Type Editor
Create, modify, and manage types, such as bus objects
Renamed from Bus Editor in R2022b
Description
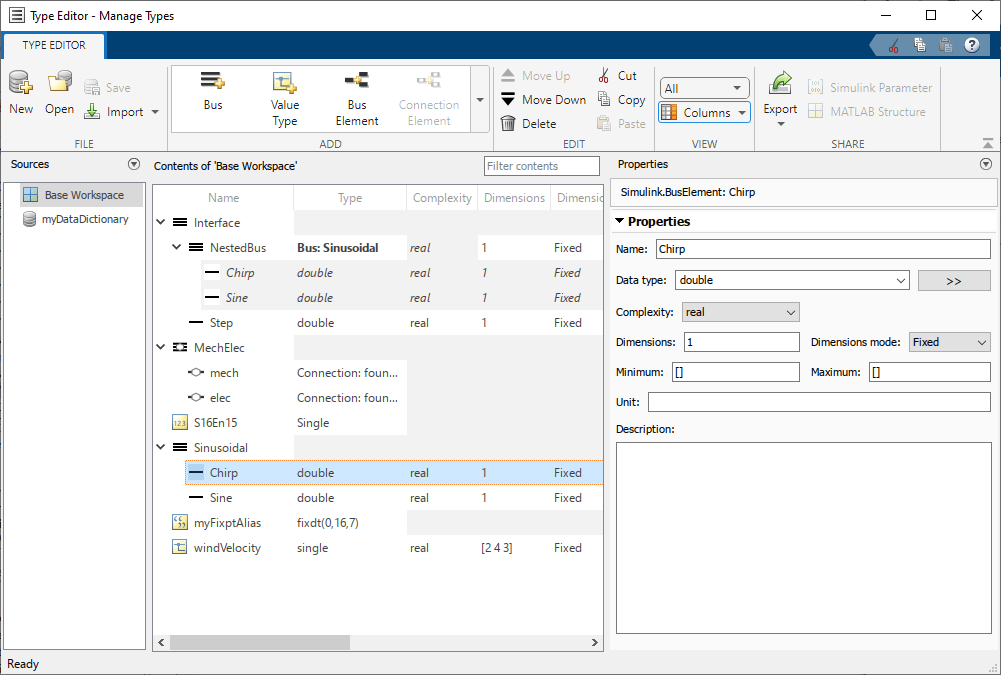
The Type Editor lets you interactively create, modify, and manage types.
Supported types include:
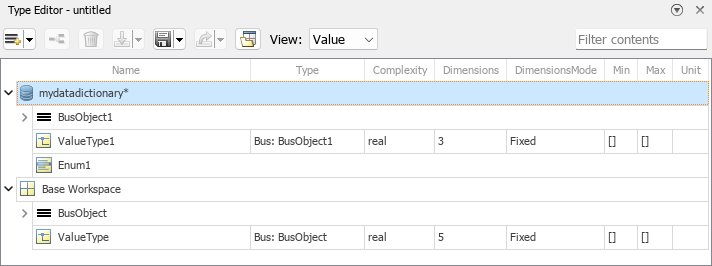
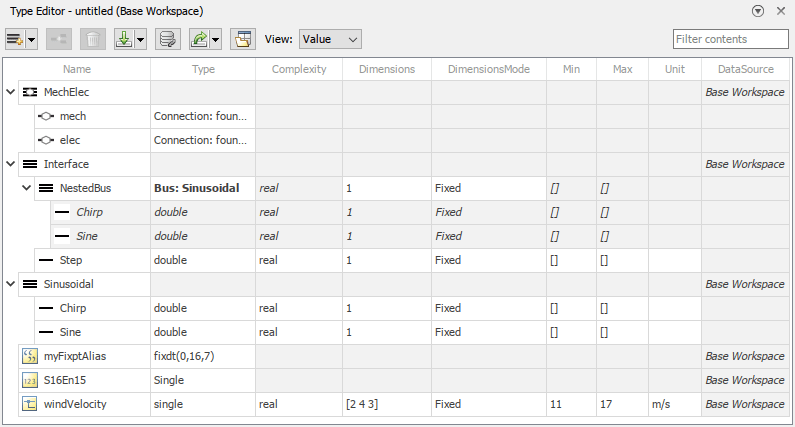
Simulink.Busobjects withSimulink.BusElementobjectsSimulink.ConnectionBusobjects withSimulink.ConnectionElementobjectsSimulink.ValueTypeobjectsSimulink.AliasTypeobjectsSimulink.NumericTypeobjectsSimulink.data.dictionary.EnumTypeDefinitionobjects in data dictionaries
The Type Editor has two variations:
The standalone Type Editor opens in a new window and supports the base workspace and data dictionaries. The Sources pane lets you quickly switch among the available sources.
