Building Heating and Cooling
In this section, you can find examples of heating and cooling systems for buildings.
Featured Examples
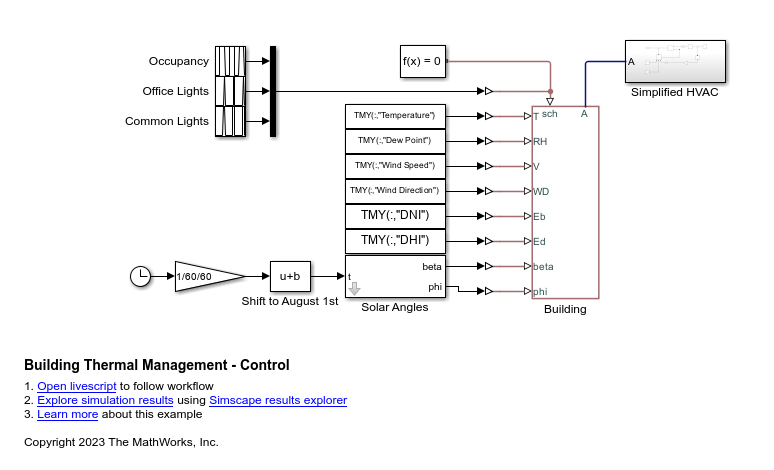
Building Thermal Management
Model temperature and humidity in a large-scale building in Simscape™ using a custom BuildingHVAC domain and corresponding custom library blocks. The first of two models shows how to estimate the sensible and latent cooling requirement to maintain a desired temperature. The second model shows how to add simple HVAC controls and estimate energy usage.
House Heating System
Model a simple house heating system. The model contains a heater, a controller, and a house structure with four radiators and four rooms. Each room exchanges heat with the environment through its exterior walls, roof, and windows. Each path is simulated as a combination of a thermal convection, thermal conduction, and the thermal mass. It is assumed that heat is not transferred internally between rooms. The heater consists of a furnace, a boiler, an accumulator, and a pump to circulate hot water in the system. The controller starts admitting fuel into the furnace if the overall average temperature of rooms falls below 21 degree C and it stops if the temperature exceeds 25 degree C. The simulation calculates the heating cost and indoor temperatures.
Refrigeration Cycle (Air Conditioning)
A refrigeration cycle for a home air conditioning system. See Model a Refrigeration Cycle for the recommended steps to build this model in the two-phase fluid domain.
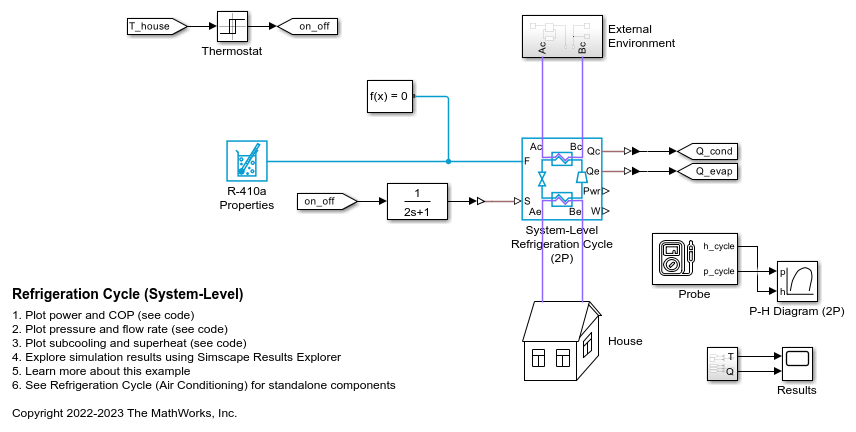
Refrigeration Cycle (System-Level)
Model a refrigeration cycle for a home air conditioning system at an abstract system level using the System-Level Refrigeration Cycle (2P) block. This block simplifies the set up of the refrigeration cycle by encapsulating the entire refrigerant loop in one block.
Residential Air Source Heat Pump
Models an air source heat pump system that is used to heat a residential building having hot-water radiators for heat distribution. The two-phase fluid refrigerant takes up heat from the environment moist air mixture and transfers heat to water. The compressor drives the R410a refrigerant through a condenser, a thermostatic expansion valve, and an evaporator. An accumulator ensures that only vapor returns to the compressor.
Residential Ground Source Heat Pump
Models a ground source heat pump system that is used to heat a residential building having hot-water radiators for heat distribution. The ground source heat pump uses R410a, a two-phase fluid refrigerant, as the working fluid. The heat pump takes up the naturally existing heat stored in the ground and transfers the heat to the hot-water radiators. The compressor drives the refrigerant through a condenser, a thermostatic expansion valve, and an evaporator. An accumulator ensures that only vapor returns to the compressor. A receiver ensures that only liquid returns to the thermostatic expansion valve.
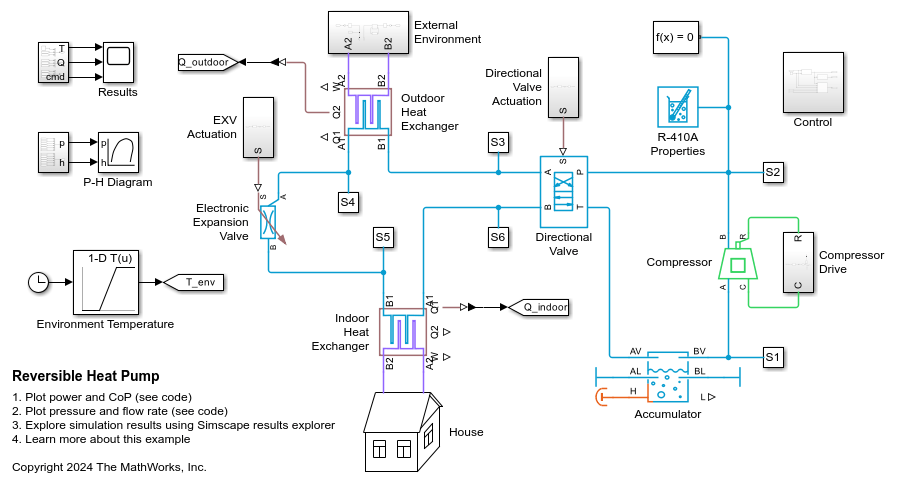
Reversible Heat Pump
A refrigeration cycle that can operate in heat pump mode for heating and in air conditioning mode for cooling. The refrigerant is R-410A. The system consists of a compressor, an outdoor heat exchanger, an electronic expansion valve (EXV), an indoor heat exchanger, and an accumulator. A 4-way directional valve separates the compressor and accumulator from the rest of the system to control the refrigerant flow direction.
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.
Website auswählen
Wählen Sie eine Website aus, um übersetzte Inhalte (sofern verfügbar) sowie lokale Veranstaltungen und Angebote anzuzeigen. Auf der Grundlage Ihres Standorts empfehlen wir Ihnen die folgende Auswahl: .
Sie können auch eine Website aus der folgenden Liste auswählen:
So erhalten Sie die bestmögliche Leistung auf der Website
Wählen Sie für die bestmögliche Website-Leistung die Website für China (auf Chinesisch oder Englisch). Andere landesspezifische Websites von MathWorks sind für Besuche von Ihrem Standort aus nicht optimiert.
Amerika
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
Europa
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)