Overview of CLA Configuration for C2000 Processors Using Subsystem
The control law accelerator (CLA) is a coprocessor available with the TI C2000™ processor that allows parallel processing. Utilizing the CLA for time-critical tasks frees up the main CPU to perform other system and communication functions concurrently.
These sections explain:
CLA Task
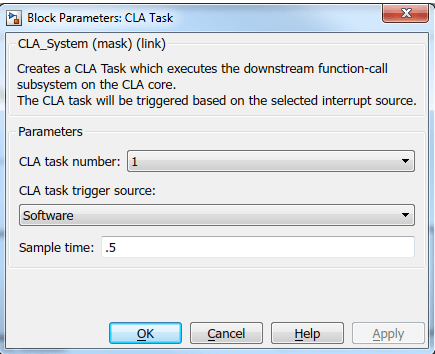
A CLA Task block is used here to trigger a CLA task. This block runs the downstream function-call subsystem on the CLA. In the block mask of the CLA Task block, specify the CLA task number and the associated interrupt triggering source. Ensure that you are using the CLA Trigger block from the library corresponding to your hardware board selected in the Configuration Parameters. CLA task trigger source options are different for different processors. The downstream function-call subsystem is executed using the selected CLA Task when the selected interrupt triggers. For more, see C28x CLA Task.
For example, CLA Task1 is used and Software is selected as the trigger source, which means that the CLA task is triggered at the sample rate provided in the sample time parameter.
Interrupt Generation after CLA Task Completion
A CLA interrupt can be generated when the CLA Task completes. CLA Task1 interrupt is used as the interrupt source on the C28x Hardware Interrupt block. The function-call subsystem triggered by the Hardware Interrupt block with CLA task interrupt (CPU = 11, PIE = 1-8) is executed at the end of the CLA task when the particular interrupt occurs.
Note
