Support Vector Data Description (SVDD)
Support Vector Data Description (SVDD)
MATLAB Code for abnormal detection using SVDD
Version 2.2, 13-MAY-2022
Email: iqiukp@outlook.com
✨ MAIN FEATURES
- SVDD model for one-class or binary classification
- Multiple kinds of kernel functions (linear, gaussian, polynomial, sigmoid, laplacian)
- Visualization of decision boundaries for 2D or 3D data
- Parameter optimization using Bayesian optimization, genetic algorithm, and pParticle swarm optimization
- Weighted SVDD model
- Hybrid-kernel SVDD model (K =w1×K1+w2×K2+...+wn×Kn)
⚠️ NOTICES
- This version of this code is not compatible with the versions lower than R2016b.
- The label must be 1 for positive sample or -1 for negative sample.
- Detailed applications please see the provided demonstrations.
- This code is for reference only.
🔨 HOW TO USE
👉 A simple SVDD model
Please see the demonstration 📝 demo_BasicSVDD.m for details.
% generate dataset
ocdata = BinaryDataset();
ocdata.generate;
[trainData, trainLabel, testData, testLabel] = ocdata.partition;
% set parameter
kernel = BaseKernel('type', 'gaussian', 'gamma', 0.04);
cost = 0.3;
svddParameter = struct('cost', cost,...
'kernelFunc', kernel);
% creat an SVDD object
svdd = BaseSVDD(svddParameter);
% train SVDD model
svdd.train(trainData, trainLabel);
% test SVDD model
results = svdd.test(testData, testLabel);-
BinaryDatasetis designed to validate the svdd model only, you can use your data and please be careful to keep the naming of variables consistent, e.g.trainData,trainLabel,testData, andtestLabel. - Specifically, if the data does not have labels, please change the inputs for training or testing to
svdd.train(trainData)andresults = svdd.test(testData).
👉 Parameter Optimization for SVDD model
A class named SvddOptimization is defined to optimized the parameters. First define an optimization setting structure, then add it to the svdd parameter structure.The parameter optimization of the polynomial kernel function can only be achieved by using Bayesian optimization.
Please see the demonstration 📝 demo_ParameterOptimization.m for details.
% optimization setting
optimization.method = 'bayes'; %
optimization.maxIteration = 20;
optimization.display = 'on';
% SVDD parameter
svddParameter = struct('cost', cost,...
'kernelFunc', kernel,...
'optimization', optimization);The full properties of optimization are
-
method: optimization methods, only supported for 'bayes', 'pso', and 'ga'. -
variableName: variables that are to be optimized, including 'cost', 'degree', 'offset', and 'gamma'. -
variableType: variable type, specified as 'real' (real variable), 'integer' (integer variable). -
lowerBound: lower bound of variables. -
upperBound: upper bound of variables. -
maxIteration: max iterations. -
points: size of group or seed. -
display: visualization, 'on' or 'off'.
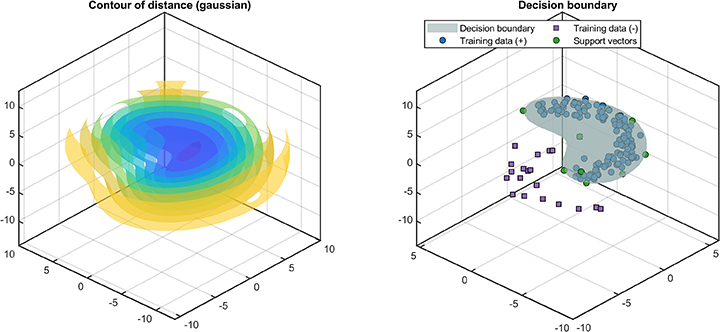
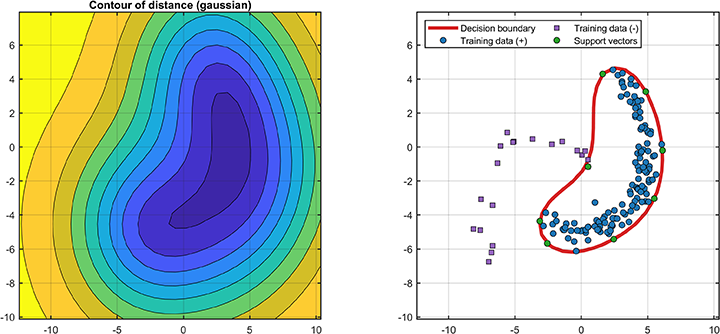
👉 Visualization of SVDD model
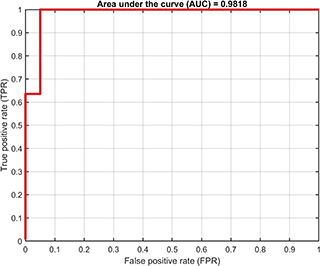
A class named SvddVisualization is defined to visualize the training and test results. Based on the trained SVDD model, the ROC curve of the training results (only supported for dataset containing both positive and negetive samples) is
% Visualization
svplot = SvddVisualization();
svplot.ROC(svdd);The decision boundaries (only supported for 2D/3D dataset) are
% Visualization
svplot = SvddVisualization();
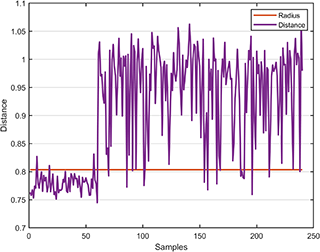
svplot.boundary(svdd);The distance between the test data and the hypersphere is
svplot.distance(svdd, results);👉 Binary Dataset for SVDD model
A class named BinaryDataset is defined to generate and partition the 2D or 3D binary dataset.
