filter
1-D digital filter of fi objects
Description
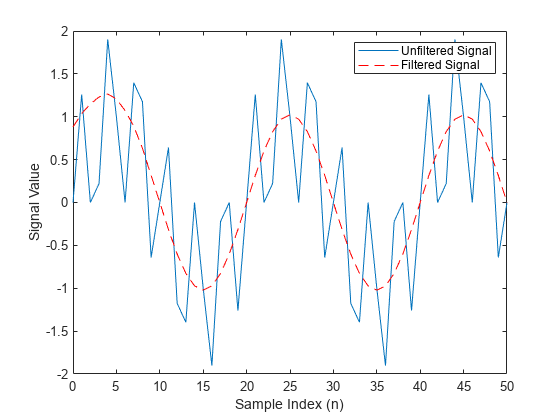
y = filter(b,1,x)x using the filter described
by the fixed-point vector b. The function returns the filtered data in
the output fi object y.
filter always operates along the first non-singleton dimension.
Thus, the filter operates along the first dimension for column vectors and nontrivial
matrices and along the second dimension for row vectors.
Examples
Input Arguments
Output Arguments
Tips
The
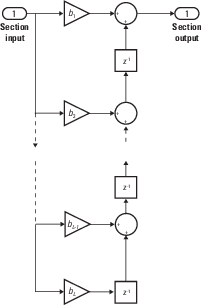
filterfunction only supports FIR filters. In the general filter representation b/a, the denominator a of an FIR filter is the scalar 1, which is the second input of this function.The
numerictypeofbcan be different than thenumerictypeofx.If you want to specify initial conditions but do not know what
numerictypeto use, first try filtering your data without initial conditions. You can do so by specifying[]for the inputzi. After performing the filtering operation, you have thenumerictypeofyandzf(if requested). Because thenumerictypeofzimust match that ofyandzf, you now know thenumerictypeto use for the initial conditions.
Algorithms
Extended Capabilities
Version History
Introduced in R2010a