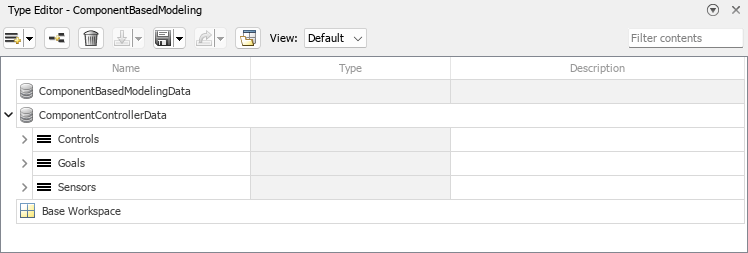
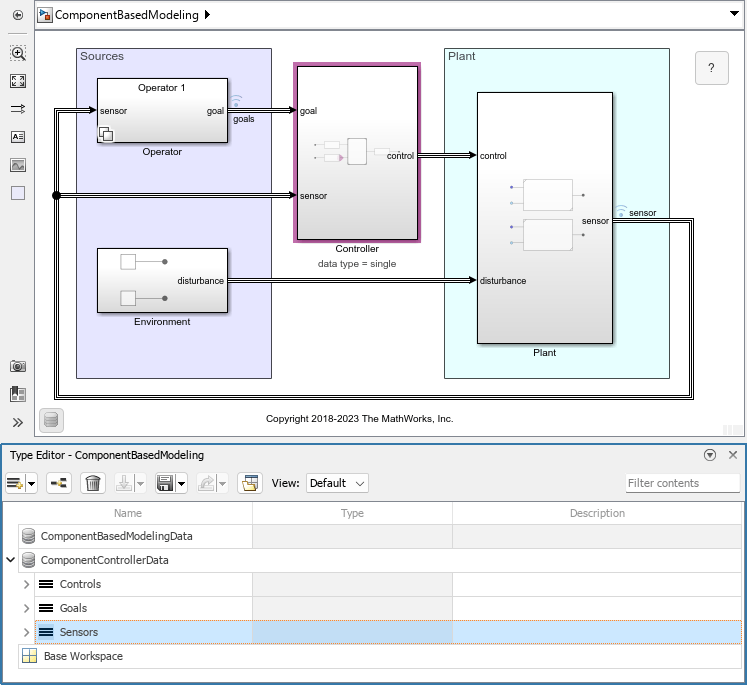
The docked Type Editor (since R2023b) opens in the context of a model window and supports the external data sources used by the model. For example, if a model uses a data dictionary and the base workspace, the docked Type Editor display the types from these sources grouped by source. (since R2024a) For more information about data sources, see Determine Where to Store Variables and Objects for Simulink Models.
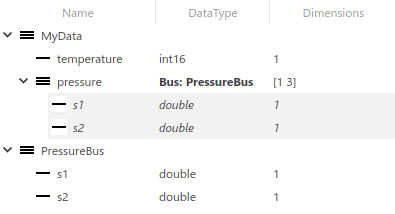
The Type Editor has an interactive table that provides information about the objects, such as hierarchy and properties.
To select which columns appear in the table, change the view. Alternatively, right-click a column title and select the desired columns. Supported views include:
Default(docked Type Editor only) — Data type and description columnsValue— Columns relevant to simulationCode(standalone Type Editor only) — Columns relevant to code generationAll— All columns
Use the table to:
Filter objects — Enter a universal filter or a column-specific filter.
Edit objects — Double-click a value in the table and enter a new value. When you enter a value that is not supported, a diagnostic message appears in this pane.
Batch edit objects — Select objects of the same type that you want to edit. Double-click a value of one of the selected objects and enter a new value. The new value applies to all selected objects.
Navigate among types — Right-click an object that references another object and select Go to. Alternatively, click an object to highlight its referenced object. Use this navigation to bring you to the editable instance of a bus object and its elements.
Reorder nested objects — Drag the nested objects to a new position.
Cut, copy, and paste objects — Right-click an object and select the desired action. Alternatively, in the standalone Type Editor, use the standard keyboard shortcuts for these actions.
Delete objects — Click
 . Alternatively, in the standalone
Type Editor, press Delete.
. Alternatively, in the standalone
Type Editor, press Delete.
Note
When you delete a bus object, you also delete the bus element objects it contains. Update any blocks that specify the deleted object. To find where a bus object is used in a model, see Finding Blocks That Use a Specific Variable.
Note
Changes that create, reorder, or delete objects take effect immediately in the base workspace. The interactive table does not support undo or redo actions.
To focus on one object at a time and edit the object properties, use the Property Inspector. When you select an object in the Type Editor, the Property Inspector shows the properties of that object. In the Property Inspector, when you enter a value that is not supported by a property, a diagnostic message appears. To undo or redo a change, right-click the corresponding box. Then, select Undo or Redo.
How you access the Property Inspector depends on the variation of the Type Editor that you have open.
Standalone Type Editor — Use the Properties pane.
Docked Type Editor — From the Simulink® Toolstrip, on the Simulation tab, in the Prepare gallery, select Property Inspector.
The Type Editor can export object definitions to a MAT file
(.mat) or function (.m).
To create a MATLAB® structure or Simulink.Parameter object from a
Simulink.Bus object, use the standalone Type
Editor.
Open the Type Editor
Open the standalone Type Editor.
In the MATLAB Command Window, enter
typeeditor.In the docked Type Editor, click
 .
.
Open the docked Type Editor.
In the Simulink Toolstrip, on the Modeling tab, in the Design section, click the down arrow on the far right. Then, under Design, click Type Editor.
In the Simulink Editor, press Ctrl+Shift+P.
Examples
Tips
A bus object cannot directly or indirectly reference itself. If you define a circular structure, the Type Editor keeps the original data type of the element that would have completed the circle.
To create
Simulink.BusandSimulink.BusElementobjects from a bus in your model, such as the output bus of a Bus Creator block or bus element port, use theSimulink.Bus.createObjectfunction.