buildInstrumentedMex
Generate compiled C code function including logging instrumentation
Description
buildInstrumentedMex
translates the MATLAB® file fcn -optionsfcn.mbuildInstrumentedMex and fiaccel are the same, except buildIntstrumentedMex has no
fi object restrictions and supports the '-coder'
option.
Note
Like the fiaccel function, the
buildInstrumentedMex function generates a MEX function. To
generate C code, use the codegen (MATLAB Coder) function.
buildInstrumentedMex
translates the MATLAB functions fcn_1... fcn_n -options -coderfcn_1fcn_n'-coder' option.
Note
Generating a MEX function for multiple entry-point functions using the
buildInstrumentedMex function requires a MATLAB
Coder™ license.
Examples
Input Arguments
Tips
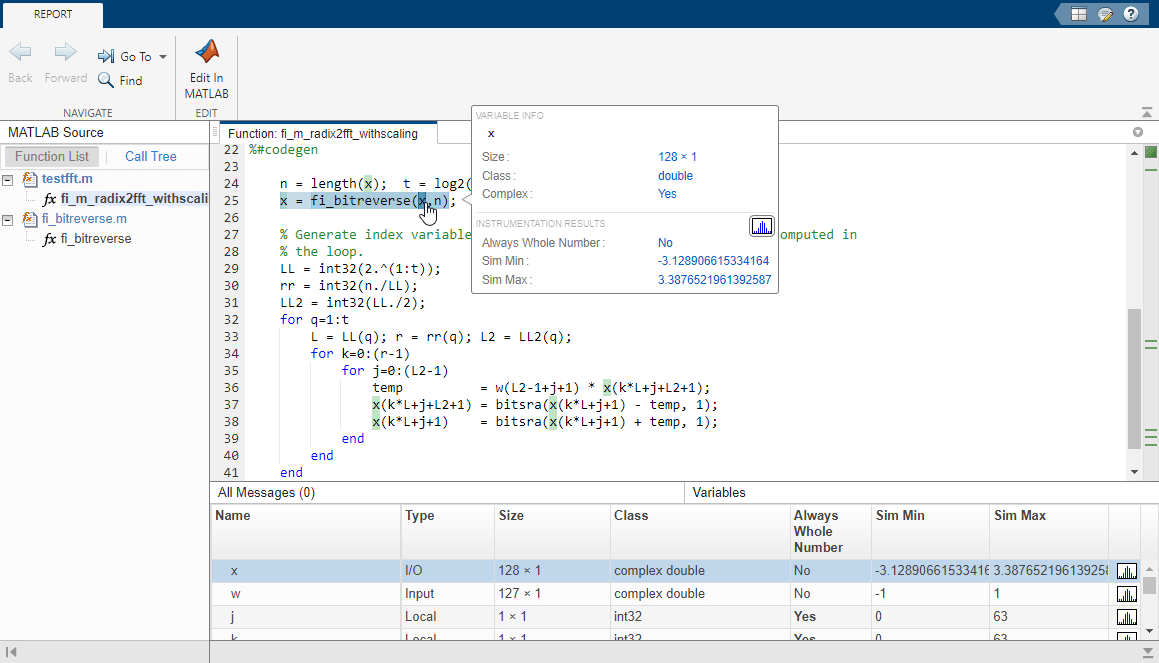
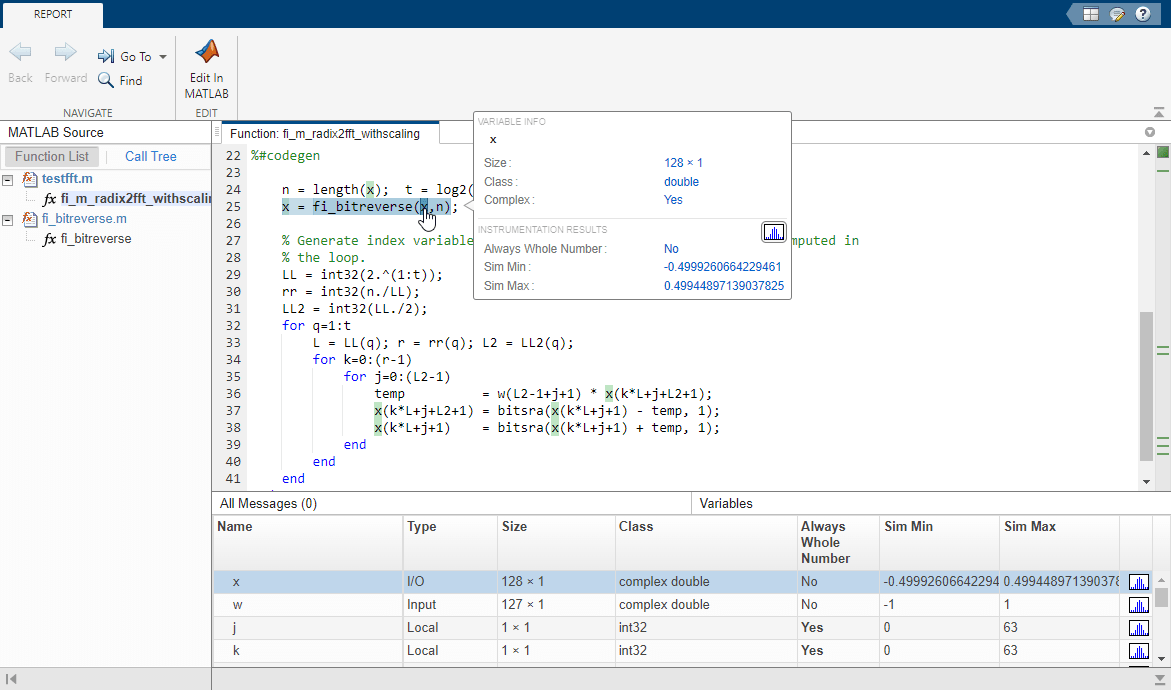
You cannot instrument MATLAB functions provided with the software. If your top-level function is such a MATLAB function, nothing is logged. You also cannot instrument scripts.