When a CLA Task is triggered by an interrupt other than software, ensure that the interrupt gets cleared at the end of the CLA task. This is achieved automatically when you use Hardware Interrupt block with CLA end of the task interrupt or the CLA source trigger interrupt.
CLA Subsystem
A CLA Subsystem block contains a subset of blocks within a model or system. CLA Subsystem is a triggered subsystem which is caused by a CLA Task block.
CLA Subsystem block can only be used along with CLA Task block. For more, see CLA Subsystem.
CLA Subsystem requires you to load tic2000demospkg package in the
model with a valid TI C2000 based hardware board. To load the tic2000demospkg package
in the model, follow the below steps.
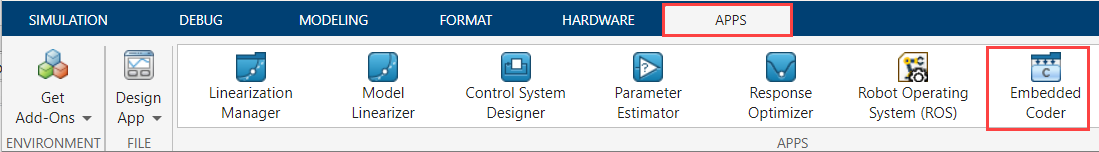
From Simulink toolstrip, navigate to Apps and click Embedded Coder.
Go to C Code > Code Interface and click Embedded Coder Dictionary (Model).
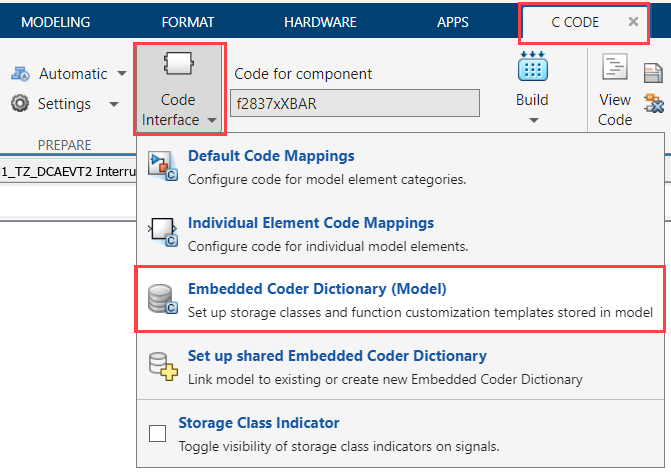
From the Embedded Coder Dictionary window, go to Storage Class and click Manage Packages. If you do not find the
tic2000demospkg, click Refresh and load the package. For more information, see Data Exchange Between CLA and C28x CPU.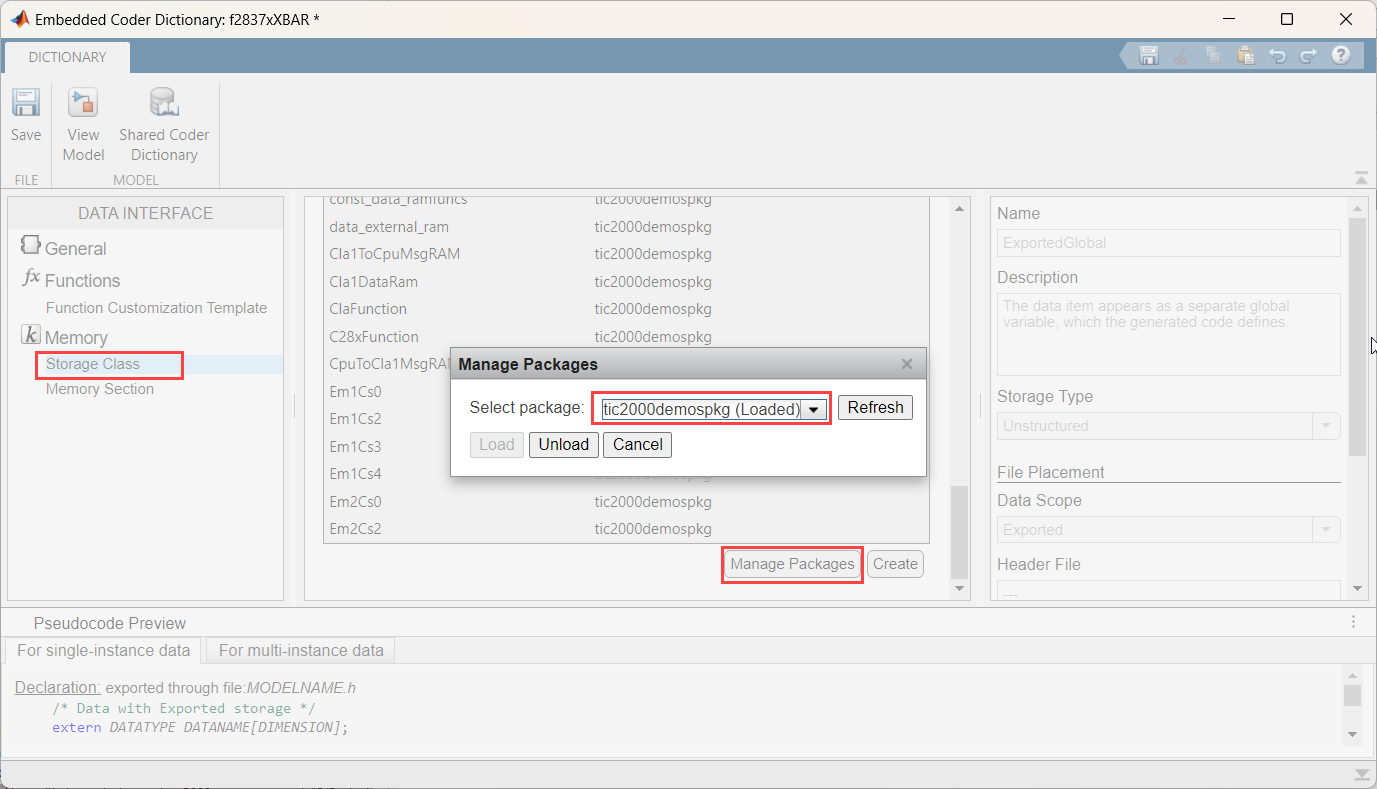
Method 1 - Nonreusable Function Code Generation for CLA Subsystem (Recommended)
In the CLA Subsystem block, the Function packaging parameter on
the Code Generation tab is set to is Nonresuable by default. To open
the block parameters, right-click on the CLA subsystem and select Block Parameters(Subsystem).
Note
This method requires tic2000demospkg package to be loaded in
the model with TI C2000 hardware board. For more, see Data Exchange Between CLA and C28x CPU.

