medicalVolume
Description
A medicalVolume object stores the voxel data and spatial
referencing information for a medical image volume contained in a single DICOM, NIfTI, or NRRD
file, or in a directory of DICOM files. The medicalVolume object specifies
the mapping between the intrinsic image coordinate system, the patient coordinate system, and
the anatomical planes. The medicalVolume object and its object functions
provide a standardized interface for accessing voxel data, spatial referencing, and intensity
scaling information.
Creation
Syntax
Description
medVol = medicalVolume(dirname)medicalVolume object for the image volume contained in a
multifile DICOM series in the directory dirname.
medVol = medicalVolume(filenames)medicalVolume object for the image volume stored in the single
DICOM, NIfTI, or NRRD file or list of DICOM files specified by
filenames.
medVol = medicalVolume(sourceTable)medicalVolume object for the image volume listed in
sourceTable. The table must contain only one row that specifies the
metadata for a DICOM volume.
medVol = medicalVolume(sourceTable,rowname)medicalVolume object for the image volume listed in the row
rowname of sourceTable. Use this syntax to
specify one row of a multirow table by name or by numeric index.
medVol = medicalVolume(imds)medicalVolume object for the image volume specified by the
image datastore object imds.
medVol = medicalVolume(voxels,VolumeGeometry)medicalVolume by directly specifying the Voxels and
VolumeGeometry properties.
Input Arguments
Name of the directory containing the medical image volume data, specified as a
string scalar or a character vector. Specify dirname as the name
of a directory containing multiple DICOM files corresponding to one image
volume.
Name of the file or files containing the medical image volume data, specified as a
string scalar, character vector, or string array. Specify
filenames as a single DICOM, NIfTI, or NRRD file or as a list
of DICOM files corresponding to one image volume.
Collection of DICOM file metadata, specified as a table returned by the dicomCollection function.
Name or index of table row, specified as a string scalar, character vector, or
positive integer. Specify rowname as a string scalar or character
vector to specify a row of sourceTable by name. Specify
rowname as a positive integer to specify a row by its numeric
index.
Datastore specifying a list of DICOM files containing medical image volume data,
specified as an ImageDataStore object. The list of files must
correspond to one medical image volume.
Properties
Image voxel values, specified as an
m-by-n-by-p numeric array or
an N-D numeric array. The first three dimensions of
Voxels correspond to the spatial dimensions of the patient
coordinate system.
For DICOM files, medicalVolume rescales the intensity values using
the RescaleIntercept and RescaleSlope metadata
attributes, if they are present in the file. Additionally,
medicalVolume converts DICOM intensities of data type
uint16 to data type int16 or
single.
If the
RescaleSlopeattribute value is unspecified or an integer, thenmedicalVolumeconverts the intensity values fromuint16toint16.If the
RescaleSlopeattribute value is fractional, thenmedicalVolumeconverts the intensity values fromuint16tosingle.
Data Types: single | double | int8 | int16 | int32 | int64 | uint8 | uint16 | uint32 | uint64 | logical
Spatial referencing information, specified as a medicalref3d
object. The coordinates and distances specified by VolumeGeometry
are in the units specified by the SpatialUnits property, if
available in the file
metadata.
Real-world spatial units, specified as a string scalar or a character vector. If the
data source is a DICOM file, then the SpatialUnits value is
"mm" (millimeters). If the data source is a NIfTI or NRRD file, the
object extracts the spatial units from the SpaceUnits or
spaceunits metadata attribute, respectively, if present in the
file.
Data Types: string
This property is read-only.
Distances between voxel centers in each dimension, specified as a 1-by-3 numeric
vector. The values of VoxelSpacing are in the units specified by
the SpatialUnits property. If
VolumeGeometry.IsAffine is false, then the
object calculates the spacing for each dimension as the average spacing across all
slices.
Data Types: double
This property is read-only.
