apskmod
Amplitude phase shift keying (APSK) modulation
Description
Y = apskmod(X,M,radii)X, based on the
specified number of constellation points per PSK ring, M, and
the radius of each PSK ring, radii. For a description of APSK
modulation, see Algorithms.
Note
apskmod specifically applies to multiple ring PSK
constellations. For a single ring PSK constellation, use pskmod.
Y = apskmod(X,M,radii,phaseoffset)
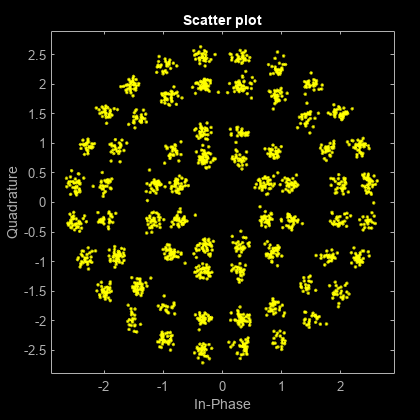
Y = apskmod(___,Name=Value)apskmod(Y,M,PlotConstellation=true) modulates using
modulation order M and plots the constellation. Specify
name-value arguments after all other input arguments.
Examples
Input Arguments
Name-Value Arguments
Output Arguments
Algorithms
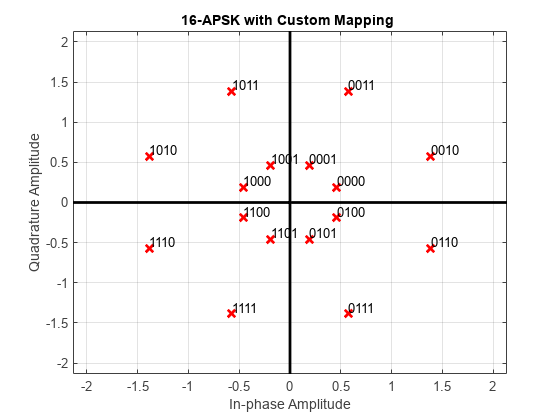
The function implements a pure APSK constellation.
A pure M-APSK constellation is composed of NC concentric rings or contours, each with uniformly spaced PSK points. The M-APSK constellation set is
where:
The modulation order is equal to the sum of all Ml for l = 1, 2, ... , NC.
NC is the number of concentric rings. NC ≥ 2.
Ml is the number of constellation points in the lth ring.
Rl is the radius of the lth ring.
ϕl is the phase offset of the lth ring.
References
[1] Corazza, Giovanni E. Digital Satellite Communications. New York: Springer Science Business Media, LLC, 2007.
[2] Liu, Z., Q. Xie, K. Peng, and Z. Yang. "APSK Constellation with Gray Mapping." IEEE Communications Letters. Vol. 15, Number 12, December 2011, pp. 1271–1273.
Extended Capabilities
Version History
Introduced in R2018a