Relevance Vector Machine (RVM)
Relevance Vector Machine (RVM)
MATLAB code for Relevance Vector Machine
Version 2.1, 31-AUG-2021
Email: iqiukp@outlook.com
Main features
- RVM model for binary classification (RVC) or regression (RVR)
- Multiple kinds of kernel functions (linear, gaussian, polynomial, sigmoid, laplacian)
- Hybrid kernel functions (K =w1×K1+w2×K2+...+wn×Kn)
- Parameter Optimization using Bayesian optimization, Genetic Algorithm, and Particle Swarm Optimization
Notices
- This version of the code is not compatible with the versions lower than R2016b.
- Detailed applications please see the demonstrations.
- This code is for reference only.
Citation
@article{tipping2001sparse,
title={Sparse Bayesian learning and the relevance vector machine},
author={Tipping, Michael E},
journal={Journal of machine learning research},
volume={1},
number={Jun},
pages={211--244},
year={2001}
}
@article{qiu2021soft,
title={Soft sensor development based on kernel dynamic time warping and a relevant vector machine for unequal-length batch processes},
author={Qiu, Kepeng and Wang, Jianlin and Wang, Rutong and Guo, Yongqi and Zhao, Liqiang},
journal={Expert Systems with Applications},
volume={182},
pages={115223},
year={2021},
publisher={Elsevier}
}
How to use
01. Classification using RVM (RVC)
A demo for classification using RVM
clc
clear all
close all
addpath(genpath(pwd))
% use fisheriris dataset
load fisheriris
inds = ~strcmp(species, 'setosa');
data_ = meas(inds, 3:4);
label_ = species(inds);
cvIndices = crossvalind('HoldOut', length(data_), 0.3);
trainData = data_(cvIndices, :);
trainLabel = label_(cvIndices, :);
testData = data_(~cvIndices, :);
testLabel = label_(~cvIndices, :);
% kernel function
kernel = Kernel('type', 'gaussian', 'gamma', 0.2);
% parameter
parameter = struct( 'display', 'on',...
'type', 'RVC',...
'kernelFunc', kernel);
rvm = BaseRVM(parameter);
% RVM model training, testing, and visualization
rvm.train(trainData, trainLabel);
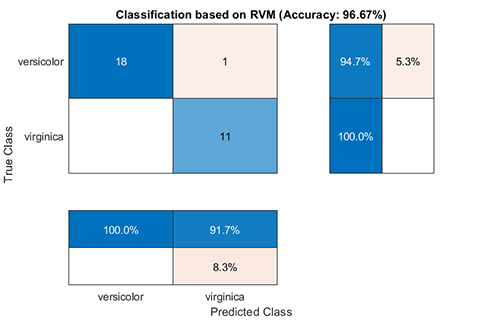
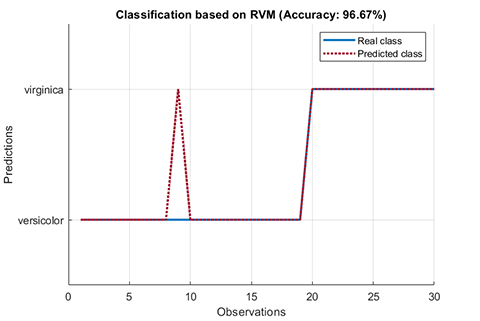
results = rvm.test(testData, testLabel);
rvm.draw(results)results:
*** RVM model (classification) train finished ***
running time = 0.1604 seconds
iterations = 20
number of samples = 70
number of RVs = 2
ratio of RVs = 2.8571%
accuracy = 94.2857%
*** RVM model (classification) test finished ***
running time = 0.0197 seconds
number of samples = 30
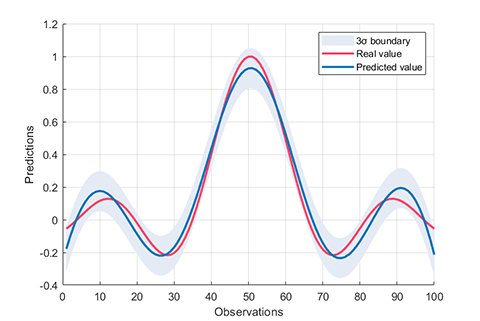
accuracy = 96.6667%02. Regression using RVM (RVR)
A demo for regression using RVM
clc
clear all
close all
addpath(genpath(pwd))
% sinc funciton
load sinc_data
trainData = x;
trainLabel = y;
testData = xt;
testLabel = yt;
% kernel function
kernel = Kernel('type', 'gaussian', 'gamma', 0.1);
% parameter
parameter = struct( 'display', 'on',...