Please see the demonstration 📝demo_BinaryDataset.m for details.
ocdata = BinaryDataset();
[data, label] = ocdata.generate;
[trainData, trainLabel, testData, testLabel] = ocdata.partition;The method generate is designed to generate dataset. The syntax of generate is
ocdata.generate;
data = ocdata.generate;
[data, label] = ocdata.generate;The method partition is designed to partition dataset into training dataset and test dataset. The syntax of partition is
[trainData, trainLabel, testData, testLabel] = ocdata.partition;The full Name-Value Arguments of class BinaryDataset are
-
shape: shape of dataset, 'banana' or 'circle'. -
dimensionality: dimensionality of dataset, 2 or 3. -
number: number of samples per class, for example: [200, 200]. -
display: visualization, 'on' or 'off'. -
noise: noise added to dataset with range [0, 1]. For example: 0.2. -
ratio: ratio of the test set with range (0, 1). For example: 0.3.
👉 Kernel funcions
A class named BaseKernel is defined to compute kernel function matrix.
Please see the demonstration 📝demo_KernelFunction.m for details.
%{
type -
linear : k(x,y) = x'*y
polynomial : k(x,y) = (γ*x'*y+c)^d
gaussian : k(x,y) = exp(-γ*||x-y||^2)
sigmoid : k(x,y) = tanh(γ*x'*y+c)
laplacian : k(x,y) = exp(-γ*||x-y||)
degree - d
offset - c
gamma - γ
%}
kernel = BaseKernel('type', 'gaussian', 'gamma', value);
kernel = BaseKernel('type', 'polynomial', 'degree', value);
kernel = BaseKernel('type', 'linear');
kernel = BaseKernel('type', 'sigmoid', 'gamma', value);
kernel = BaseKernel('type', 'laplacian', 'gamma', value);👉 Cross Validation
In this code, two cross-validation methods are supported: 'K-Folds' and 'Holdout'. For example, the cross-validation of 5-Folds is
svddParameter = struct('cost', cost,...
'kernelFunc', kernel,...
'KFold', 5);For example, the cross-validation of the Holdout method with a ratio of 0.3 is
svddParameter = struct('cost', cost,...
'kernelFunc', kernel,...
'Holdout', 0.3);👉 Dimensionality reduction using PCA
For example, reducing the data to 2 dimensions can be set as
% SVDD parameter
svddParameter = struct('cost', cost,...
'kernelFunc', kernel,...
'PCA', 2);Please see the demonstration 📝demo_demo_DimReduPCA.m for details.
Notice: you only need to set PCA in svddParameter, and you don't need to process training data and test data separately.
👉 Weighted SVDD
An Observation-weighted SVDD is supported in this code.
Please see the demonstration 📝demo_ObservationWeight.m for details.
weight = rand(size(trainData, 1), 1);
% SVDD parameter
svddParameter = struct('cost', cost,...
'kernelFunc', kernel,...
'weight', weight);Notice: the size of 'weigh' should be m×1, where m is the number of training samples.
👉 Hybrid-kernel SVDD model
A demo for SVDD using Hybrid kernel functions (K =w1×K1+w2×K2+...+wn×Kn).
Please see the demonstration 📝demo_HybridKernelSVDD.m for details.
kernel_1 = BaseKernel('type', 'gaussian', 'gamma', 1);
kernel_2 = BaseKernel('type', 'polynomial', 'degree', 3);
kernelWeight = [0.5, 0.5];
cost = 0.9;
svddParameter = struct('cost', cost,...
'kernelFunc', [kernel_1, kernel_2],...
'kernelWeight', kernelWeight);Zitieren als
Kepeng Qiu (2024). Support Vector Data Description (SVDD) (https://github.com/iqiukp/SVDD-MATLAB/releases/tag/v2.2), GitHub. Abgerufen.
Kompatibilität der MATLAB-Version
Plattform-Kompatibilität
Windows macOS LinuxKategorien
- AI and Statistics > Deep Learning Toolbox > Deep Learning Fundamentals > Visualize and Verify Deep Neural Networks >
Tags
Community Treasure Hunt
Find the treasures in MATLAB Central and discover how the community can help you!
Start Hunting!Live Editor erkunden
Erstellen Sie Skripte mit Code, Ausgabe und formatiertem Text in einem einzigen ausführbaren Dokument.
Svdd
Versionen, die den GitHub-Standardzweig verwenden, können nicht heruntergeladen werden
| Version | Veröffentlicht | Versionshinweise | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2.2 | See release notes for this release on GitHub: https://github.com/iqiukp/SVDD-MATLAB/releases/tag/v2.2 |
||
| 2.1.5 | See release notes for this release on GitHub: https://github.com/iqiukp/SVDD-MATLAB/releases/tag/v2.1.5 |
||
| 2.1.4.1 | * Fixed bugs with Display Settings for Parameter Optimization. |
|
|
| 2.1.4 | * Fixed bugs with Display Settings for Parameter Optimization. |
|
|
| 2.1.3 | Update Description |
|
|
| 2.1.2 | Visit https://github.com/iqiukp/Support-Vector-Data-Description-SVDD for more information. |
|
|
| 2.1.1 | Visit https://github.com/iqiukp/Support-Vector-Data-Description-SVDD for more information. |
|
|
| 2.1 | Visit https://github.com/iqiukp/Support-Vector-Data-Description-SVDD for more information. |
|
|
| 2.0 | Details please see Description |
|
|
| 1.1 | 1. Added the SMO algorithm to solve the Lagrange dual problem of SVDD |
|
|
| 1.0.2 | 1. Added descriptions for the calculation of the radius
|
|
|
| 1.0.1 | 1. Fixed some function descriptions
|
|
|
| 1.0.0 |
|