Slice plane with the greatest spatial resolution, specified as one of these values:
"coronal"— Coronal plane."sagittal"— Sagittal plane."transverse"— Transverse plane."mixed"— Image volume slices are not parallel. This value occurs when theIsMixedproperty of theVolumeGeometryobject istrue."oblique"— Image slices are not aligned with the anatomical axes."unknown"— Mapping between image coordinate system and anatomical axes is unknown. This value occurs when thePatientCoordinateSystemproperty of theVolumeGeometryobject is"unknown".
Data Types: string
This property is read-only.
Number of slices in the coronal direction, specified as a numeric scalar or empty
array. NumCoronalSlices is empty in these cases:
PatientCoordinateSystemproperty of theVolumeGeometryobject is"unknown".Image volume is oblique.
Image volume contains a temporal dimension with multiple slices at each spatial location.
Data Types: double
This property is read-only.
Number of slices in the sagittal direction, specified as a numeric scalar or empty
array. NumSagittalSlices is empty in these cases:
PatientCoordinateSystemproperty of theVolumeGeometryobject is"unknown".Image volume is oblique.
Image volume contains a temporal dimension with multiple slices at each spatial location.
Data Types: double
This property is read-only.
Number of slices in the transverse direction, specified as a numeric scalar or empty
array. NumTransverseSlices is empty in these cases:
PatientCoordinateSystemproperty of theVolumeGeometryobject is"unknown".Image volume is oblique.
Image volume contains a temporal dimension with multiple slices at each spatial location.
Data Types: double
This property is read-only.
Mapping between voxel data dimensions and anatomical planes, specified as a 1-by-3
string array. If the spatial referencing for the volume is defined, then
PlaneMapping contains the strings
"transverse", "coronal", and
"sagittal". For example, if the first element of
PlaneMapping is "coronal", then moving along
the first dimension of Voxels corresponds to moving between slices
in the coronal plane.
If the PatientCoordinateSystem property of the
VolumeGeometry object is "unknown", or if the
volume is oblique, the values of PlaneMapping are
"unknown" or "oblique", respectively.
Example:
["transverse","coronal","sagittal"]
Data Types: string
Since R2025a
This property is read-only.
Mapping between the voxel data dimensions and anatomical axes directions, specified
as a 1-by-3 string array. If the Orientation property value is "coronal",
"saggital", or "transverse", then
DataDimensionMeaning contains one option from each of these pairs
of strings:
"left"and"right""inferior"and"superior""posterior"and"anterior"
In this case, each string maps the corresponding dimension of the voxel
data to an anatomical axis and defines the positive direction for that axis. For
example, if the first element of DataDimensionMeaning is
"anterior", then increasing the row indices of
Voxels corresponds to moving anteriorly through the patient in
the coronal plane.
If the Orientation property is "unknown",
"mixed", or "oblique", all values of
DataDimensionMeaning are "unknown",
"mixed", or "oblique", respectively.
Example: ["left" "posterior" "inferior"]
Data Types: string
This property is read-only.
Unit vector normal to the first slice of the image volume, specified as a 1-by-3
numeric vector. The first slice of the volume corresponds to the points stored in
Voxels(:,:,1).
Data Types: double
This property is read-only.
Imaging modality used to capture the image volume data, specified as a string
scalar. The modality is extracted from the file metadata, if present. Common values
include, but are not limited to, "CT" for computed tomography,
"MR" for magnetic resonance, "NM" for nuclear
medicine, and "US" for ultrasound. If the modality is not specified
in the file metadata, the default value is "unknown".
Data Types: string
This property is read-only.
Center of the display range window for each slice, specified as a numeric scalar or
as a p-by-1 numeric vector, where p is the number
of slices in the image volume along the third dimension. If
WindowCenters is a scalar, the value defines the window center
for the overall volume. If WindowCenters is a vector, each element
defines the window center for the corresponding slice. The object extracts the
WindowCenters property value from the file metadata, if
available. If the display window metadata is not available, then
WindowCenters is
empty.
Data Types: double
This property is read-only.
