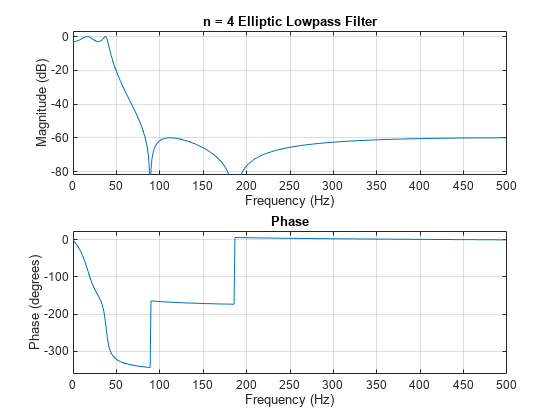
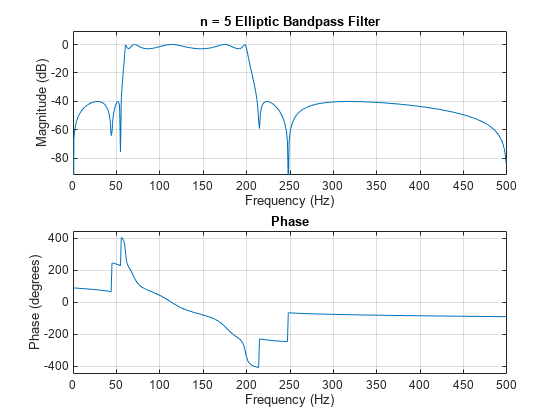
ellipord
Minimum order for elliptic filters
Description
[
returns the lowest order, n,Wn] = ellipord(Wp,Ws,Rp,Rs)n, of the digital elliptic filter with no
more than Rp dB of passband ripple and at least Rs
dB of attenuation in the stopband. Wp and Ws, are
respectively, the passband and stopband edge frequencies of the filter, normalized from 0 to
1, where 1 corresponds to π rad/sample. The scalar (or vector) of
corresponding cutoff frequencies, Wn, is also returned. To design an
elliptic filter, use the output arguments n and Wn
as inputs to ellip.
Examples
Input Arguments
Output Arguments
Algorithms
ellipord uses the elliptic lowpass filter order prediction formula
described in [1]. The function performs its
calculations in the analog domain for both the analog and digital cases. For the digital case,
it converts the frequency parameters to the s-domain before estimating
the order and natural frequencies, and then converts them back to the
z-domain.
ellipord initially develops a lowpass filter prototype by transforming
the passband frequencies of the desired filter to 1 rad/s (for low and highpass filters) and
to –1 and 1 rad/s (for bandpass and bandstop filters). It then computes the minimum order
required for a lowpass filter to meet the stopband specification.
References
[1] Rabiner, Lawrence R., and B. Gold. Theory and Application of Digital Signal Processing. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall, 1975.
Extended Capabilities
Version History
Introduced before R2006a