ROI. roiPositions = hROI.Vertices; % Transform |roiPositions| from world coordinates to the intrinsic % image indices at the given resolution level. roiPositions = (roiPositions - xyStart) ./ pixelExtent + 1; blockMask = poly2mask(roiPositions(:,1),roiPositions(:,2), ... numRows, numCols); % Set the pixel values of the block. setBlock(bmask,1,xyStart,blockMask); end end
Display the mask.
figure bigimageshow(bmask)
Input Arguments
Big image, specified as a bigimage object.
Resolution level, specified as a positive integer that is less than or equal to the
number of resolution levels of bigimg.
Coordinate of a point, specified as a 1-by-2 numeric vector of the form [x
y]. The location is specified in world coordinates, which are the pixel
locations relative to the highest resolution level. The position must be a valid
position within bigimg.
Pixel data, specified as a numeric array of the same data type as the big image,
bigimg.ClassUnderlyinglevel.
Tips
Create a writeable
bigimageby using a syntax that does not initialize image data. If you create abigimageby specifying the file name, directory name, or variable name of image data, or by using theapplyfunction, then thebigimageis not writeable and you cannot use thesetBlockfunction.If the size of
datais less than the block sizebigimg.BlockSize, thensetBlockpads the data with the default value,bigimg.UnloadedValue.setBlocktrims data for partial edge blocks.
Version History
Introduced in R2019bThe setBlock function issues a warning that it will be removed
in a future release.
The bigimage object and this function will be removed in a future
release. Use the setBlock
function of the blockedImage
object instead.
To update your code, first create a writeable blockedImage object to
write your image data. Then, follow these steps:
Convert from (x, y) world coordinates to (row, column) world coordinates by switching the order of the two elements.
Convert the world coordinates to pixel subscripts using the
world2subfunction. If you want to set the block at a resolution level other than level 1, then specify that level by using theLevelname-value argument.Convert the pixel subscripts to block subscripts using the
sub2blocksubfunction. If you want to set the block at a resolution level other than level 1, then specify that level by using theLevelname-value argument.The
blockedImagesetBlockfunction requires the size of the data to be equal to the block size. If you want to setblockedImagedata of size smaller than the block size, then you can pad the data.Pass the blocked image, the block subscript, and the data to write to the
setBlockfunction. If you want to set the block at a resolution level other than level 1, then specify that level by using theLevelname-value argument.After you are done writing data to the
blockedImageobject, then you must change the mode of the object to read-only before getting the image data. For example, change the mode ofblockedImageobjectblockedMaskby setting theModeproperty to"r"using dot notation:blockedMask.Mode = "r";In contrast, you can read written data from a
bigimageobject without changing the object properties.
| Discouraged Usage | Recommended Replacement |
|---|---|
This example uses the % Create a writeable bigimage object filename = "tumor_091R.tif"; bim = bigimage(filename); ref = bim.SpatialReferencing(1); blockSize = bim.BlockSize(1,1:2); bigMask = bigimage(ref,1,"logical"); % Identify a coordinate coordWorld = [1000 2500]; % Specify the data to write, then write the data blockSize = bim.BlockSize(1,1:2); data = logical(checkerboard(blockSize(1)/16,8)); setBlock(bigMask,1,coordWorld,data); | Here is equivalent code using a % Create a writeable blockedImage object filename = "tumor_091R.tif"; blockedIm = blockedImage(filename); imgSize = blockedIm.Size(1,1:2); blockSize = blockedIm.BlockSize(1,1:2); initVal = logical(0); blockedMask = blockedImage([],imgSize,blockSize,initVal,Mode="w"); % Identify the block containing a coordinate coordWorld = [1000 2500]; coordRC = flip(coordWorld); subPixel = world2sub(blockedMask,coordRC); subBlock = sub2blocksub(blockedMask,subPixel); % Specify the data to write, then write the data to the block data = logical(checkerboard(blockSize(1)/16,8)); setBlock(blockedMask,subBlock,data); |
This example uses the % Create a writeable bigimage object % (same as above) % Identify a coordinate % (same as above) % Specify the data to write, then write the data data = logical(checkerboard(10,8)); setBlock(bmask,1,coordWorld,data); | Here is equivalent code using a % Create a writeable blockedImage object % (same as above) % Identify a coordinate % (same as above) % Specify the data to write, then write the data to the block data = logical(checkerboard(10,8)); data = padarray(data,blockSize-size(data),initVal,"post"); setBlock(blockedMask,subBlock,data); |
The setBlock function of the bigimage object is
not recommended. Use the setBlock
function of the blockedImage
object instead. The
blockedImage object offers several advantages including extension to N-D
processing, a simpler interface, and custom support for reading and writing nonstandard image
formats.
See Also
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.
Website auswählen
Wählen Sie eine Website aus, um übersetzte Inhalte (sofern verfügbar) sowie lokale Veranstaltungen und Angebote anzuzeigen. Auf der Grundlage Ihres Standorts empfehlen wir Ihnen die folgende Auswahl: .
Sie können auch eine Website aus der folgenden Liste auswählen:
So erhalten Sie die bestmögliche Leistung auf der Website
Wählen Sie für die bestmögliche Website-Leistung die Website für China (auf Chinesisch oder Englisch). Andere landesspezifische Websites von MathWorks sind für Besuche von Ihrem Standort aus nicht optimiert.
Amerika
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
Europa
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)