Width of display window of each slice, specified as a numeric scalar or as a
p-by-1 numeric vector, where p is the number of
slices in the image volume along the third dimension. If
WindowWidths is a scalar, the value defines the window width for
the overall volume. If WindowWidths is a vector, each element
defines the window width for the corresponding slice. The object extracts the
WindowWidths property value from the file metadata, if available.
If the display window metadata is not available, then WindowWidths
is
empty.
Data Types: double
Object Functions
extractSlice | Extract voxels and spatial details for one slice of medical volume |
replaceSlice | Replace voxel values for one slice of medical volume |
resample | Resample medical image volume in different patient coordinate system |
reposition | Update position of medical volume in patient coordinates |
updateOrientation | Update slice orientation of medical volume voxels |
sliceCorners | Extract coordinates of corner voxels for one slice of medical volume |
sliceLimits | Extract X-, Y-, Z-limits for one slice of medical volume |
volshow | Display medical volume in patient coordinates |
montage | Display medical image slices or frames as montage in patient coordinates |
write | Write affine medical volume data to NIfTI file |
Examples
Create a medical volume object using a chest CT volume saved as a directory of DICOM files. The volume is part of a data set containing three CT volumes. The size of the entire data set is approximately 81 MB. Download the data set from the MathWorks® website, then unzip the folder.
zipFile = matlab.internal.examples.downloadSupportFile("medical","MedicalVolumeDICOMData.zip"); filepath = fileparts(zipFile); unzip(zipFile,filepath)
Specify the directory of DICOM files for the first CT volume in the data set.
dataFolder = fullfile(filepath,"MedicalVolumeDICOMData","LungCT01");
Create a medical volume object for the CT volume.
medVol = medicalVolume(dataFolder)
medVol =
medicalVolume with properties:
Voxels: [512×512×88 int16]
VolumeGeometry: [1×1 medicalref3d]
SpatialUnits: "mm"
Orientation: "transverse"
VoxelSpacing: [0.7285 0.7285 2.5000]
NormalVector: [0 0 1]
NumCoronalSlices: 512
NumSagittalSlices: 512
NumTransverseSlices: 88
PlaneMapping: ["sagittal" "coronal" "transverse"]
Modality: "CT"
WindowCenters: [88×1 double]
WindowWidths: [88×1 double]
Create a medical volume object using a CT chest volume from the Medical Segmentation Decathlon data set [1]. Download the MedicalVolumNIfTIData.zip file from the MathWorks website, then unzip the file. The file contains two CT chest volumes and corresponding label images, stored in the NIfTI file format. The size of the data file is approximately 76 MB.
zipFile = matlab.internal.examples.downloadSupportFile("medical","MedicalVolumeNIfTIData.zip"); filepath = fileparts(zipFile); unzip(zipFile,filepath) dataFolder = fullfile(filepath,"MedicalVolumeNIfTIData");
Specify the file name of the first CT volume.
filePath = fullfile(dataFolder,"lung_027.nii.gz");Create a medical volume object for the CT volume.
medVol = medicalVolume(filePath)
medVol =
medicalVolume with properties:
Voxels: [512×512×264 single]
VolumeGeometry: [1×1 medicalref3d]
SpatialUnits: "mm"
Orientation: "transverse"
VoxelSpacing: [0.8594 0.8594 1.2453]
NormalVector: [0 0 -1]
NumCoronalSlices: 512
NumSagittalSlices: 512
NumTransverseSlices: 264
PlaneMapping: ["sagittal" "coronal" "transverse"]
Modality: "unknown"
WindowCenters: 0
WindowWidths: 0
[1] Medical Segmentation Decathlon. "Lung." Tasks. Accessed May 10, 2018. http://medicaldecathlon.com/.
The Medical Segmentation Decathlon data set is provided under the CC-BY-SA 4.0 license. All warranties and representations are disclaimed. See the license for details.
