Merge Multiple Raster Tiles Using Datastore
This topic shows how to:
Create a custom datastore for reading and merging data from multiple DTED files.
Use the custom datastore to read and merge data from multiple DTED files.
Adapt the custom datastore to GTOPO30 and GLOBE DEM files.
A datastore is a repository for a collection of files. Datastores enable you to read data from all files in the collection without specifying the names of individual files, which is convenient when the collection contains a large number of files. Custom datastores enable you to define additional functions that manipulate the data. In this case, the datastore defines a function that simultaneously reads and merges the data from the files.
This topic assumes familiarity with datastores and with creating classes. For more information about datastores, see Getting Started with Datastore. For more information about creating classes, see Creating a Simple Class.
Create Custom Datastore
Create a custom datastore, DTEDDatastore, for reading and merging
DTED files. The steps for creating a custom datastore include:
Creating a class definition file that defines the custom datastore.
Inheriting from the base datastore class.
Implementing a method that creates datastore objects.
Implementing methods that read and merge data from files in the datastore.
The Merge DTED Tiles Using Datastore example at the end
of this topic includes the completed DTEDDatastore class as a
supporting file.
Create Class Definition File
Create a class definition in an .m file called
DTEDDatastore.m. This file defines the
DTEDDatastore class, including its properties and methods.
The file must be on the MATLAB® path.
Inherit from Base Datastore Class
Within the file, write code that inherits from the base matlab.io.Datastore class. Inheriting from the base
matlab.io.Datastore class enables you to use methods that are
common to all datastore objects, without explicitly defining the methods. For
example, you can use the readall method to read all the
files contained in a DTED datastore, even though the
DTEDDatastore class does not define a
readall
method.
classdef DTEDDatastore < matlab.io.Datastore % DTEDDatastore Datastore for a collection of DTED files
Add Properties to Class
Write code that adds the CurrentFileIndex and
FileSet properties to the class.
CurrentFileIndexstores the index of the next file to be read by the datastore. Theread,reset, andprogressmethods use this property.FileSetstores information about the files in the datastore using aDsFileSetobject. Thehasdata,read,reset, andprogressmethods use this property.
properties (Access = private)
CurrentFileIndex double
FileSet matlab.io.datastore.DsFileSet
endImplement Creation Function
Implement a method that creates DTEDDatastore objects.
Write code that defines the DTEDDatastore method. The
method creates a datastore for a collection of DTED files. The files exist in
the folder specified by location and have the extension
specified by extension. The function sets the
FileSet property of the datastore to a
DsFileSet object that stores the extension and enables the
datastore to access subfolders of location. The function
also resets the datastore to an initial state.
methods
function dtedDS = DTEDDatastore(location,extension)
% Create a DTEDDatastore object
arguments
location {mustBeFolder}
extension {mustBeTextScalar}
end
dtedDS.FileSet = matlab.io.datastore.DsFileSet(location, ...
FileExtensions=extension,IncludeSubfolders=true);
reset(dtedDS)
endImplement Methods
Custom datastores that use a DsFileSet object require you to
define the hasdata, read,
reset, progress, and
copyElement methods. You must also define a method that
reads and merges data from all files in the datastore.
Implement the hasdata method, which returns logical
1 (true) if there is data available to
read from the datastore. Otherwise, it returns logical 0
(false).
function tf = hasdata(dtedDS) % Return true if there is data available to read in the % datastore tf = hasfile(dtedDS.FileSet); end
Implement the read method, which reads data and information
from the next file in the datastore. The function returns the data in
data and returns information about the file in
info.
Within the method:
If there is no data to read, issue an error.
Get the name of the next file in the datastore.
Read data from the file by using the
readgeorasterfunction. The function returns an array that contains the elevation data and a raster reference object that contains spatial referencing information. To use the elevation data with other Mapping Toolbox™ functions, specify the output type as"double".Get information about the file by using the
georasterinfofunction. Store the information in theinfooutput argument.Collect the array and the raster reference object into a cell array. Store the cell array in the
dataoutput argument.Increment the index of the next file to be read.
function [data,info] = read(dtedDS) % Read data and information from the next file in the datastore % If there is no data to read, issue error if ~hasdata(dtedDS) error(sprintf("No more data to read. Reset datastore " + ... "to initial state by using reset.")) end % Get name of next file fileInfo = nextfile(dtedDS.FileSet); filename = fileInfo.FileName; % Read file [Z,R] = readgeoraster(filename,OutputType="double"); % Get information about file info = georasterinfo(filename); % Collect array and raster reference object into cell array data = {Z,R}; % Increment index of next file to read dtedDS.CurrentFileIndex = dtedDS.CurrentFileIndex + 1; end
Implement the reset method, which resets the datastore to the
state where no data has been read from it. Resetting enables you to re-read from
the same datastore.
function reset(dtedDS) % Reset datastore to initial state reset(dtedDS.FileSet) dtedDS.CurrentFileIndex = 1; end
Implement the readMergedTiles method, which reads data from
all the files in the datastore, and then merges the data into one array and one
raster reference object.
