perObservationLoss
Per observation regression or classification error of incremental drift-aware learner
Since R2022b
Description
Err = perObservationLoss(Mdl,X,Y)Mdl trained using the predictors in X and true
observed values in Y.
Err is an n-by-1 vector, where
n is the number of observations.
The fit function
internally calls perObservationLoss during incremental drift-aware learning.
perObservationLoss is suitable for using in custom workflows.
Err = perObservationLoss(Mdl,X,Y,Name=Value)
Examples
Load the human activity dataset. Randomly shuffle the data.
load humanactivity; n = numel(actid); rng(123) % For reproducibility idx = randsample(n,n);
For details on the data set, enter Description at the command line.
Define the predictor and response variables.
X = feat(idx,:); Y = actid(idx);
Responses can be one of five classes: Sitting, Standing, Walking, Running, or Dancing.
Dichotomize the response by identifying whether the subject is moving (actid > 2).
Y = Y > 2;
Flip labels for the second half of the dataset to simulate drift.
Y(floor(numel(Y)/2):end,:) = ~Y(floor(numel(Y)/2):end,:);
Initiate a default incremental drift-aware model for classification as follows:
Create a default incremental linear SVM model for binary classification.
Initiate a default incremental drift-aware model using the incremental linear SVM model as the base learner.
BaseLearner = incrementalClassificationLinear(); idaMdl = incrementalDriftAwareLearner(BaseLearner);
idaMdl is an incrementalDriftAwareLearner model. All its properties are read-only.
Preallocate the number of variables in each chunk for creating a stream of data and the variable to store the classification error.
numObsPerChunk = 50; nchunk = floor(n/numObsPerChunk); ce = array2table(zeros(nchunk,3),VariableNames=["Cumulative" "Window" "Loss"]); PoL = zeros(nchunk,numObsPerChunk); % To store per observation loss values driftTimes = [];
Simulate a data stream with incoming chunks of 50 observations each. At each iteration:
Call
updateMetricsto measure the cumulative performance and the performance within a window of observations. Overwrite the previous incremental model with a new one to track performance metrics.Call
fitto fit the model to the incoming chunk. Overwrite the previous incremental model with a new one fitted to the incoming observations.Call
perObservationLossto compute classification error on each observation in the incoming chunk of data.Call
lossto measure the model performance on the incoming chunk.Store all performance metrics in
ceto see how they evolve during incremental learning. TheMetricsproperty ofidaMdlstores the cumulative and window classification error, which is updated at each iteration. Store the loss values for each chunk in the third column ofce.
for j = 1:nchunk ibegin = min(n,numObsPerChunk*(j-1)+1); iend = min(n,numObsPerChunk*j); idx = ibegin:iend; idaMdl = updateMetrics(idaMdl,X(idx,:),Y(idx)); idaMdl = fit(idaMdl,X(idx,:),Y(idx)); PoL(j,:) = perObservationLoss(idaMdl,X(idx,:),Y(idx)); ce{j,["Cumulative" "Window"]} = idaMdl.Metrics{"ClassificationError",:}; ce{j,"Loss"} = loss(idaMdl,X(idx,:),Y(idx)); if idaMdl.DriftDetected driftTimes(end+1) = j; end end
The updateMetrics function evaluates the performance of the model as it processes incoming observations. The function writes specified metrics, measured cumulatively and within a specified window of processed observations, to the Metrics model property. The fit function fits the model by updating the base learner and monitoring for drift given an incoming batch of data.
Plot the cumulative and per window classification error. Mark the warmup and training periods, and where the drift was introduced.
