EtherCAT Init
Initialize EtherCAT main device node with data in the EtherCAT Network Information (ENI) file
Libraries:
Simulink Real-Time /
EtherCAT
Description
The EtherCAT Init block initializes the EtherCAT® main device stack. The block specifies the Ethernet interface cards in the network.
Before you use this block, create and save an EtherCAT Network Information (ENI) file. You export the ENI file from the Beckhoff® TwinCAT® or the acontis EC-Engineer. See Configure EtherCAT Network by Using TwinCAT 3.
To find the ENI file, click Browse. To read the ENI file and store the data in the EtherCAT Init block, click Refresh Data.
The Simulink® Real-Time™ software supports multiple EtherCAT networks. To use multiple networks:
Use a different Ethernet card interface for each EtherCAT network.
In the model, use one EtherCAT Init block for each network.
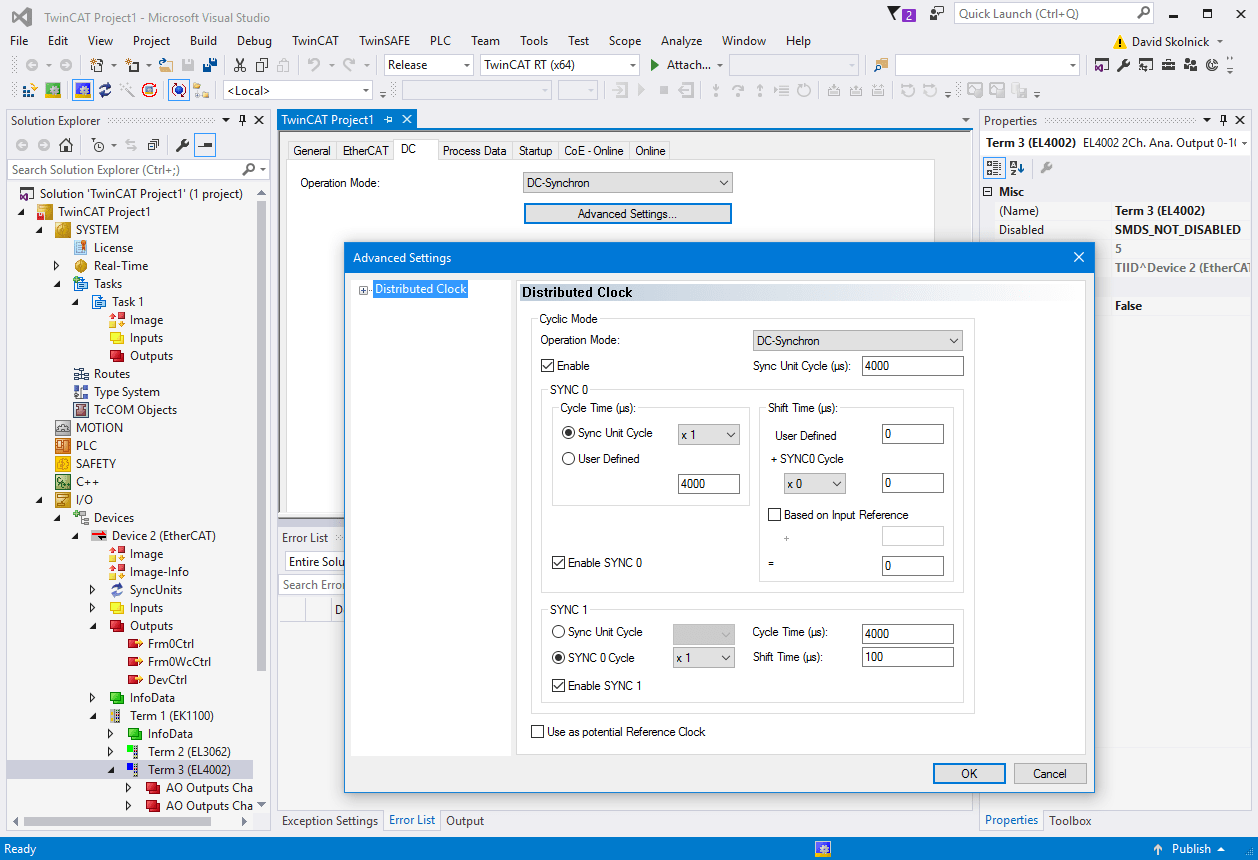
To include EtherCAT distributed clocks when PTP is enabled for the model, use EtherCAT bus shift mode.
Examples
EtherCAT Protocol with Beckhoff Analog IO Subordinate Devices EL3062 and EL4002
Communicate with EtherCAT devices using the Beckhoff® analog I/O terminals EL3062 and EL4002.
EtherCAT Protocol with Beckhoff Digital IO Subordinate Devices EL1004 and EL2004
Communicate with EtherCAT devices using the Beckhoff digital I/O terminals EL1004 and EL2004.
EtherCAT Protocol Sequenced Writing SoE Subordinate Device Configuration Variables
Use SoE blocks and a simple state machine to write configuration values to variables that can only be written before going to EtherCAT Op state.
EtherCAT Protocol Sequenced Writing CoE Subordinate Device Configuration Variables
Use CoE blocks and a simple state machine to write configuration values to variables that can only be written before going to EtherCAT Op state.
EtherCAT Protocol Detect Network Failure and Reset
Use the EtherCAT Notifications block to detect a failure in the connected network and to restart the network when the failure is corrected.
EtherCAT Protocol Motor Velocity Control with Accelnet Drive
Control the velocity of a motor by using EtherCAT communication.
EtherCAT Protocol Motor Position Control with Accelnet Drive
Control the position of a motor by using EtherCAT communication.
