sigmaoptions
Sigma plot options
Description
Use the sigmaoptions command to create a
SigmaOptions object to customize your sigma plot appearance. You can also
use the command to override the plot preference settings in the MATLAB® session in which you create the sigma plots.
Creation
Description
plotoptions = sigmaoptionssigmaplot command. You can use these options to customize sigma plot
appearance using the command line. This syntax is useful when you want to write a script
to generate plots that look the same regardless of the preference settings of the
MATLAB session in which you run the script.
plotoptions = sigmaoptions('cstprefs')
Properties
FreqUnits — Frequency units
'rad/s' (default)
Frequency units, specified as one of the following values:
'Hz''rad/s''rpm''kHz''MHz''GHz''rad/nanosecond''rad/microsecond''rad/millisecond''rad/minute''rad/hour''rad/day''rad/week''rad/month''rad/year''cycles/nanosecond''cycles/microsecond''cycles/millisecond''cycles/hour''cycles/day''cycles/week''cycles/month''cycles/year'
FreqScale — Frequency scale
'log' (default) | 'linear'
Frequency scale, specified as either 'log' or
'linear'.
MagUnits — Magnitude units
'dB' (default) | 'abs'
Magnitude units, specified as either 'dB' or absolute value
'abs'.
MagScale — Magnitude scale
'linear' (default) | 'log'
Magnitude scale, specified as either 'log' or
'linear'.
IOGrouping — Grouping of input-output pairs
'none' (default) | 'inputs' | 'outputs' | 'all'
Grouping of input-output (I/O) pairs, specified as one of the following:
'
none' — No input-output grouping.'
inputs' — Group only the inputs.'
outputs' — Group only the outputs.'
all' — Group all the I/O pairs.
InputLabels — Input label style
structure (default)
Input label style, specified as a structure with the following fields:
FontSize— Font size, specified as a scalar value greater than zero in point units. The default font size depends on the specific operating system and locale. One point equals1/72inch.FontWeight— Character thickness, specified as 'Normal' or 'bold'. MATLAB uses theFontWeightproperty to select a font from those available on your system. Not all fonts have a bold weight. Therefore, specifying a bold font weight can still result in the normal font weight.FontAngle— Character slant, specified as 'Normal' or 'italic'. Not all fonts have both font styles. Therefore, the italic font might look the same as the normal font.Color— Text color, specified as an RGB triplet. The default color is dark grey with the RGB triplet[0.4,0.4,0.4].Interpreter— Text interpreter, specified as one of these values:'
tex' — Interpret characters using a subset of TeX markup. This is the default value ofInterpreter.'
latex' — Interpret characters using LaTeX markup.'
none' — Display literal characters.
OutputLabels — Output label style
structure (default)
Output label style, specified as a structure with the following fields:
FontSize— Font size, specified as a scalar value greater than zero in point units. The default font size depends on the specific operating system and locale. One point equals1/72inch.FontWeight— Character thickness, specified as 'Normal' or 'bold'. MATLAB uses theFontWeightproperty to select a font from those available on your system. Not all fonts have a bold weight. Therefore, specifying a bold font weight can still result in the normal font weight.FontAngle— Character slant, specified as 'Normal' or 'italic'. Not all fonts have both font styles. Therefore, the italic font might look the same as the normal font.Color— Text color, specified as an RGB triplet. The default color is dark grey with the RGB triplet[0.4,0.4,0.4].Interpreter— Text interpreter, specified as one of these values:'
tex' — Interpret characters using a subset of TeX markup. This is the default value ofInterpreter.'
latex' — Interpret characters using LaTeX markup.'
none' — Display literal characters.
InputVisible — Input visibility toggle
{'on'} (default) | {'off'} | cell array
Input visibility toggle, specified as either {'on'},
{'off'} or a cell array with multiple elements.