'type', 'RVR',...
'kernelFunc', kernel);
rvm = BaseRVM(parameter);
% RVM model training, testing, and visualization
rvm.train(trainData, trainLabel);
results = rvm.test(testData, testLabel);
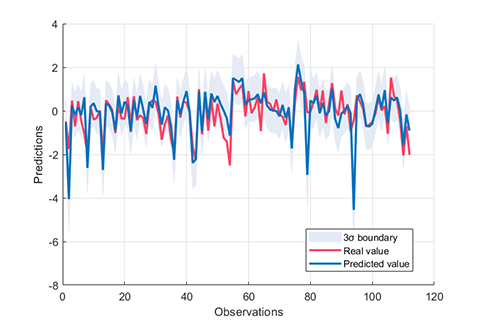
rvm.draw(results)results:
*** RVM model (regression) train finished ***
running time = 0.1757 seconds
iterations = 76
number of samples = 100
number of RVs = 6
ratio of RVs = 6.0000%
RMSE = 0.1260
R2 = 0.8821
MAE = 0.0999
*** RVM model (regression) test finished ***
running time = 0.0026 seconds
number of samples = 50
RMSE = 0.1424
R2 = 0.8553
MAE = 0.110603. Kernel funcions
A class named Kernel is defined to compute kernel function matrix.
%{
type -
linear : k(x,y) = x'*y
polynomial : k(x,y) = (γ*x'*y+c)^d
gaussian : k(x,y) = exp(-γ*||x-y||^2)
sigmoid : k(x,y) = tanh(γ*x'*y+c)
laplacian : k(x,y) = exp(-γ*||x-y||)
degree - d
offset - c
gamma - γ
%}
kernel = Kernel('type', 'gaussian', 'gamma', value);
kernel = Kernel('type', 'polynomial', 'degree', value);
kernel = Kernel('type', 'linear');
kernel = Kernel('type', 'sigmoid', 'gamma', value);
kernel = Kernel('type', 'laplacian', 'gamma', value);For example, compute the kernel matrix between X and Y
X = rand(5, 2);
Y = rand(3, 2);
kernel = Kernel('type', 'gaussian', 'gamma', 2);
kernelMatrix = kernel.computeMatrix(X, Y);
>> kernelMatrix
kernelMatrix =
0.5684 0.5607 0.4007
0.4651 0.8383 0.5091
0.8392 0.7116 0.9834
0.4731 0.8816 0.8052
0.5034 0.9807 0.727404. Hybrid kernel
A demo for regression using RVM with hybrid_kernel (K =w1×K1+w2×K2+...+wn×Kn)
clc
clear all
close all
addpath(genpath(pwd))
% sinc funciton
load sinc_data
trainData = x;
trainLabel = y;
testData = xt;
testLabel = yt;
% kernel function
kernel_1 = Kernel('type', 'gaussian', 'gamma', 0.3);
kernel_2 = Kernel('type', 'polynomial', 'degree', 2);
kernelWeight = [0.5, 0.5];
% parameter
parameter = struct( 'display', 'on',...
'type', 'RVR',...
'kernelFunc', [kernel_1, kernel_2],...
