read
Read HERE HD Live Map layer data
Description
layerData = read(reader,layerType)hereHDLMReader
object and returns an array of layer objects. These layer objects contain map layer data for
the HERE map tiles whose IDs correspond to the IDs stored in the TileIds property of reader.
layerData = read(reader,layerType,fields)HereTileId field, and for the specified fields. All other fields in the
returned layer objects are returned as empty: []. If you do not require
data from all fields within the layer objects, use this syntax to speed up performance of
this function.
Examples
Use the HERE HD Live Map (HERE HDLM) service to read the lane topology data of a driving route and its surrounding area. Plot this data, and then stream the route on a geographic player.
Load the latitude and longitude coordinates of a driving route in Natick, Massachusetts, USA.
route = load('geoSequenceNatickMA.mat');
lat = route.latitude;
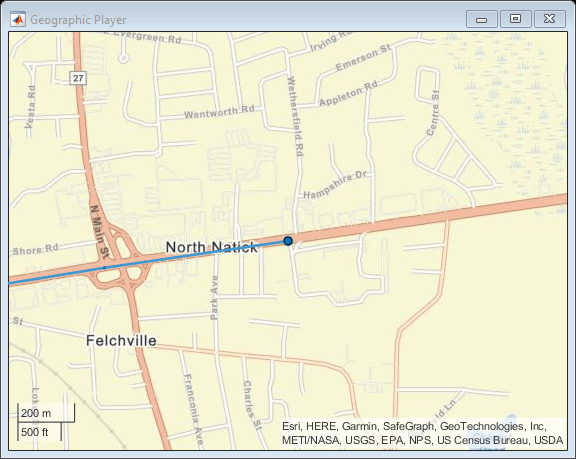
lon = route.longitude;Stream the coordinates on a geographic player.
player = geoplayer(lat(1),lon(1),'HistoryDepth',5); plotRoute(player,lat,lon) for idx = 1:length(lat) plotPosition(player,lat(idx),lon(idx)) end
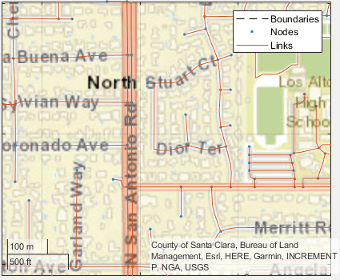
Create a HERE HDLM reader from the route coordinates. If you have not previously set up HERE HDLM credentials, a dialog box prompts you to enter them. The reader contains map data for the two map tiles that the route crosses.
reader = hereHDLMReader(lat,lon);
Read lane topology data from the LaneTopology layer of the map tiles. Plot the lane topology.
laneTopology = read(reader,'LaneTopology');
plot(laneTopology)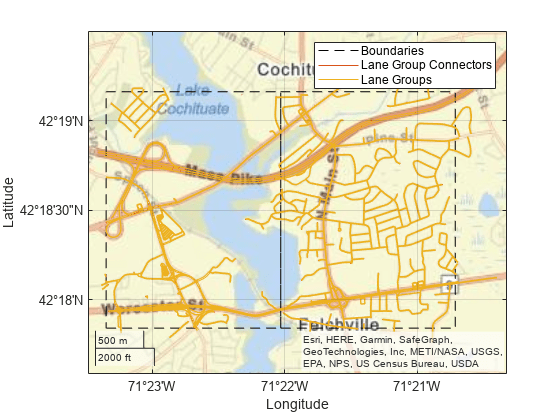
Overlay the route data on the plot.
hold on geoplot(lat,lon,'bo-','DisplayName','Route'); hold off
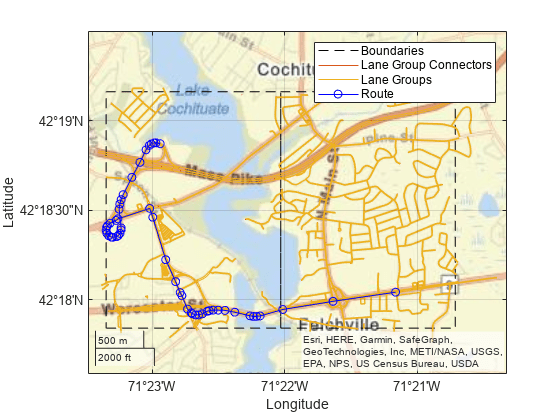
Overlay the lane topology data on the geographic player. Stream the route again.