Generate ENI Files for EtherCAT Devices
Generate EtherCAT network information (ENI) files to use in Simulink® Real-Time™ with EtherCAT devices.
Ports
Output
The Status vector contains these values:
ErrVal, MdeviceState,
DCErrVal,
MdeviceToNetworkClkDiff,
DCInitState, and
NetworkToSubDeviceClkDiff.
ErrVal— Error status:No error:
0Error: Value less than
0.
Because
ErrValshows the latest error status, the propagation of errors can hide the original error. To find the original error, add an EtherCAT Get Notifications block and use theslrealtime.EtherCAT.filterNotificationscommand to print the status codes that the EtherCAT stack transmits.MdeviceState— Operating state of the EtherCAT network.State Value Description INIT1 Initialization — The system finds terminal devices and initializes the communication controller. PREOP2 Preoperational — The system uses the communication controller to exchange system-specific initialization data. In this state, the network cannot transmit or receive signal data. SAFEOP4 Safe operational — The network is running and ready for full operation. The supervisor sends input data to the terminal device. The terminal device output remains in a safe state. OP8 Operational — The network is in full operation. The supervisor sends input data to the terminal device. The terminal device responds with output data. DCErrVal— DC error status for the main device shift controller:No DC Error for main device shift controller:
0DC error for main device shift controller: Value from EtherCAT Init Block DC Error Values.
When you select main device shift controller mode, the value
0indicates successful clock distribution. TheDCErrValdoes not apply when the distributed clock is disabled.MdeviceToNetworkClkDiff— Time difference, in nanoseconds, between the main device stack clock and the clock on the first subordinate device that has enabled DC.DCInitState— Operating state of the distributed clock:DC not enabled, not initialized, or single EtherCAT DC subordinate device:
0DC has been started and the EtherCAT DC subordinate devices are in sync with each other:
1
NetworkToSubDeviceClkDiff— Time difference, in nanoseconds, between the clock on the first EtherCAT subordinate device and the least closely locked clock on the remaining subordinate devices.This value applies only to subordinate devices that have enabled DC. If only one device on the network has enabled DC, this value is
0.
Data Types: int32
Parameters
Specify the ENI file that you exported from the EtherCAT configurator.
You can specify the absolute path name or a relative path name from the current folder. If you specify only the file name, the software searches for the file in the current folder and on the MATLAB® path. If more than one file with that name exists on the path, MATLAB displays a message box that indicates a clearer file specification is needed.
Clicking Browse inserts a full, editable path name.
Programmatic Use
Block Parameter:
config_file
|
A unique integer in the range 0–15 that identifies the Ethernet card
for an EtherCAT network.
For each EtherCAT network, the software generates a unique device index. The software inserts that device index as Device index into the EtherCAT Init block that represents the network. For more information about Speedgoat Target Machine settings, see Install EtherCAT Network for Execution.
Programmatic Use
Block Parameter:
device_id
|
The first port reserved for EtherCAT by the
speedgoat.configureEthernet function is port 1 here. For more
information, see the description of the speedgoat.configureEthernet
function in Speedgoat documentation. For more
information about Speedgoat Target Machine settings, see Install EtherCAT Network for Execution.
Programmatic Use
Block Parameter:
portnum
|
Enter the initialization end state parameter from one of these values:
Op(default) — Select OP statePreOp— Select PREOP stateSafeOp— Select SAFEOP state
This parameter sets the EtherCAT master stack into the requested state, just after the creation of the master. This approach is useful when there is work to be done in states such as SAFEOP. After completing that work, use the EtherCAT Set State to set the block to INIT.
Programmatic Use
Block Parameter:
initstate
|
Enter the distributed clock initialization parameter from one of these values:
Large model(default) — Sends16,000timing initialization packets and allows1second of settling time. Provides best initial synchronization between multiple subordinate devices that have DC enabled.Medium model— Sends8,000timing initialization packets and allows0.3seconds of settling time. The model reaches operational state about a second earlier than it does with theLarge modelsetting.Small model— Sends2,000timing initialization packets and allows0.2seconds of settling time. The model reaches operational state earlier than it does with the other settings.
Observe device synchronization at the moment that the model enters the operational state. If the ENI file enables DC, make sure that the devices are synchronized closely enough for your application.
Programmatic Use
Block Parameter:
dctuning
|
The selections choose:
Off— Skip all except fatal errors in log.Warning— Include warnings and fatal errors in log.Info— Include information displays, warnings, and fatal errors in log.Verbose— Include sequencing information from EtherCAT stack, information displays, warnings, and fatal errors in log.All— include low level debugging information and all other categories in log.
The Verbose and All logging levels
can produce so much data that it can cause overloads at fast task
rates.
The target log file name is E_Mdevice%d, where
%d is the device id value.
Programmatic Use
Block Parameter:
enaDebug
|
Extended Capabilities
C/C++ Code Generation
Generate C and C++ code using Simulink® Coder™.
Version History
Introduced in R2020b
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.
Website auswählen
Wählen Sie eine Website aus, um übersetzte Inhalte (sofern verfügbar) sowie lokale Veranstaltungen und Angebote anzuzeigen. Auf der Grundlage Ihres Standorts empfehlen wir Ihnen die folgende Auswahl: .
Sie können auch eine Website aus der folgenden Liste auswählen:
So erhalten Sie die bestmögliche Leistung auf der Website
Wählen Sie für die bestmögliche Website-Leistung die Website für China (auf Chinesisch oder Englisch). Andere landesspezifische Websites von MathWorks sind für Besuche von Ihrem Standort aus nicht optimiert.
Amerika
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
Europa
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)