'kernelWeight', kernelWeight);
rvm = BaseRVM(parameter);
% RVM model training, testing, and visualization
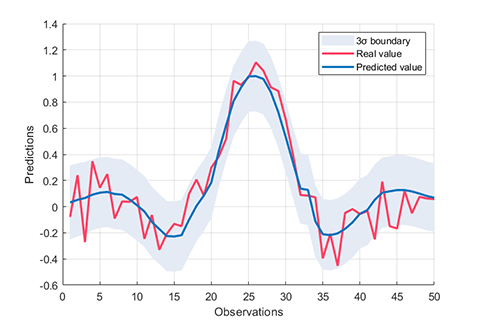
rvm.train(trainData, trainLabel);
results = rvm.test(testData, testLabel);
rvm.draw(results)05. Parameter Optimization for single-kernel-RVM
A demo for RVM model with Parameter Optimization
clc
clear all
close all
addpath(genpath(pwd))
% use fisheriris dataset
load fisheriris
inds = ~strcmp(species, 'setosa');
data_ = meas(inds, 3:4);
label_ = species(inds);
cvIndices = crossvalind('HoldOut', length(data_), 0.3);
trainData = data_(cvIndices, :);
trainLabel = label_(cvIndices, :);
testData = data_(~cvIndices, :);
testLabel = label_(~cvIndices, :);
% kernel function
kernel = Kernel('type', 'gaussian', 'gamma', 5);
% parameter optimization
opt.method = 'bayes'; % bayes, ga, pso
opt.display = 'on';
opt.iteration = 20;
% parameter
parameter = struct( 'display', 'on',...
'type', 'RVC',...
'kernelFunc', kernel,...
'optimization', opt);
rvm = BaseRVM(parameter);
% RVM model training, testing, and visualization
rvm.train(trainData, trainLabel);
results = rvm.test(trainData, trainLabel);
rvm.draw(results)
results:
*** RVM model (classification) train finished ***
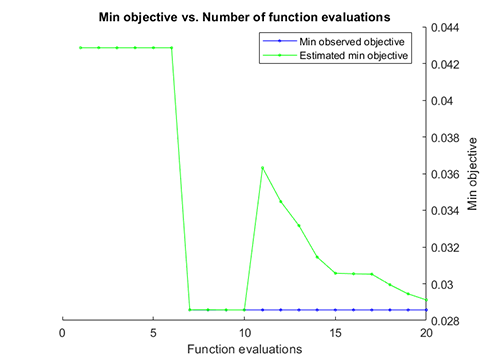
running time = 13.3356 seconds
iterations = 88
number of samples = 70
number of RVs = 4
ratio of RVs = 5.7143%
accuracy = 97.1429%
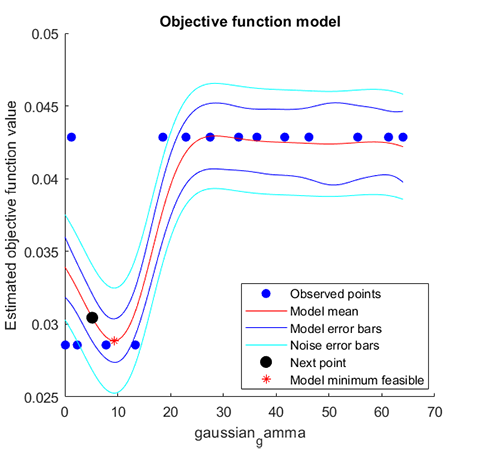
Optimized parameter table
gaussian_gamma
______________
7.8261
*** RVM model (classification) test finished ***
running time = 0.0195 seconds
number of samples = 70
accuracy = 97.1429%06. Parameter Optimization for hybrid-kernel-RVM
A demo for RVM model with Parameter Optimization
%{
A demo for hybrid-kernel RVM model with Parameter Optimization
%}
clc
clear all
close all
addpath(genpath(pwd))
% data
load UCI_data
trainData = x;
trainLabel = y;
testData = xt;
testLabel = yt;
% kernel function
kernel_1 = Kernel('type', 'gaussian', 'gamma', 0.5);
kernel_2 = Kernel('type', 'polynomial', 'degree', 2);
% parameter optimization
opt.method = 'bayes'; % bayes, ga, pso
opt.display = 'on';
opt.iteration = 30;
% parameter
parameter = struct( 'display', 'on',...
'type', 'RVR',...
'kernelFunc', [kernel_1, kernel_2],...
'optimization', opt);
rvm = BaseRVM(parameter);
% RVM model training, testing, and visualization
rvm.train(trainData, trainLabel);
results = rvm.test(testData, testLabel);
rvm.draw(results)
results:
*** RVM model (regression) train finished ***
running time = 24.4042 seconds
iterations = 377
number of samples = 264
number of RVs = 22
ratio of RVs = 8.3333%
RMSE = 0.4864
R2 = 0.7719
MAE = 0.3736
Optimized parameter 1×6 table
gaussian_gamma polynomial_gamma polynomial_offset polynomial_degree gaussian_weight polynomial_weight
______________ ________________ _________________ _________________ _______________ _________________
22.315 13.595 44.83 6 0.042058 0.95794
*** RVM model (regression) test finished ***
running time = 0.0008 seconds
number of samples = 112
RMSE = 0.7400
R2 = 0.6668
MAE = 0.486707. Cross Validation
In this code, two cross-validation methods are supported: 'K-Folds' and 'Holdout'. For example, the cross-validation of 5-Folds is
parameter = struct( 'display', 'on',...