plot(laneTopology,'Axes',player.Axes) for idx = 1:length(lat) plotPosition(player,lat(idx),lon(idx)) end
Use the HERE HD Live Map (HERE HDLM) web service to read the topology geometry data from a map tile. Use this data to find the shortest path between two nodes within the map tile.
Define a HERE tile ID for an area of Stockholm, Sweden.
tileID = uint32(378373553);
Create a HERE HDLM reader for the tile ID. Configure the reader to search for the tile in only the Western Europe catalog. If you have not previously set up HERE HDLM credentials, a dialog box prompts you to enter them. The reader contains map data for the specified map tile.
config = hereHDLMConfiguration("hrn:here:data::olp-here-had:here-hdlm-protobuf-weu-2");
reader = hereHDLMReader(tileID,Configuration=config);Read the link definitions from the TopologyGeometry layer of the map tile. The returned layer object contains the specified LinksStartingInTile field and the required map tile fields, such as the tile ID. The other fields are empty. Your map data and catalog version might differ from the ones shown here.
topology = read(reader,TopologyGeometry="LinksStartingInTile")topology =
TopologyGeometry with properties:
Data:
HereTileId: 378373553
IntersectingLinkRefs: []
LinksStartingInTile: [1269×1 struct]
NodesInTile: []
TileCenterHere2dCoordinate: [59.3372 18.0505]
Metadata:
Catalog: 'hrn:here:data::olp-here-had:here-hdlm-protobuf-weu-2'
CatalogVersion: 21501
Use plot to visualize TopologyGeometry data.
Find the start and end nodes for each link in the LinksStartingInTile field.
startNodes = [topology.LinksStartingInTile.StartNodeId]; endNodesRef = [topology.LinksStartingInTile.EndNodeRef]; endNodes = [endNodesRef.NodeId];
Find the length of each link in meters.
linkLengths = [topology.LinksStartingInTile.LinkLengthMeters];
Create an undirected graph for the links in the map tile.
G = graph(string(startNodes),string(endNodes),double(linkLengths)); H = plot(G,Layout="force"); title("Undirected Graph")

Specify a start and end node to find the shortest path between them. Use the first and last node in the graph as the start and end nodes, respectively. Overlay the nodes on the graph.
startNode = G.Nodes.Name(1); endNode = G.Nodes.Name(end); highlight(H,[startNode endNode],NodeColor="red",MarkerSize=6) title("Undirected Graph - Start and End Nodes")

Find the shortest path between the two nodes. Plot the path.
path = shortestpath(G,startNode,endNode); highlight(H,path,EdgeColor="red",LineWidth=2); title("Undirected Graph - Shortest Path")

Input Arguments
Input HERE HDLM reader, specified as a hereHDLMReader object.
Layer object fields from which to read data, specified as a string scalar, character
vector, string array, or cell array of character vectors. All fields must be valid
fields of the layer specified by layerType. You can specify only
the top-level fields of this layer. You cannot specify its metadata fields.
In the returned array of layer objects, only required fields, such as the
HereTileId field, and the specified fields contain data. All other
fields are returned as empty: [].
For a list of the valid top-level data fields for each layer type, see the
data output argument.
Example: 'LinkAttribution'
Example: "NodeAttribution"
Example: ["LinkAttribution" "NodeAttribution"]
Example: {'LinkAttribution','NodeAttribution'}
Output Arguments
HERE HDLM layer data, returned as a T-by-1 array of layer
objects. T is the number of map tile IDs stored in the TileIds property of the specified reader. Each layer
object contains map data that is of type layerType for a HERE map
tile that was read from reader. Such data can include:
The geometry of links (streets) and nodes (intersections and dead ends) within map tiles
Various road-level and lane-level attributes
Landmark-based localization information, such as the barriers, signs, and poles along a road
The layer objects also contain metadata specifying the catalog name and
catalog version from which the read function obtained the
data.