Within the method:
Read data from all the files in the datastore by using the
readallfunction. Thereadallfunction returns a two-column cell array. The first column contains the elevation data and the second column contains the raster reference objects.Reshape the data into a one-row cell array that you can use as input with the
mergetilesfunction.Extract the data from the cell array, and merge the data by using the
mergetilesfunction.
function [Z,R] = readMergedTiles(dtedDS) % Read data from all files and merge into one array and one % raster reference object % Read all data alldata = readall(dtedDS)'; % Reshape data alldata = alldata(:)'; % Extract data from cell array and merge data [Z,R] = mergetiles(alldata{:}); end end
Implement the progress method, which determines the
percentage of data that has been read from the
datastore.
methods (Hidden = true)
function frac = progress(dtedDS)
% Determine percentage of data read from datastore
if hasdata(dtedDS)
frac = (dtedDS.CurrentFileIndex-1)/dtedDS.FileSet.NumFiles;
else
frac = 1;
end
end
end Implement the copyElement method, which you must use when
you store a DsFileSet object within a property of the
datastore. Implementing the copyElement method enables the
class to create a deep copy of the datastore object.
methods (Access = protected)
% Enable class to create deep copy of datastore object
function dscopy = copyElement(ds)
dscopy = copyElement@matlab.mixin.Copyable(ds);
dscopy.FileSet = copy(ds.FileSet);
end
end
endMerge DTED Tiles Using Datastore
Read and merge multiple DTED files by using a custom datastore. A supporting file for the example, DTEDDatastore.m, defines a custom datastore for reading and merging DTED files. To read and merge files using the custom datastore, the DTED files must form a filled quadrangle. A quadrangle is a region bounded by two parallels and two meridians.
Create DTED Datastore Object
Specify the location of the folder that contains the DTED files, in this case the current folder. Two supporting folders for the example, w106 and w107, contain several DTED files.
location = pwd;
Specify the extension of the DTED files. Valid extensions for DTED files are .dt0, .dt1, and .dt2.
extension = ".dt0";Create a DTEDDatastore object by specifying the location and extension. The amount of time MATLAB® requires to create the object depends on the number of subfolders.
dtedDS = DTEDDatastore(location,extension);
Read and Merge Data from Files
Read and merge the files in the DTED datastore by using the readMergedTiles function. The DTEDDatastore.m file defines the readMergedTiles function for DTEDDatastore objects.
[Z,R] = readMergedTiles(dtedDS);
Display Data on Map
Create a map for the region and display the elevation data as a surface.
figure
usamap(Z,R)
geoshow(Z,R,DisplayType="surface")Apply a colormap that is appropriate for elevation data by using the demcmap function. Add a labeled color bar.
demcmap(Z)
c = colorbar;
c.Label.String = "Elevation (m)";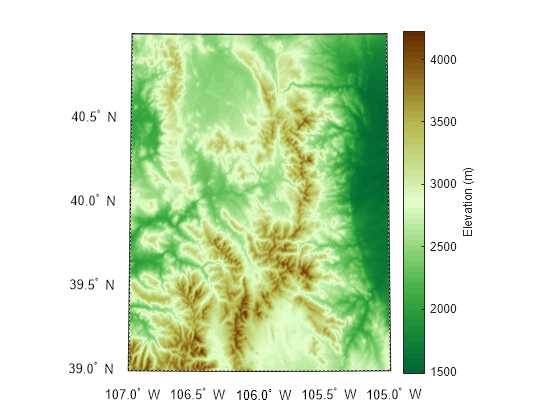
This example uses modified data from the US Geological Survey.
Adapt DTED Datastore for Other Data Sets
You can use a custom datastore that is similar to the DTED datastore to read and
merge other tiled data, such as data from GTOPO30 or GLOBE DEM files. Depending on
the data set, you might encounter limitations or need to change the implementation
of the read method.
For GTOPO30 files:
The
readMergedTilesmethod requires the data to fill a quadrangle, but the data stored in the southernmost GTOPO30 tiles have different longitude limits than the tiles that are adjacent to the north. As a result, this custom datastore does not support collections that mix southernmost tiles with other tiles.When you create the datastore object, specify the extension as
".dem".
For GLOBE DEM files:
When you implement the
readmethod, you must update the use of thereadgeorasterfunction so that the function specifies a geographic coordinate system type, as inCoordinateSystemType="geographic".When you implement the
readmethod, you can suppress and reenable warnings from thegeorasterinfofunction by adding this code.warning("off","map:io:UnableToDetermineCoordinateSystemType") info = georasterinfo(filename); warning("on","map:io:UnableToDetermineCoordinateSystemType")
When you create the datastore object, specify the extension as
"".