The CLA Subsystem block generates the CLA algorithm code as a separate
.C filealong with the data.The initialize/terminate functions are prefixed with compiler directives so it is compiled with only C compiler and execution functions prefixed to ensure that it gets compiled by CLA compiler.
The constants, parameters, and internal data are configured automatically to be stored in
Cla1DataRAM.Save only the input signals from CPU to CLA as a signal and store them in the
CpuToCla1MsgRAMstorage class using the Code Mappings editor.Use this method to Monitor & Tune (External mode) signals outside the CLA subsystem.
The Nonreusable Function Code Generation for CLA Subsystem feature is available starting R2021b.
Method 2 - Inline Code Generation for CLA Subsystem
In the CLA Subsystem block, select the Function packaging as
Inline under the Code Generation tab of the
Block Parameters. To open the Block Parameters, right-click on the CLA subsystem and
select Block Parameters(Subsystem).

In this method, the entire algorithm inside CLA gets
inlinedand is part of CLA task file (cla_task.cla).All the input signals to the CLA must be configured manually to store
CpuToCla1MsgRAMstorage class.All the output signals from the CLA to CPU configured manually to store
Cla1ToCpuMsgRAMstorage class.All discrete state variables used inside CLA function-call subsystems configured manually to store
Cla1DataRam. For example, delay blocks and integrators must be set to use the Cla1DataRam storage class for state variables. See the State Attributes of the Delay block insidecla_subsysteminc28035blink_cla.slxexample.With this method, you cannot perform Monitor & Tune (External mode) for the signals outside CLA subsystem.
Data Exchange Between CLA and C28x CPU
CLA storage classes can be loaded in the model (Embedded Coder > Code Interface > Embedded Coder Dictionary > Manage Packages) as shown.


The Code Mappings editor is the primary location to configure model data elements for code generation. For more information, refer to Code Mappings Editor — C (Simulink Coder).
All the interfaces between the CLA and the CPU need to be placed in specific memory sections. To gain specific access to these sections, Select Embedded Coder > Code Mappings > Data stores and Signal/States for CpuToCla1MsgRAM and Cla1ToCpuMsgRAM. For more information, refer to Code Mappings Editor — C (Simulink Coder).
Memory Section Data
The data in the model is stored in the various memory sections which has the following access rules.
Memory Storage Class
Memory Section | CPU | CLA |
|---|---|---|
| CpuToCla1MsgRAM | Read & Write | Read only |
| Cla1ToCpuMsgRAM | Read only | Read & Write |
| Cla1DataRAM | Read & Write | Read & Write |
Note
Signal or states with
Cla1ToCpuMsgRAMstorage class will add initialization in the function compiled by CPU (model initialization function) but CPU does not have write access to the above memory section. If initialization is required for a particular variable and needs to be editable by CLA as well, it is recommended to useCla1DataRAM.For F2803x processor, the
Cla1DataRAMbehave similar toCla1ToCpuMsgRami.e. CPU does not have write access to any of the above storage class exceptCpuToCla1MsgRAM.
Memory Section Code
The functions with the following memory section are prefixed with compiler directives to control the compilation of the code.
C28xFunction is compiled by
C28x compilerClaFunction is compiled by
CLA compiler.
The following figures show the configurations of specific memory section between CPU and CLA in the model.
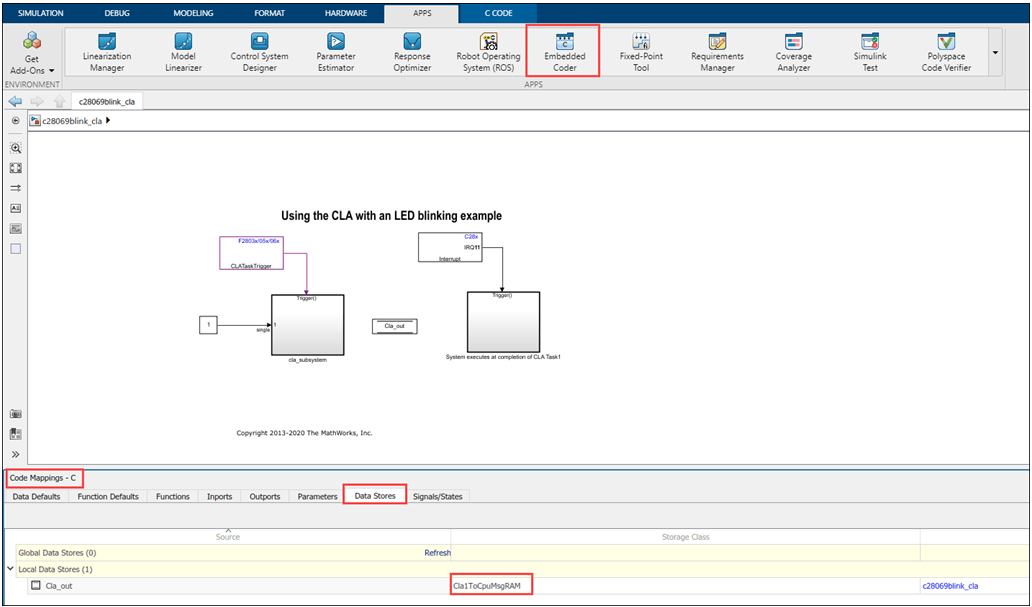

Required Model Configuration When Using CLA
In Model Configuration Parameters > Code Generation > Optimization,
the Default parameter behavior parameter must be set to
Inlined. This avoids the creation of model structure global variables,
as CLA cannot access global data.
Change Standard Linker Command File
For F28035 and F28069 processors, a specific linker command file has to be selected to
assign CLA memory sections. In the Model Configuration Parameters, under
Hardware Implementation > Target hardware
resources > Build options, and select Use
custom linker command file. A preconfigured c28069_cla.cmd
is used as linker command file. This file adds CLA memory sections description and can be
found in the src directory at the root of the blockset
installation.