OutputVisible — Output visibility toggle
{'on'} (default) | {'off'} | cell array
Output visibility toggle, specified as either {'on'},
{'off'} or a cell array with multiple elements.
Title — Title text and style
structure (default)
Title text and style, specified as a structure with the following fields:
String— Label text, specified as a character vector. By default, the plot is titled 'Singular Values'.FontSize— Font size, specified as a scalar value greater than zero in point units. The default font size depends on the specific operating system and locale. One point equals1/72inch.FontWeight— Character thickness, specified as 'Normal' or 'bold'. MATLAB uses theFontWeightproperty to select a font from those available on your system. Not all fonts have a bold weight. Therefore, specifying a bold font weight can still result in the normal font weight.FontAngle— Character slant, specified as 'Normal' or 'italic'. Not all fonts have both font styles. Therefore, the italic font might look the same as the normal font.Color— Text color, specified as an RGB triplet. The default color is black specified by the RGB triplet[0,0,0].Interpreter— Text interpreter, specified as one of these values:'
tex' — Interpret characters using a subset of TeX markup. This is the default value ofInterpreter.'
latex' — Interpret characters using LaTeX markup.'
none' — Display literal characters.
XLabel — X-axis label text and style
structure (default)
X-axis label text and style, specified as a structure with the following fields:
String— Label text, specified as a character vector. By default, the axis is titled based on the frequency unitsFreqUnits.FontSize— Font size, specified as a scalar value greater than zero in point units. The default font size depends on the specific operating system and locale. One point equals1/72inch.FontWeight— Character thickness, specified as 'Normal' or 'bold'. MATLAB uses theFontWeightproperty to select a font from those available on your system. Not all fonts have a bold weight. Therefore, specifying a bold font weight can still result in the normal font weight.FontAngle— Character slant, specified as 'Normal' or 'italic'. Not all fonts have both font styles. Therefore, the italic font might look the same as the normal font.Color— Text color, specified as an RGB triplet. The default color is black specified by the RGB triplet[0,0,0].Interpreter— Text interpreter, specified as one of these values:'
tex' — Interpret characters using a subset of TeX markup. This is the default value ofInterpreter.'
latex' — Interpret characters using LaTeX markup.'
none' — Display literal characters.
YLabel — Y-axis label text and style
structure (default)
Y-axis label text and style, specified as a structure with the following fields:
String— Label text, specified as a cell array of character vectors. By default, the axis is titled based on the magnitude unitsMagUnits.FontSize— Font size, specified as a scalar value greater than zero in point units. The default font size depends on the specific operating system and locale. One point equals1/72inch.FontWeight— Character thickness, specified as 'Normal' or 'bold'. MATLAB uses theFontWeightproperty to select a font from those available on your system. Not all fonts have a bold weight. Therefore, specifying a bold font weight can still result in the normal font weight.FontAngle— Character slant, specified as 'Normal' or 'italic'. Not all fonts have both font styles. Therefore, the italic font might look the same as the normal font.Color— Text color, specified as an RGB triplet. The default color is black specified by the RGB triplet[0,0,0].Interpreter— Text interpreter, specified as one of these values:'
tex' — Interpret characters using a subset of TeX markup. This is the default value ofInterpreter.'
latex' — Interpret characters using LaTeX markup.'
none' — Display literal characters.
TickLabel — Tick label style
structure (default)
Tick label style, specified as a structure with the following fields:
FontSize— Font size, specified as a scalar value greater than zero in point units. The default font size depends on the specific operating system and locale. One point equals1/72inch.FontWeight— Character thickness, specified as 'Normal' or 'bold'. MATLAB uses theFontWeightproperty to select a font from those available on your system. Not all fonts have a bold weight. Therefore, specifying a bold font weight can still result in the normal font weight.FontAngle— Character slant, specified as 'Normal' or 'italic'. Not all fonts have both font styles. Therefore, the italic font might look the same as the normal font.Color— Text color, specified as an RGB triplet. The default color is black specified by the RGB triplet[0,0,0].
