mkpp
Make piecewise polynomial
Description
Examples
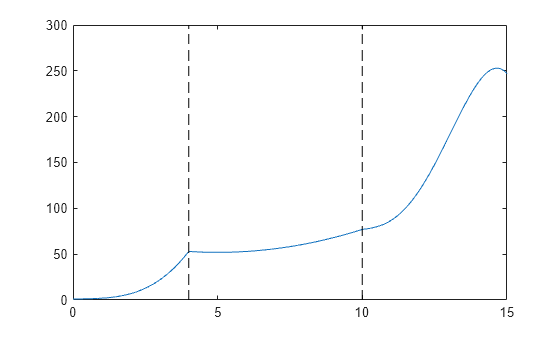
Create a piecewise polynomial that has a cubic polynomial in the interval [0,4], a quadratic polynomial in the interval [4,10], and a quartic polynomial in the interval [10,15].
breaks = [0 4 10 15]; coefs = [0 1 -1 1 1; 0 0 1 -2 53; -1 6 1 4 77]; pp = mkpp(breaks,coefs)
pp = struct with fields:
form: 'pp'
breaks: [0 4 10 15]
coefs: [3×5 double]
pieces: 3
order: 5
dim: 1
Evaluate the piecewise polynomial at many points in the interval [0,15] and plot the results. Plot vertical dashed lines at the break points where the polynomials meet.
xq = 0:0.01:15; plot(xq,ppval(pp,xq)) line([4 4],ylim,'LineStyle','--','Color','k') line([10 10],ylim,'LineStyle','--','Color','k')
Create and plot a piecewise polynomial with four intervals that alternate between two quadratic polynomials.
The first two subplots show a quadratic polynomial and its negation shifted to the intervals [-8,-4] and [-4,0]. The polynomial is
The third subplot shows a piecewise polynomial constructed by alternating these two quadratic pieces over four intervals. Vertical lines are added to show the points where the polynomials meet.
subplot(2,2,1) cc = [-1/4 1 0]; pp1 = mkpp([-8 -4],cc); xx1 = -8:0.1:-4; plot(xx1,ppval(pp1,xx1),'k-') subplot(2,2,2) pp2 = mkpp([-4 0],-cc); xx2 = -4:0.1:0; plot(xx2,ppval(pp2,xx2),'k-') subplot(2,1,2) pp = mkpp([-8 -4 0 4 8],[cc;-cc;cc;-cc]); xx = -8:0.1:8; plot(xx,ppval(pp,xx),'k-') hold on line([-4 -4],ylim,'LineStyle','--') line([0 0],ylim,'LineStyle','--') line([4 4],ylim,'LineStyle','--') hold off

Input Arguments
Break points, specified as a vector of length L+1 with
strictly increasing elements that represent the start and end of each
of L intervals.
Data Types: single | double
Polynomial coefficients, specified as an L-by-k matrix
with the ith row coefs(i,:) containing the local
coefficients of an order k polynomial on the ith
interval, [breaks(i), breaks(i+1)]. In other words,
the polynomial is coefs(i,1)*(X-breaks(i))^(k-1) + coefs(i,2)*(X-breaks(i))^(k-2)
+ ... + coefs(i,k-1)*(X-breaks(i)) + coefs(i,k).
Data Types: single | double
Dimension, specified as a scalar or vector of integers. Specify d to
signify that the piecewise polynomial has coefficient values of size d.
Data Types: single | double
Output Arguments
Piecewise polynomial, returned as a structure. Use this structure
with the ppval function to
evaluate the piecewise polynomial at one or more query points. The
structure has these fields.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
form |
|
breaks | Vector of length |
coefs |
|
pieces | Number of pieces, |
order | Order of the polynomials |
dim | Dimensionality of target |
Since the polynomial coefficients in coefs are
local coefficients for each interval, you must subtract the lower
endpoint of the corresponding knot interval to use the coefficients
in a conventional polynomial equation. In other words, for the coefficients [a,b,c,d] on
the interval [x1,x2], the corresponding polynomial
is
Extended Capabilities
Usage notes and limitations:
The output structure
ppdiffers from theppstructure in MATLAB®. In MATLAB,ppvalcannot use theppstructure from the code generator. For code generation,ppvalcannot use appstructure created by MATLAB.unmkppcan use a MATLABppstructure for code generation.To create a MATLAB
ppstructure from appstructure created by the code generator:In code generation, use
unmkppto return the piecewise polynomial details to MATLAB.In MATLAB, use
mkppto create theppstructure.
If you do not provide
d, thencoefsmust be two-dimensional and have a fixed number of columns. In this case, the number of columns is the order.To define a piecewise constant polynomial,
coefsmust be a column vector ordmust have at least two elements.If you provide
danddis1, thendmust be a constant. Otherwise, if the input toppvalis nonscalar, then the shape of the output ofppvalcan differ fromppvalin MATLAB.If you provide
d, then it must have a fixed length. One of the following sets of statements must be true:Suppose that
m = length(d)andnpieces = length(breaks) - 1.size(coefs,j) = d(j) size(coefs,m+1) = npieces size(coefs,m+2) = order
j= 1,2,...,m. The dimensionm+2must be fixed length.Suppose that
m = length(d)andnpieces = length(breaks) - 1.The second dimension must be fixed length.size(coefs,1) = prod(d)*npieces size(coefs,2) = order
If you do not provide
d, then the following statements must be true:Suppose that
m = length(d)andnpieces = length(breaks) - 1.The second dimension must be fixed length.size(coefs,1) = prod(d)*npieces size(coefs,2) = order
This function fully supports thread-based environments. For more information, see Run MATLAB Functions in Thread-Based Environment.
Version History
Introduced before R2006a
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.
Website auswählen
Wählen Sie eine Website aus, um übersetzte Inhalte (sofern verfügbar) sowie lokale Veranstaltungen und Angebote anzuzeigen. Auf der Grundlage Ihres Standorts empfehlen wir Ihnen die folgende Auswahl: .
Sie können auch eine Website aus der folgenden Liste auswählen:
So erhalten Sie die bestmögliche Leistung auf der Website
Wählen Sie für die bestmögliche Website-Leistung die Website für China (auf Chinesisch oder Englisch). Andere landesspezifische Websites von MathWorks sind für Besuche von Ihrem Standort aus nicht optimiert.
Amerika
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
Europa
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)