Create a medical volume object using a chest CT volume saved as a directory of DICOM files. The volume is part of a data set containing three CT volumes. The size of the entire data set is approximately 81 MB. Download the data set from the MathWorks website, then unzip the folder.
zipFile = matlab.internal.examples.downloadSupportFile("medical","MedicalVolumeDICOMData.zip"); filepath = fileparts(zipFile); unzip(zipFile,filepath)
Specify the directory of DICOM files for the first CT volume in the data set.
dataFolder = fullfile(filepath,"MedicalVolumeDICOMData","LungCT01");
Gather the details about the DICOM files in the dataFolder directory into a table by using the dicomCollection function. The files belong to one CT volume series, so the table has one row.
sourceTable = dicomCollection(dataFolder);
Create a medical volume object for the CT volume by specifying the single-row DICOM collection table.
medVol = medicalVolume(sourceTable)
medVol =
medicalVolume with properties:
Voxels: [512×512×88 int16]
VolumeGeometry: [1×1 medicalref3d]
SpatialUnits: "mm"
Orientation: "transverse"
VoxelSpacing: [0.7285 0.7285 2.5000]
NormalVector: [0 0 1]
NumCoronalSlices: 512
NumSagittalSlices: 512
NumTransverseSlices: 88
PlaneMapping: ["sagittal" "coronal" "transverse"]
Modality: "CT"
WindowCenters: [88×1 double]
WindowWidths: [88×1 double]
Create a medical volume object using a data set containing three chest CT scans. Each CT scan is saved as a directory of DICOM files. The size of the data set is approximately 81 MB. Download the data set from the MathWorks website, then unzip the folder.
zipFile = matlab.internal.examples.downloadSupportFile("medical","MedicalVolumeDICOMData.zip"); filepath = fileparts(zipFile); unzip(zipFile,filepath) dataFolder = fullfile(filepath,"MedicalVolumeDICOMData");
Gather the details about the DICOM files in the dataFolder directory into a table by using the dicomCollection function. The table contains three rows, each corresponding to one of three CT DICOM series.
sourceTable = dicomCollection(dataFolder);
Create a medical volume object for the second CT volume by specifying the DICOM collection table and a numeric row index.
medVol = medicalVolume(sourceTable,2)
medVol =
medicalVolume with properties:
Voxels: [512×512×88 int16]
VolumeGeometry: [1×1 medicalref3d]
SpatialUnits: "mm"
Orientation: "transverse"
VoxelSpacing: [0.7617 0.7617 2.5000]
NormalVector: [0 0 1]
NumCoronalSlices: 512
NumSagittalSlices: 512
NumTransverseSlices: 88
PlaneMapping: ["sagittal" "coronal" "transverse"]
Modality: "CT"
WindowCenters: [88×1 double]
WindowWidths: [88×1 double]
Create a medical volume object using a chest CT volume saved as a directory of DICOM files. The volume is part of a data set containing three CT volumes. The size of the entire data set is approximately 81 MB. Download the data set from the MathWorks website, then unzip the folder.
zipFile = matlab.internal.examples.downloadSupportFile("medical","MedicalVolumeDICOMData.zip"); filepath = fileparts(zipFile); unzip(zipFile,filepath)
Specify the directory of DICOM files for the first CT volume in the data set.
dataFolder = fullfile(filepath,"MedicalVolumeDICOMData","LungCT01");
Create an image datastore containing the DICOM files in the dataFolder directory. Specify a custom read function to read the DICOM files.
dicomds = imageDatastore(dataFolder, ... FileExtensions=".dcm",ReadFcn=@(x) dicomread(x));
Create a medical volume object for the CT volume.
medVol = medicalVolume(dicomds)
medVol =
medicalVolume with properties:
Voxels: [512×512×88 int16]
VolumeGeometry: [1×1 medicalref3d]
SpatialUnits: "mm"
Orientation: "transverse"
VoxelSpacing: [0.7285 0.7285 2.5000]
NormalVector: [0 0 1]
NumCoronalSlices: 512
NumSagittalSlices: 512
NumTransverseSlices: 88
PlaneMapping: ["sagittal" "coronal" "transverse"]
Modality: "CT"
WindowCenters: [88×1 double]
WindowWidths: [88×1 double]
Create a medical volume object using a chest CT volume saved as a directory of DICOM files. The volume is part of a data set containing three CT volumes. The size of the entire data set is approximately 81 MB. Download the data set from the MathWorks website, then unzip the folder.
