Simulieren Sie Trägheitssensorwerte aus einem Fahrszenario
Generieren Sie synthetische Sensordaten aus IMU, GPS und Radgebern mithilfe der Tools zur Fahrszenariogenerierung von Automated Driving Toolbox ™. Das drivingScenario-Objekt simuliert das Fahrszenario und aus den imuSensor-, gpsSensor- und wheelEncoderAckermann-Objekten werden Sensordaten generiert.
Szenario definieren
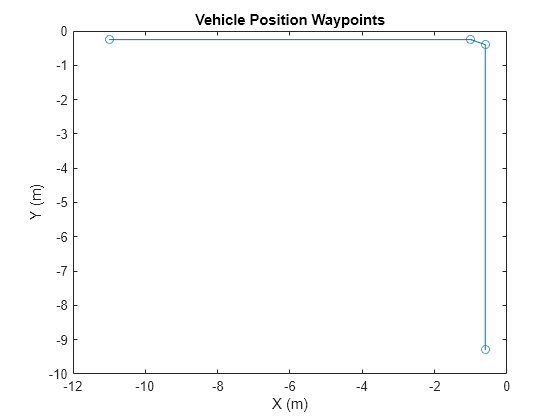
Erstellen Sie ein Fahrszenario mit einem Fahrzeug. Definieren Sie Wegpunkte, um das Fahrzeug vorwärtsfahren und abbiegen zu lassen. Um GPS-Messwerte zu simulieren, geben Sie den Referenzstandort in geodätischen Koordinaten an. Generieren Sie die Fahrzeugtrajektorie mit der Objektfunktion smoothTrajectory. Zeichnen Sie die Wegpunkte auf.
lla0 = [42 -71 50]; s = drivingScenario('GeoReference',lla0); v = vehicle(s); waypoints = [-11 -0.25 0; -1 -0.25 0; -0.6 -0.4 0; -0.6 -9.3 0]; speed = [1.5;0;0.5;1.5]; smoothTrajectory(v,waypoints,speed); figure plot(waypoints(:,1),waypoints(:,2),'-o') xlabel('X (m)') ylabel('Y (m)') title('Vehicle Position Waypoints')
Sensoren erstellen
Erstellen Sie die IMU-, GPS- und Radgebersensoren. Geben Sie den Offset-Standort und die Winkel der IMU und des GPS an. Diese können bearbeitet werden, um die Montageposition und Ausrichtung der Sensoren am Fahrzeug zu ändern.
mountingLocationIMU = [1 2 3]; mountingAnglesIMU = [0 0 0]; % Convert orientation offset from Euler angles to quaternion. orientVeh2IMU = quaternion(mountingAnglesIMU,'eulerd','ZYX','frame'); % ReferenceFrame must be specified as ENU. imu = imuSensor('SampleRate',1/s.SampleTime,'ReferenceFrame','ENU'); mountingLocationGPS = [1 2 3]; mountingAnglesGPS = [50 40 30]; % Convert orientation offset from Euler angles to quaternion. orientVeh2GPS = quaternion(mountingAnglesGPS,'eulerd','ZYX','frame'); % The GeoReference property in drivingScenario is equivalent to % the ReferenceLocation property in gpsSensor. % ReferenceFrame must be specified as ENU. gps = gpsSensor('ReferenceLocation',lla0,'ReferenceFrame','ENU'); encoder = wheelEncoderAckermann('TrackWidth',v.Width,... 'WheelBase',v.Wheelbase,'SampleRate',1/s.SampleTime);
Simulation ausführen
Führen Sie die Simulation aus und protokollieren Sie die generierten Sensorwerte.
% IMU readings. accel = []; gyro = []; % Wheel encoder readings. ticks = []; % GPS readings. lla = []; gpsVel = []; % Define the rate of the GPS compared to the simulation rate. simSamplesPerGPS = (1/s.SampleTime)/gps.SampleRate; idx = 0; while advance(s) groundTruth = state(v); % Unpack the ground truth struct by converting the orientations from % Euler angles to quaternions and converting angular velocities form % degrees per second to radians per second. posVeh = groundTruth.Position; orientVeh = quaternion(fliplr(groundTruth.Orientation), 'eulerd', 'ZYX', 'frame'); velVeh = groundTruth.Velocity; accVeh = groundTruth.Acceleration; angvelVeh = deg2rad(groundTruth.AngularVelocity); % Convert motion quantities from vehicle frame to IMU frame. [posIMU,orientIMU,velIMU,accIMU,angvelIMU] = transformMotion( ... mountingLocationIMU,orientVeh2IMU, ... posVeh,orientVeh,velVeh,accVeh,angvelVeh); [accel(end+1,:), gyro(end+1,:)] = imu(accIMU,angvelIMU,orientIMU); ticks(end+1,:) = encoder(velVeh, angvelVeh, orientVeh); % Only generate a new GPS sample when the simulation has advanced % enough. if (mod(idx, simSamplesPerGPS) == 0) % Convert motion quantities from vehicle frame to GPS frame. [posGPS,orientGPS,velGPS,accGPS,angvelGPS] = transformMotion(... mountingLocationGPS, orientVeh2GPS,... posVeh,orientVeh,velVeh,accVeh,angvelVeh); [lla(end+1,:), gpsVel(end+1,:)] = gps(posGPS,velGPS); end idx = idx + 1; end
Ergebnisse visualisieren
Zeichnen Sie die generierten Sensorwerte auf.
figure plot(ticks) ylabel('Wheel Ticks') title('Wheel Encoder')
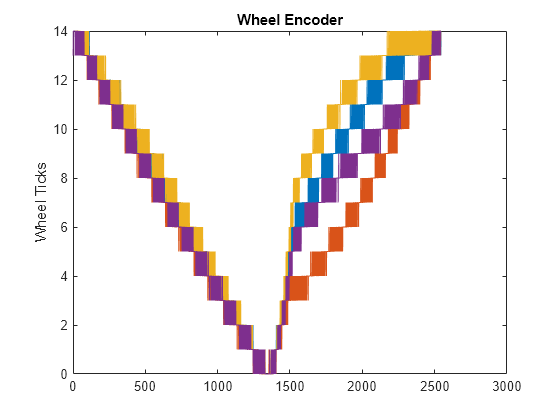
figure plot(accel) ylabel('m/s^2') title('Accelerometer')

figure plot(gyro) ylabel('rad/s') title('Gyroscope')

figure
geoplot(lla(:,1),lla(:,2))
title('GPS Position')
figure plot(gpsVel) ylabel('m/s') title('GPS Velocity')
