animate
Replace existing data with new data for animation
Description
Examples
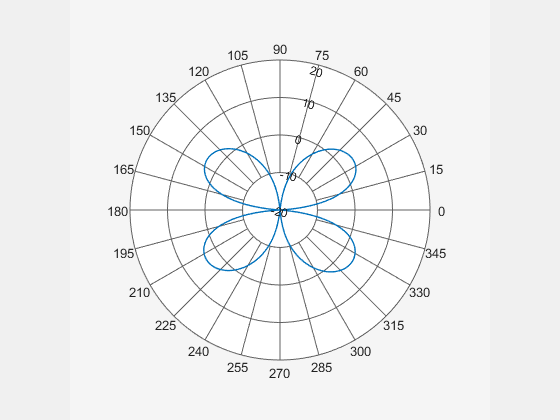
Create a helix antenna that has a 28 mm radius, a 1.2 mm width, and 4 turns. Plot the directivity of the antenna at 1.8 GHz.
hx = helix(Radius=28e-3, Width=1.2e-3, Turns=4); H = pattern(hx,1.8e9,0,0:1:360); P = polarpattern(H);

Create a dipole antenna and calculate its directivity at 270 MHz.
d = dipole; D = pattern(d,270e6,0,0:1:360);
Replace the existing polar plot of the helix antenna with the directivity of the dipole using the animate method.
animate(P,D);
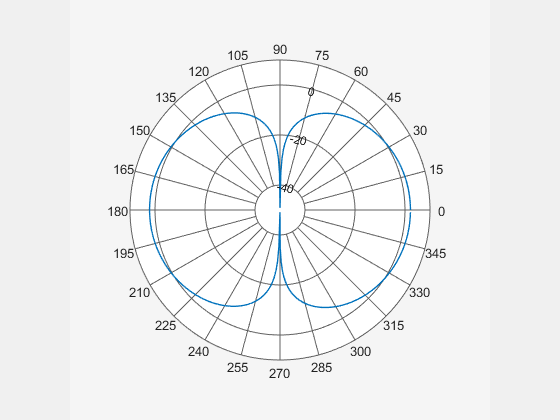
Create a default dipole antenna and plot the polar pattern of its directivity at 1 GHz.
d = dipole; D = pattern(d,75e6,0,0:1:360); P = polarpattern(D);
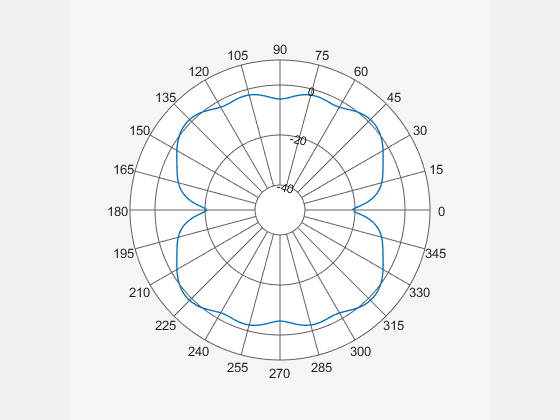
Create a default cavity antenna. Calculate the directivity of the antenna and write the data to cavity.pln using the msiwrite function.
c = cavity; msiwrite(c,2.8e9,"cavity.pln",Name="Cavity Antenna Specifications");
Read the cavity specifications file into Horizontal, Vertical and Optional structures using the msiread function.
[Horizontal,Vertical,optional]= msiread("cavity.pln")Horizontal = struct with fields:
PhysicalQuantity: 'Gain'
Magnitude: [360×1 double]
Units: 'dBi'
Azimuth: [360×1 double]
Elevation: 0
Frequency: 2.8000e+09
Slice: 'Elevation'
Vertical = struct with fields:
PhysicalQuantity: 'Gain'
Magnitude: [360×1 double]
Units: 'dBi'
Azimuth: 0
Elevation: [360×1 double]
Frequency: 2.8000e+09
Slice: 'Azimuth'
optional = struct with fields:
name: 'Cavity Antenna Specifications'
frequency: 2.8000e+09
gain: [1×1 struct]
Replace data from the dipole antenna with data from cavity antenna.
animate(P,Horizontal.Azimuth,Horizontal.Magnitude);
Input Arguments
Polar plot, specified as a scalar handle.
Example: polarpattern
Antenna or array pattern data, specified as one of the following:
A real length-M vector, where M contains the magnitude values with angles assumed to be degrees.
A real M-by-N matrix, where M contains the magnitude values and N contains the independent data sets. Each column in the matrix has angles taken from the vector degrees. The set of each angle can vary for each column.
A real N-D array, where N is the number of dimensions. Arrays with dimensions
2and greater are independent data sets.A complex vector or matrix, where
datacontains Cartesian coordinates ((x,y) of each point. x contains the real part ofdataand y contains the imaginary part ofdata.
When data is in a logarithmic form such as dB, magnitude values
can be negative. In this case,polarpattern plots
the lowest magnitude values at the origin of the polar plot and highest
magnitude values at the maximum radius.
Example: pattern(dipole,70e6)
Set of angles, specified as a vector in degrees.
Set of magnitude values, specified as a vector or a matrix. For a matrix of magnitude values, each column is an independent set of magnitude values and corresponds to the same set of angles.
Version History
Introduced in R2016a
See Also
add | addCursor | createLabels | findLobes | replace | showPeaksTable | showSpan
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.
Website auswählen
Wählen Sie eine Website aus, um übersetzte Inhalte (sofern verfügbar) sowie lokale Veranstaltungen und Angebote anzuzeigen. Auf der Grundlage Ihres Standorts empfehlen wir Ihnen die folgende Auswahl: .
Sie können auch eine Website aus der folgenden Liste auswählen:
So erhalten Sie die bestmögliche Leistung auf der Website
Wählen Sie für die bestmögliche Website-Leistung die Website für China (auf Chinesisch oder Englisch). Andere landesspezifische Websites von MathWorks sind für Besuche von Ihrem Standort aus nicht optimiert.
Amerika
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
Europa
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)