zipFile = matlab.internal.examples.downloadSupportFile("medical","MedicalVolumeDICOMData.zip"); filepath = fileparts(zipFile); unzip(zipFile,filepath)
Specify the directory of DICOM files for the first CT volume in the data set.
dataFolder = fullfile(filepath,"MedicalVolumeDICOMData","LungCT01");
Create a medical volume object for the CT volume.
medVol = medicalVolume(dataFolder);
The Voxels property contains the intensity values of each voxel. The VolumeGeometry property contains a medicalref3d object defining the spatial referencing for the image volume.
V = medVol.Voxels; R = medVol.VolumeGeometry;
Modify the voxel data by applying a 3-D Gaussian filter.
sigma = 2; filterV = imgaussfilt3(V,sigma);
Create a new medicalVolume object that contains the smoothed voxel values. To maintain the same spatial referencing as the original volume, specify the original medicalref3d object R.
medVolFiltered = medicalVolume(filterV,R);
Run this code to download a data set from the MathWorks® website and unzip the downloaded folder. The data set contains three CT volumes that are each saved as a directory of DICOM files. The size of the entire data set is approximately 81 MB.
zipFile = matlab.internal.examples.downloadSupportFile("medical","MedicalVolumeDICOMData.zip"); filepath = fileparts(zipFile); unzip(zipFile,filepath)
The folder dataFolder contains the downloaded scan used by this example, LungCT01.
dataFolder = fullfile(filepath,"MedicalVolumeDICOMData","LungCT01");
Create a medical image volume object that contains the image data and spatial referencing information for the CT volume. The Orientation property indicates that the primary slice direction is "transverse".
medVol = medicalVolume(dataFolder)
medVol =
medicalVolume with properties:
Voxels: [512×512×88 int16]
VolumeGeometry: [1×1 medicalref3d]
SpatialUnits: "mm"
Orientation: "transverse"
VoxelSpacing: [0.7285 0.7285 2.5000]
NormalVector: [0 0 1]
NumCoronalSlices: 512
NumSagittalSlices: 512
NumTransverseSlices: 88
PlaneMapping: ["sagittal" "coronal" "transverse"]
Modality: "CT"
WindowCenters: [88×1 double]
WindowWidths: [88×1 double]
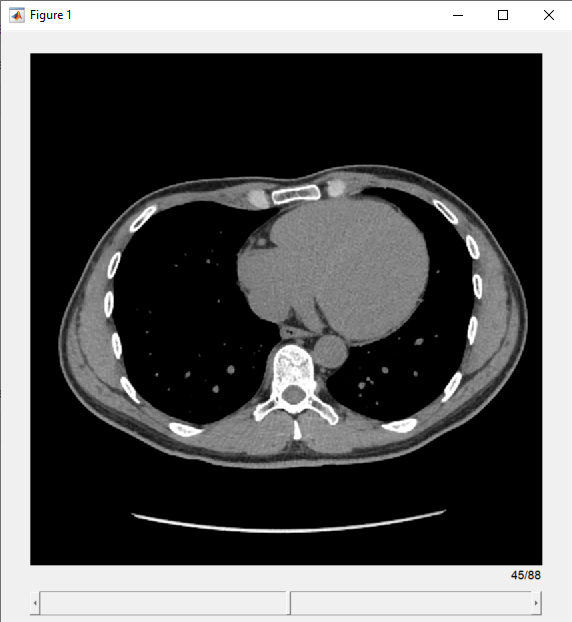
View the transverse slices of the volume in the slice viewer. By default, the viewer uses the properties of medVol to scale anisotropic voxels, set the intensity display range, and orient slices. The viewer opens on the center slice. Use the scroll bar to navigate to other slices.
