Configure Variants for AUTOSAR Elements
AUTOSAR software components can use VariationPoint elements to enable or disable AUTOSAR elements, such as ports and runnables, based on defined conditions. In Simulink®, to configure variants that enable or disable AUTOSAR ports and runnables:
Use Variant Sink and Variant Source blocks to define variant condition logic and propagate variant conditions.
Use
AUTOSAR.Parameterdata objects with storage classSystemConstantto model AUTOSAR system constants. The system constants represent the condition values that enable or disable ports and runnables.
open_system('mAutosarInlineVariant.slx');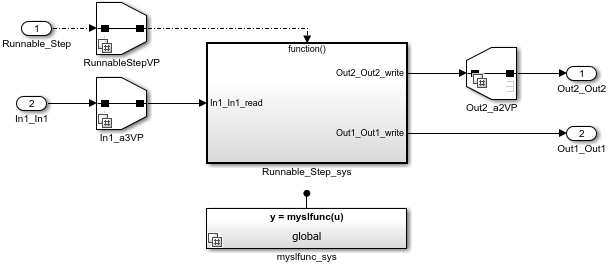
To model an AUTOSAR system constant, the model defines AUTOSAR.Parameter data object SysConA:
SysConA = AUTOSAR.Parameter; SysConA.CoderInfo.StorageClass = 'Custom'; SysConA.CoderInfo.CustomStorageClass = 'SystemConstant'; SysConA.DataType = 'int32'; SysConA.Value = 1;
Each Variant Source or Variant Sink block defines variant condition logic, which is based on the system constant value. You can specify an expression or a Simulink.VariantExpression object containing an expression. Here is the variant condition logic for Variant Source block RunnableStepVP.

When you generate code for the model:
The exported ARXML code contains definitions for variation point proxies and variation points. In this example, the
VARIATION-POINT-PROXYentry has a short-namec0, which is referenced in the generated C code.SysConAappears as a system constant representing the associated condition value.
<VARIATION-POINT-PROXYS>
<VARIATION-POINT-PROXY UUID="...">
<SHORT-NAME>c0</SHORT-NAME>
<CATEGORY>CONDITION</CATEGORY>
<CONDITION-ACCESS BINDING-TIME="PRE-COMPILE-TIME">
<SYSC-REF DEST="SW-SYSTEMCONST">/mInlineVariant_pkg/mInlineVariant_dt/SystemConstants/SysConA</SYSC-REF>
== 0 ||
<SYSC-REF DEST="SW-SYSTEMCONST">/mInlineVariant_pkg/mInlineVariant_dt/SystemConstants/SysConA</SYSC-REF>
== 1</CONDITION-ACCESS>
</VARIATION-POINT-PROXY>
</VARIATION-POINT-PROXYS>
VARIATION-POINT entries appear for AUTOSAR ports, runnables, and runnable accesses to external data.
<R-PORT-PROTOTYPE UUID="..."> <SHORT-NAME>In1</SHORT-NAME> <VARIATION-POINT> <SHORT-LABEL>In1_a3VP</SHORT-LABEL> <SW-SYSCOND BINDING-TIME="PRE-COMPILE-TIME"> <SYSC-REF DEST="SW-SYSTEMCONST">/mInlineVariant_pkg/mInlineVariant_dt/SystemConstants/SysConA</SYSC-REF> == 0 || <SYSC-REF DEST="SW-SYSTEMCONST">/mInlineVariant_pkg/mInlineVariant_dt/SystemConstants/SysConA</SYSC-REF> == 1</SW-SYSCOND> </VARIATION-POINT> ... </R-PORT-PROTOTYPE>
In the RTE compatible C code, short-name
c0is encoded in the names of preprocessor symbols used in the variant condition logic. For example:
#if Rte_SysCon_c0 ... #endif
For more information, see Variant Systems.
See Also
AUTOSAR.Parameter | Variant Sink | Variant Source
Topics
- Model AUTOSAR Variants
- Variant Systems (Simulink Coder)
- System Constants