Grid — Toggle grid display
'off' (default) | 'on'
Toggle grid display on the plot, specified as either 'off' or
'on'.
GridColor — Color of the grid lines
[0.15,0.15,0.15] (default) | RGB triplet
Color of the grid lines, specified as an RGB triplet. The default color is light
grey specified by the RGB triplet [0.15,0.15,0.15].
XLimMode — X-axis limit selection mode
'auto' (default) | 'manual' | cell array
Selection mode for the x-axis limits, specified as one of these values:
'
auto' — Enable automatic limit selection, which is based on the total span of the plotted data.'
manual' — Manually specify the axis limits. To specify the axis limits, set theXLimproperty.
YLimMode — Y-axis limit selection mode
'auto' (default) | 'manual' | cell array
Selection mode for the y-axis limits, specified as one of these values:
'
auto' — Enable automatic limit selection, which is based on the total span of the plotted data.'
manual' — Manually specify the axis limits. To specify the axis limits, set theYLimproperty.
XLim — X-axis limits
'{[1,10]}' (default) | cell array of two-element vector of the form [min,max] | cell array
X-axis limits, specified as a cell array of two-element vector of the form
[min,max].
YLim — Y-axis limits
'{[1,10]}' (default) | cell array of two-element vector of the form [min,max] | cell array
Y-axis limits, specified as a cell array of two-element vector of the form
[min,max].
Object Functions
sigmaplot | Plot singular values of frequency response with additional plot customization options |
Examples
Customize Sigma Plot Using Plot Handle
For this example, use the plot handle to change the frequency units to Hz and turn on the grid.
Generate a random state-space model with 5 states and create the sigma plot with plot handle h.
rng("default")
sys = rss(5);
h = sigmaplot(sys);
Change the units to Hz and turn on the grid. To do so, edit properties of the plot handle, h using setoptions.
setoptions(h,'FreqUnits','Hz','Grid','on');
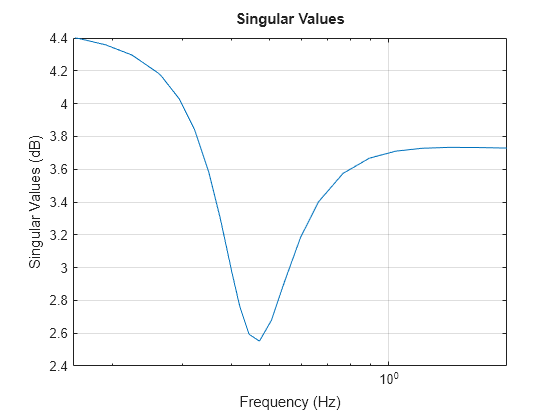
The sigma plot automatically updates when you call setoptions.
Alternatively, you can also use the sigmaoptions command to specify the required plot options. First, create an options set based on the toolbox preferences.
p = sigmaoptions('cstprefs');Change properties of the options set by setting the frequency units to Hz and enable the grid.
p.FreqUnits = 'Hz'; p.Grid = 'on'; sigmaplot(sys,p);

You can use the same option set to create multiple sigma plots with the same customization. Depending on your own toolbox preferences, the plot you obtain might look different from this plot. Only the properties that you set explicitly, in this example Grid and FreqUnits, override the toolbox preferences.
Custom Sigma Plot Settings Independent of Preferences
For this example, create a sigma plot that uses 15-point red text for the title. This plot should look the same, regardless of the preferences of the MATLAB session in which it is generated.