The properties of the layer objects correspond to valid HERE HDLM layer fields. In these layer objects, the names of the layer fields are modified to fit the MATLAB® naming convention for object properties. For each layer field name, the first letter and first letter after each underscore are capitalized and the underscores are removed. This table shows sample name changes.
| HERE HDLM Layer Fields | MATLAB Layer Object Property |
|---|---|
here_tile_id | HereTileId |
tile_center_here_2d_coordinate | TileCenterHere2dCoordinate |
nodes_in_tile | NodesInTile |
The layer objects are MATLAB structures whose properties correspond to structure fields. To access data from these fields, use dot notation.
For example, this code selects the NodeId subfield from the
NodeAttribution field of a
layer:
layerData.NodeAttribution.NodeId
This table summarizes the valid types of layer objects and their top-level data fields. The available layers are for the Road Centerline Model, HD Lane Model, and HD Localization Model. For an overview of HERE HDLM layers and the models that they belong to, see HERE HD Live Map Layers.
| Layer Object | Description | Top-Level Data Fields (Layer Object Properties) | Plot Support |
|---|---|---|---|
AdasAttributes | Precision geometry measurements, such as slope, elevation, and curvature of roads. Use this data to develop advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS). |
| Not available |
ExternalReferenceAttributes | References to external map links, nodes, and topologies for other HERE maps. |
| Not available |
LaneAttributes | Lane-level attributes, such as direction of travel and lane type. |
| Not available |
LaneGeometryPolyline | 3-D lane geometry composed of a set of 3-D points joined into polylines. |
| Available — Use the
|
LaneRoadReferences | Road and lane group references and range information. Use this data to translate positions between the Road Centerline Model and the HD Lane Model. |
| Not available |
LaneTopology | Topologies of the HD Lane model, including lane group, lane group connector, lane, and lane connector topologies. This layer also contains the simplified 2-D boundary geometry of the lane model for determining map tile affinity and overflow. |
| Available — Use the
|
LocalizationBarrier | Positions, dimensions, and attributes of barriers such as guardrails and Jersey barriers found along roads |
| Not available |
LocalizationPole | Positions, dimensions, and attributes of traffic signal poles and other poles found along or hanging over roads |
| Not available |
LocalizationSign | Positions, dimensions, and attributes of traffic-sign faces found along roads |
| Not available |
RoutingAttributes | Road attributes related to navigation and conditions. These attributes are mapped parametrically to the 2-D polyline geometry in the topology layer. |
| Not available |
RoutingLaneAttributes | Core navigation lane attributes and conditions, such as the number of lanes in a road. These values are mapped parametrically to 2-D polylines along the road links. |
| Not available |
SpeedAttributes | Speed-related road attributes, such as speed limits. These attributes are mapped to the 2-D polyline geometry of the topology layer. |
| Not available |
TopologyGeometry | Topology and 2-D line geometry of the road. This layer also contains definitions of the nodes and links in the map tile. |
| Available — Use the
|
Version History
Introduced in R2019a
See Also
hereHDLMCredentials | hereHDLMConfiguration | plot | hereHDLMReader
1 You need to enter into a separate agreement with HERE in order to gain access to the HDLM services and to get the required credentials (access_key_id and access_key_secret) for using the HERE Service.
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.
Website auswählen
Wählen Sie eine Website aus, um übersetzte Inhalte (sofern verfügbar) sowie lokale Veranstaltungen und Angebote anzuzeigen. Auf der Grundlage Ihres Standorts empfehlen wir Ihnen die folgende Auswahl: .
Sie können auch eine Website aus der folgenden Liste auswählen:
So erhalten Sie die bestmögliche Leistung auf der Website
Wählen Sie für die bestmögliche Website-Leistung die Website für China (auf Chinesisch oder Englisch). Andere landesspezifische Websites von MathWorks sind für Besuche von Ihrem Standort aus nicht optimiert.
Amerika
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
Europa
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)