mslowess
Smooth signal with peaks using nonparametric method
Syntax
Yout = mslowess(X, Intensities)
mslowess(..., 'Order', OrderValue,
...)
mslowess(..., 'Span', SpanValue,
...)
mslowess(..., 'Kernel', KernelValue,
...)
mslowess(..., 'RobustIterations', RobustIterationsValue,
...)
mslowess(..., 'ShowPlot', ShowPlotValue,
...)
Arguments
X | Vector of separation-unit values for
a set of signals with peaks. The number of elements in the vector
equals the number of rows in the matrix Intensities.
The separation unit can quantify wavelength, frequency, distance,
time, or m/z depending on the instrument that generates the signal
data. |
Intensities | Matrix of intensity values for a set
of peaks that share the same separation-unit range. Each row corresponds
to a separation-unit value, and each column corresponds to either
a set of signals with peaks or a retention time. The number of rows
equals the number of elements in vector X. |
Description
Tip
Use the following syntaxes with data from any separation technique that produces signal data, such as spectroscopy, NMR, electrophoresis, chromatography, or mass spectrometry.
Yout = mslowess(X, Intensities)Intensities, using
a locally weighted linear regression (Lowess) method with a default
span of 10 samples.
Note
mslowess assumes the input vector, X,
may not have uniformly spaced separation units. Therefore, the sliding
window for smoothing is centered using the closest samples in terms
of the X value and not in terms of the X index.
Note
When the input vector, X, does not
have repeated values or NaN values, the algorithm is approximately
twice as fast.
mslowess( calls X, Intensities,
...'PropertyName', PropertyValue,
...)mslowess with optional properties
that use property name/property value pairs. You can specify one or
more properties in any order. Each PropertyName must
be enclosed in single quotation marks and is case insensitive. These
property name/property value pairs are as follows:
mslowess(..., 'Order', specifies the order (OrderValue,
...)OrderValue1 (linear polynomial
fit or Lowess), 2 (quadratic polynomial fit or
Loess), or 0 (equivalent to a weighted local mean
estimator and presumably faster because only a mean computation is
performed instead of a least-squares regression). The default value
is 1.
Note
Curve Fitting Toolbox™ software also refers to Lowess smoothing
of order 2 as Loess smoothing.
mslowess(..., 'Span', specifies the window size for the smoothing kernel.
If SpanValue,
...)SpanValue1, the window is equal to SpanValue number
of samples independent of the separation-unit vector, X.
The default value is 10 samples. Higher values
will smooth the signal more at the expense of computation time. If SpanValue is
less than 1, the window size is taken to be a fraction
of the number of points in the data. For example, when SpanValue is 0.005,
the window size is equal to 0.50% of the number
of points in X.
mslowess(..., 'Kernel',
selects the function specified by KernelValue,
...)KernelValue for weighting
the observed intensities. Samples close to the separation-unit location being smoothed
have the most weight in determining the estimate. KernelValue
can be any of the following character vectors (or strings):
'tricubic'(default) —(1 - (dist/dmax).^3).^3'gaussian'—exp(-(2*dist/dmax).^2)'linear'—1-dist/dmax
mslowess(..., 'RobustIterations', specifies the number of iterations (RobustIterationsValue,
...)RobustValueRobustIterationsValue is 0 (default),
no robust fit is performed. For robust smoothing, small residual values
at every span are outweighed to improve the new estimate. 1 or 2 robust
iterations are usually adequate, while larger values might be computationally
expensive.
Note
For an X vector that has uniformly
spaced separation units, a nonrobust smoothing with OrderValue equal
to 0 is equivalent to filtering the signal with
the kernel vector.
mslowess(..., 'ShowPlot', plots the smoothed signal over the original signal.
When you call ShowPlotValue,
...)mslowess without output arguments,
the signals are plotted unless ShowPlotValue is false.
When ShowPlotValue is true,
only the first signal in Intensities is
plotted. ShowPlotValue can also contain
an index to one of the signals in Intensities.
Examples
Load a MAT-file, included with the Bioinformatics Toolbox™ software, that contains some sample data.
load sample_lo_resSmooth the spectra and draw a figure of the first spectrum with original and smoothed signals.
YS = mslowess(MZ_lo_res,Y_lo_res,'Showplot',true);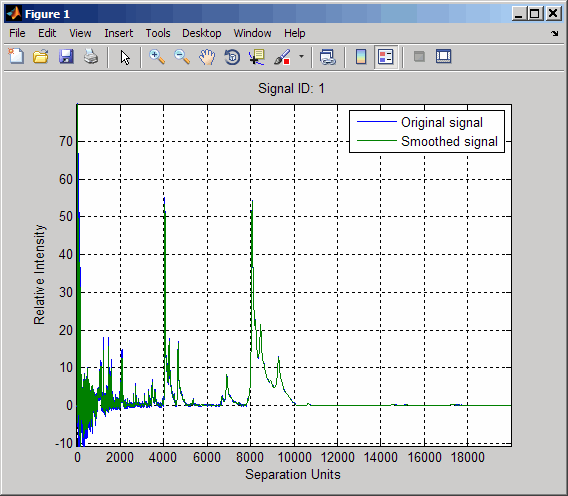
Zoom in on a region of the figure to see the difference in the original and smoothed signals.
axis([7350 7550 0.1 1.0])

Version History
Introduced before R2006a
See Also
mspalign | msbackadj | msdotplot | msalign | msheatmap | msnorm | mspeaks | msresample | msppresample | mssgolay | msviewer
Topics
- Mass Spectrometry and Bioanalytics
- Preprocessing Raw Mass Spectrometry Data
- Visualizing and Preprocessing Hyphenated Mass Spectrometry Data Sets for Metabolite and Protein/Peptide Profiling
- Differential Analysis of Complex Protein and Metabolite Mixtures Using Liquid Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry (LC/MS)