Single-Acting Actuator (G)
Libraries:
Simscape /
Fluids /
Gas /
Actuators
Description
The Single-Acting Actuator (G) block models a linear actuator with a piston controlled by a single gas chamber. The actuator generates force in the extension and retraction strokes, but the actuation force depends on the gauge pressure at a single chamber.
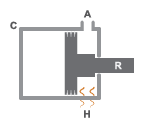
The figure shows the key components of an actuator. Port A represents the gas chamber inlet. Port R represents the translating actuator piston, and port C represents the actuator case. Port H represents the thermal interface between the gas chamber and the environment.
Displacement
The block measures the piston displacement as the position at port R
relative to port C. The Mechanical
orientation parameter identifies the direction of piston
displacement. The piston displacement is neutral, or 0, when the
chamber volume is equal to the value of the Dead volume
parameter. When the Piston displacement parameter is
Provide input signal from Multibody joint, you input
the piston displacement using port p. You can ensure that the
derivative of the position signal is equal to the piston velocity by using a Translational Multibody Interface block to
provide the piston displacement.
The direction of the piston motion depends on the Mechanical orientation parameter. If the mechanical orientation is positive, then the piston translation is positive in relation to the actuator case when the gauge pressure at port A is positive. The direction of motion reverses when the mechanical orientation is negative.
Hard Stop
A set of hard stops limit the piston range of motion. The block uses an implementation of the Translational Hard Stop block, which treats hard stops like spring-damper systems. The spring stiffness coefficient controls the restorative component of the hard-stop contact force and the damping coefficient the dissipative component.
The hard stops are located at the distal ends of the piston stroke. If the mechanical orientation is positive, then the lower hard stop is at x = 0, and the upper hard stop is at x = +stroke. If the mechanical orientation is negative, then the lower hard stop is at x = -stroke, and the upper hard stop is at x = 0.
Block Composite
This block is a composite component based on these Simscape™ Foundation blocks:

Ports
Input
Output
Conserving
Parameters
Extended Capabilities
Version History
Introduced in R2023b