Instrumentation results are accumulated every time the instrumented MEX function is called. Use
clearInstrumentationResultsto clear previous results in the log.Some coding patterns pass a significant amount of data, but only use a small portion of that data. In such cases, you may see degraded performance when using
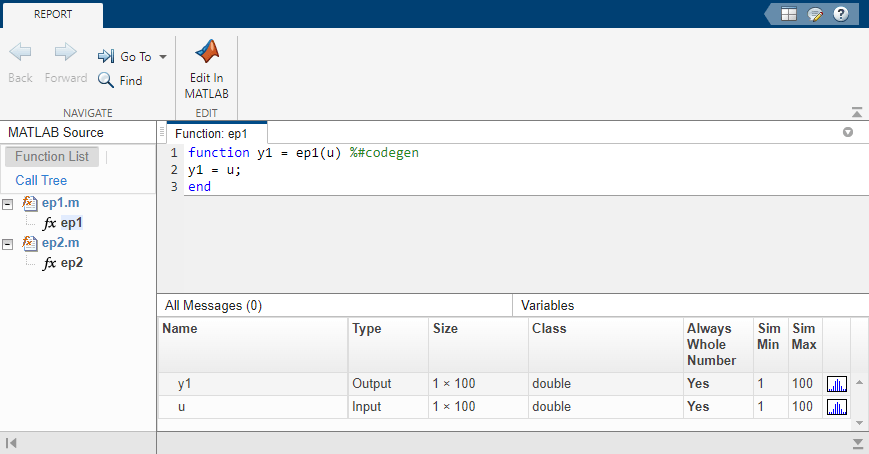
buildInstrumentedMex. In the following pattern,subfunonly uses one element of input array,A. For normal execution, the amount of time to executesubfunonce remains constant regardless of the size ofA. The functiontopfuncallssubfunNtimes, and thus the total time to executetopfunis proportional toN. When instrumented, however, the time to executesubfunonce becomes proportional toN^2. This change occurs because the minimum and maximum data are calculated over the entire array. WhenAis large, the calculations can lead to significant performance degradation. Therefore, whenever possible, you should pass only the data that the function actually needs.function A = topfun(A) N = numel(A); for i=1:N A(i) = subfun(A,i); end end function b = subfun(A,i) b = 0.5 * A(i); end function A = topfun(A) N = numel(A); for i=1:N A(i) = subfun(A(i)); end end function b = subfun(a) b = 0.5 * a; end
Version History
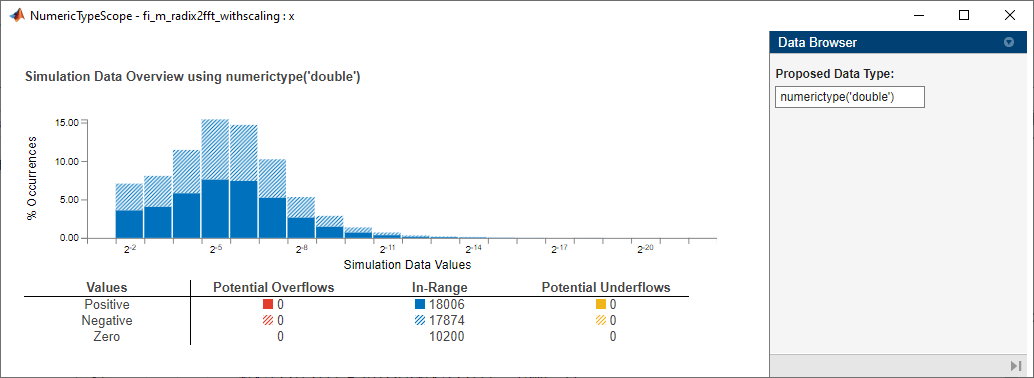
Introduced in R2011bSee Also
fiaccel | clearInstrumentationResults | showInstrumentationResults | NumericTypeScope | codegen (MATLAB Coder) | mex