First, create a default options set using sigmaoptions.
plotoptions = sigmaoptions;
Next, change the required properties of the options set plotoptions.
plotoptions.Title.FontSize = 15; plotoptions.Title.Color = [1 0 0]; plotoptions.FreqUnits = 'Hz'; plotoptions.Grid = 'on';
Now, create a sigma plot using the options set plotoptions.
h = sigmaplot(tf(1,[1,1]),plotoptions);
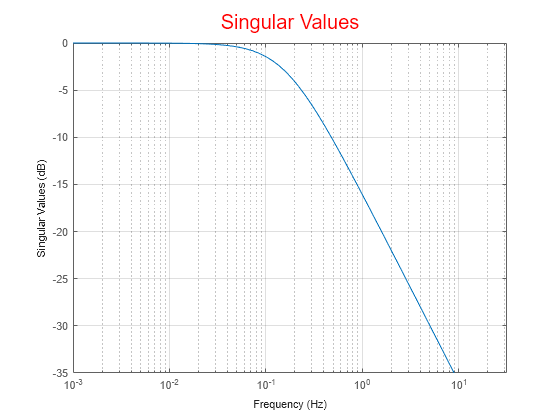
Because plotoptions begins with a fixed set of options, the plot result is independent of the toolbox preferences of the MATLAB session.
Customized Sigma Plot of Transfer Function
For this example, create a sigma plot of the following continuous-time SISO dynamic system. Then, turn the grid on, rename the plot and change the frequency scale.
Create the transfer function sys.
sys = tf([1 0.1 7.5],[1 0.12 9 0 0]);
Next, create the options set using sigmaoptions and change the required plot properties.
plotoptions = sigmaoptions; plotoptions.Grid = 'on'; plotoptions.FreqScale = 'linear'; plotoptions.Title.String = 'Singular Value Plot of Transfer Function';
Now, create the sigma plot with the custom option set plotoptions.
h = sigmaplot(sys,plotoptions);

sigmaplot automatically selects the plot range based on the system dynamics.
Singular Value Plot of Identified Parametric and Nonparametric Models
For this example, compare the SV for the frequencies of a parametric model, identified from input/output data, to a non-parametric model identified using the same data. Identify parametric and non-parametric models based on the data.
Load the data and create the parametric and non-parametric models using tfest and spa, respectively.
load iddata2 z2; w = linspace(0,10*pi,128); sys_np = spa(z2,[],w); sys_p = tfest(z2,2);
spa and tfest require System Identification Toolbox™ software. The model sys_np is a non-parametric identified model while, sys_p is a parametric identified model.
Create an options set to turn the grid on. Then, create a sigma plot that includes both systems using this options set.
plotoptions = sigmaoptions; plotoptions.Grid = 'on'; h = sigmaplot(sys_p,'b--',sys_np,'r--',w,plotoptions); legend('Parametric Model','Non-Parametric model');

Modified Singular Value Plot of MIMO System
Consider the following two-input, two-output dynamic system.
Plot the singular value responses of H(s) and I + H(s). Set appropriate titles using the plot option set.
H = [0, tf([3 0],[1 1 10]) ; tf([1 1],[1 5]), tf(2,[1 6])]; opts1 = sigmaoptions; opts1.Grid = 'on'; opts1.Title.String = 'Singular Value Plot of H(s)'; h1 = sigmaplot(H,opts1);

Use input 2 to plot the modified SV of type, I + H(s).
opts2 = sigmaoptions; opts2.Grid = 'on'; opts2.Title.String = 'Singular Value Plot of I+H(s)'; h2 = sigmaplot(H,[],2,opts2);

Version History
Introduced in R2008a
MATLAB-Befehl
Sie haben auf einen Link geklickt, der diesem MATLAB-Befehl entspricht:
Führen Sie den Befehl durch Eingabe in das MATLAB-Befehlsfenster aus. Webbrowser unterstützen keine MATLAB-Befehle.

Select a Web Site
Choose a web site to get translated content where available and see local events and offers. Based on your location, we recommend that you select: .
You can also select a web site from the following list:
How to Get Best Site Performance
Select the China site (in Chinese or English) for best site performance. Other MathWorks country sites are not optimized for visits from your location.
Americas
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
Europe
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)