sv = sliceViewer(medVol,Parent=figure)
sv =
sliceViewer with properties:
SliceDirection: [0 0 1]
SliceNumber: 45
Parent: [1×1 Panel]
Colormap: [256×3 double]
DisplayRange: [-160 240]
ScaleFactors: [1 1 1]
DisplayRangeInteraction: 'on'
Since R2024a
Read the voxels of an MRI volume from a TIFF file using the tiffreadVolume function.
voxels = tiffreadVolume("mri.tif");Create a medicalref3d object containing the volume geometry using only the volume size of the MRI volume.
volGeometry = medicalref3d(size(voxels))
volGeometry =
medicalref3d with properties:
VolumeSize: [128 128 27]
Position: [27×3 double]
VoxelDistances: {[1 0 0] [0 1 0] [0 0 1]}
PatientCoordinateSystem: "Unknown"
PixelSpacing: [1 1]
IsAffine: 1
IsAxesAligned: 1
IsMixed: 0
Specify a patient coordinate system for visualization.
volGeometry.PatientCoordinateSystem = "LPS+";Create a medicalVolume object using the voxel data and the volume geometry.
medVol = medicalVolume(voxels,volGeometry)
medVol =
medicalVolume with properties:
Voxels: [128×128×27 uint8]
VolumeGeometry: [1×1 medicalref3d]
SpatialUnits: "unknown"
Orientation: "transverse"
VoxelSpacing: [1 1 1]
NormalVector: [0 0 1]
NumCoronalSlices: 128
NumSagittalSlices: 128
NumTransverseSlices: 27
PlaneMapping: ["sagittal" "coronal" "transverse"]
DataDimensionMeaning: ["left" "posterior" "superior"]
Modality: "unknown"
WindowCenters: []
WindowWidths: []
Visualize a slice of the medical volume.
slice = extractSlice(medVol,15,"transverse");
figure
imshow(slice)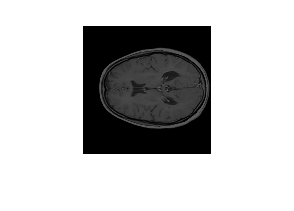
Version History
Introduced in R2022bThe new DataDimensionMeaning property specifies the mapping between
the voxel data dimensions, defined by rows, slices, and columns, and anatomical axes.
When reading DICOM files, the medicalVolume object converts intensity
values of data type uint16 to data type int16 or
single. If the DICOM file specifies the
RescaleIntercept and RescaleSlope metadata
attributes, medicalVolume converts the values before rescaling them. By
converting unsigned uint16 values to signed values before rescaling, the
new behavior preserves the full data range of the rescaled intensities, including negative values.
If the
RescaleSlopeattribute value is unspecified or an integer, thenmedicalVolumeconverts the intensities fromuint16toint16.If the
RescaleSlopeattribute value is fractional, thenmedicalVolumeconverts the intensities fromuint16tosingle.
In R2022b, medicalVolume stored intensity values as the same
data type as in the DICOM file. For DICOM files that stored intensities as data type
uint16, medicalVolume limited rescaled values to the
range [0, 216-1], and set all negative intensities to
0 before storing them in the Voxels
property.
See Also
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.
Website auswählen
Wählen Sie eine Website aus, um übersetzte Inhalte (sofern verfügbar) sowie lokale Veranstaltungen und Angebote anzuzeigen. Auf der Grundlage Ihres Standorts empfehlen wir Ihnen die folgende Auswahl: .
Sie können auch eine Website aus der folgenden Liste auswählen:
So erhalten Sie die bestmögliche Leistung auf der Website
Wählen Sie für die bestmögliche Website-Leistung die Website für China (auf Chinesisch oder Englisch). Andere landesspezifische Websites von MathWorks sind für Besuche von Ihrem Standort aus nicht optimiert.
Amerika
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
Europa
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)