'type', 'RVC',...
'kernelFunc', kernel,...
'KFold', 5);For example, the cross-validation of the Holdout method with a ratio of 0.3 is
parameter = struct( 'display', 'on',...
'type', 'RVC',...
'kernelFunc', kernel,...
'HoldOut', 0.3);08. Other option
%% custom optimization option
%{
opt.method = 'bayes'; % bayes, ga, pso
opt.display = 'on';
opt.iteration = 20;
opt.point = 10;
% gaussian kernel function
opt.gaussian.parameterName = {'gamma'};
opt.gaussian.parameterType = {'real'};
opt.gaussian.lowerBound = 2^-6;
opt.gaussian.upperBound = 2^6;
% laplacian kernel function
opt.laplacian.parameterName = {'gamma'};
opt.laplacian.parameterType = {'real'};
opt.laplacian.lowerBound = 2^-6;
opt.laplacian.upperBound = 2^6;
% polynomial kernel function
opt.polynomial.parameterName = {'gamma'; 'offset'; 'degree'};
opt.polynomial.parameterType = {'real'; 'real'; 'integer'};
opt.polynomial.lowerBound = [2^-6; 2^-6; 1];
opt.polynomial.upperBound = [2^6; 2^6; 7];
% sigmoid kernel function
opt.sigmoid.parameterName = {'gamma'; 'offset'};
opt.sigmoid.parameterType = {'real'; 'real'};
opt.sigmoid.lowerBound = [2^-6; 2^-6];
opt.sigmoid.upperBound = [2^6; 2^6];
%}
%% RVM model parameter
%{
'display' : 'on', 'off'
'type' : 'RVR', 'RVC'
'kernelFunc' : kernel function
'KFolds' : cross validation, for example, 5
'HoldOut' : cross validation, for example, 0.3
'freeBasis' : 'on', 'off'
'maxIter' : max iteration, for example, 1000
%}Zitieren als
@article{tipping2001sparse, title={Sparse Bayesian learning and the relevance vector machine}, author={Tipping, Michael E}, journal={Journal of machine learning research}, volume={1}, number={Jun}, pages={211--244}, year={2001} }
@article{qiu2021soft, title={Soft sensor development based on kernel dynamic time warping and a relevant vector machine for unequal-length batch processes}, author={Qiu, Kepeng and Wang, Jianlin and Wang, Rutong and Guo, Yongqi and Zhao, Liqiang}, journal={Expert Systems with Applications}, volume={182}, pages={115223}, year={2021}, publisher={Elsevier} }
Kompatibilität der MATLAB-Version
Plattform-Kompatibilität
Windows macOS LinuxKategorien
- AI and Statistics > Statistics and Machine Learning Toolbox > Regression > Model Building and Assessment > Bayesian Regression >
Tags
Community Treasure Hunt
Find the treasures in MATLAB Central and discover how the community can help you!
Start Hunting!Live Editor erkunden
Erstellen Sie Skripte mit Code, Ausgabe und formatiertem Text in einem einzigen ausführbaren Dokument.
RvmModel
SB2_Release_200
Versionen, die den GitHub-Standardzweig verwenden, können nicht heruntergeladen werden
| Version | Veröffentlicht | Versionshinweise | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2.1.2 | * Updated demo_optimization.m |
|
|
| 2.1.1 |
|
||
| 2.1 | RVM model for binary classification (RVC) or regression (RVR)
|
|
|
| 2.0.1 | Update Description |
|
|
| 2.0 | 1. added support for hybrid kernel functions
|
|
|
| 1.3.0 | 1. Added support for multiple kernel functions. |
|
|
| 1.2.0 | 1. Fixed some errors
|
|
|
| 1.1.0 | 1. Fixed some errors
|
|
|
| 1.0.0 |
|