Profiling with XCP External Mode
When performing profiling with XCP External mode for a model containing CLA subsystem, ensure to disable the parameter Terminate function required under Configuration Parameters > Code Generation > Interface > Advanced parameters.

Note
For a model containing CLA, running profiling with XCP External mode, will not profile the tasks executed in CLA.
CLA LSRAM Memory Configuration
In the Model Configuration Parameters, you can configure the local shared RAM (LSRAM) as CLA program and data memory.
In Model Configuration Parameters, navigate to Hardware Implementation > Target hardware resources > Build options and select Configure CLA program and data memory. For information, refer to C28x-Build Options.

The following table describes the total LSRAM memory available for the processors.
CLA LSRAM Memory Allocation
| Processor | Total LSRAM Memory available in KiloWords (KW) |
|---|---|
| F2837x/F2807x | 12 |
| F28004x/F2838x | 16 |
Debug CLA
The debug function /*__mdebugstop()*/ is present at the beginning of
the CLA task (__interrupt void Cla1Task1 ( void )) in the generated
cla_task.cla file.
Enable the debug function
__mdebugstop()by removing the block comments around it.Compile the source code or build the CCS project.
Code Replacement Library in CLA
The following trigonometric function blocks from Simulink® will be replaced by the corresponding CLA math library functions if used within the subsystem triggered by CLA task.
Note
For CRL replacement inside CLA, a tag is added to the function call subsystem triggered by CLA task. Do not use this tag for any other subsystem.
Sin with approximation set as
noneCos with approximation set as
noneasin, acos, atan, atan2, log to the base 10, log to the base e, exponential function, and square root function.
CLA Limitations and Troubleshooting
Limitations
Due to interactions between the CLA (Control Law Accelerator) and the C28x CPU, as well as limitations of the CLA C compiler, certain modeling practices must be followed.
Only a C28x event can trigger CLA application code. The C28x CPU can initiate a CLA task either through software or by using peripheral interrupts.
Interfaces between the CLA and the CPU must be placed in specific memory sections. Use the CpuToCla1MsgRAM memory section to exchange data from the C28x to the CLA and the Cla1ToCpuMsgRAM section for data from the CLA to the C28x.
Constants with a sample time of inf, mapped to CpuToCla1MsgRAM or Cla1ToCpuMsgRAM, are always initialized to 0. Ensure the sample time for such constants is set to -1 or a positive integer.
For models using a CLA subsystem in external mode, data cannot be logged within the CLA subsystem. To monitor data, move it outside the CLA subsystem.
The CLA application code does not have access to global variables.
Recursive function calls are not supported by the CLA C compiler.
The CLA C compiler does not support integer division or unsigned integer comparisons. Use MATLAB® functions to access CLA math library functions provided by TI for these operations.
You cannot use more than one instance of a DAC block with the same module when one instance is used inside the CLA.
The CLA does not support CAN, IPC, SPI, or SCI blocks.
Blocks that create reset functions cannot be used inside the CLA. Simulink does not control the definition and compilation of reset functions for the CLA core. For example, PID integrators and conditional blocks that reset states are not supported.
Constants used within a MATLAB function are stored in the constant section of the C28x, which the CLA cannot access. To address this, use constants in Simulink with appropriate storage classes and pass them as inputs to the MATLAB function.
Consider these limitations when creating a model in Simulink.
Other Guidelines to Consider While Using CLA
Avoid creating sub-functions using atomic subsystems within CLA function-call subsystems, as this generates nested functions that cannot be compiled by the CLA. These functions are not prefixed with the necessary CLA compiler tags.
Certain CLA configurations may require additional operations on the model or may restrict the use of Simulink features. Refer to the CLA C compiler documentation for a list of limitations. To ensure compatibility, use Embedded Coder® features to limit the generated code to the syntax supported by the CLA C compiler.
Troubleshooting
Ensure that the Code Generation Tools version your are using supports the CLA C Compiler.
Ensure that you have installed the latest C/C++ header files with CLA support on your system.