h = plot(ce.Variables); xlim([0 nchunk]) ylim([0 0.07]) ylabel("Classification Error") xlabel("Iteration") xline(idaMdl.MetricsWarmupPeriod/numObsPerChunk,"g-.","Warmup Period",LineWidth= 1.5) xline(idaMdl.TrainingPeriod/numObsPerChunk,"b-.","Training Period",LabelVerticalAlignment="middle",LineWidth= 1.5) %xline(floor(numel(Y)/2)/numObsPerChunk,"m--","Drift",LabelVerticalAlignment="middle",LineWidth= 1.5) xline(driftTimes,"m--","Drift",LabelVerticalAlignment="middle",LineWidth=1.5) legend(h,ce.Properties.VariableNames) legend(h,Location="best")
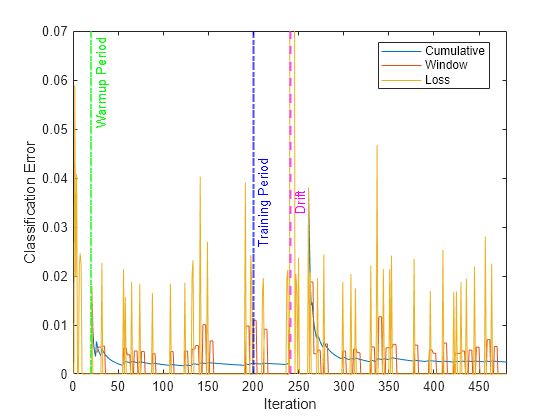
The yellow line represents the classification error on each incoming chunk of data. loss is agnostic of the metrics warm-up period, so it measures the classification error for all iterations. After the metrics warm-up period, idaMdl tracks the cumulative and window metrics.
Plot the per observation loss.
figure()
plot(PoL,'b.');
perObservationLoss computes the classification loss for each observation in the incoming chunk of data.
Create the random concept data and the concept drift generator using the helper functions HelperRegrGenerator and HelperConceptDriftGenerator, respectively.
concept1 = HelperRegrGenerator(NumFeatures=100,NonZeroFeatures=[1,20,40,50,55], ... FeatureCoefficients=[4,5,10,-2,-6],NoiseStd=1.1); concept2 = HelperRegrGenerator(NumFeatures=100,NonZeroFeatures=[1,20,40,50,55], ... FeatureCoefficients=[4,7,10,-1,-5],NoiseStd=1.1); driftGenerator = HelperConceptDriftGenerator(concept1,concept2,15000,1250);
HelperRegrGenerator generates streaming data using features and feature coefficients for regression specified in the call to the function. At each step, the function samples the predictors from a normal distribution. Then, it computes the response using the feature coefficients and predictor values and adding a random noise from a normal distribution with mean zero and specified noise standard deviation.
HelperConceptDriftGenerator establishes the concept drift. The object uses a sigmoid function 1./(1+exp(-4*(numobservations-position)./width)) to decide the probability of choosing the first stream when generating data [3]. In this case, the position argument is 15000 and the width argument is 1250. As the number of observations exceeds the position value minus half of the width, the probability of sampling from the first stream when generating data decreases. The sigmoid function allows a smooth transition from one stream to the other. Larger width values indicate a larger transition period where both streams are approximately equally likely to be selected.
Configure an incremental drift-aware model for regression as follows:
Create an incremental linear model for regression: Track the mean absolute deviation (MAD) to measure the performance of the model. Create an anonymous function that measures the absolute error of each new observation. Create a structure array containing the name
MeanAbsoluteErrorand its corresponding function. Specify a metrics warm-up period of 1000 observations. Specify a metrics window size of 500 observations.Initiate an incremental concept drift detector for continuous data. Use the Hoeffding's Bounds Drift Detection Method with moving average (HDDMA).
Using the incremental linear model and the concept drift detector, instantiate an incremental drift-aware model. Specify the training period as 1000 observations.
maefcn = @(z,zfit,w)(abs(z - zfit)); % Mean absolute deviation function maemetric = struct(MeanAbsoluteError=maefcn); baseMdl = incrementalRegressionLinear(MetricsWarmupPeriod=1000,MetricsWindowSize=400,Metrics=maemetric,EstimationPeriod=0); dd = incrementalConceptDriftDetector("hddma",Alternative="greater",InputType="continuous"); idaMdl = incrementalDriftAwareLearner(baseMdl,DriftDetector=dd,TrainingPeriod=2000);
Generate an initial sample of 20 observations and configure the model to predict responses by fitting it to the initial sample.
initobs = 20;
rng(1234); % For reproducibility
[driftGenerator,X,Y] = hgenerate(driftGenerator,initobs);
idaMdl = fit(idaMdl,X,Y);Preallocate the number of variables in each chunk and number of iterations for creating a stream of data, the variables to store the classification error, drift status, and drift time(s).
numObsPerChunk = 50; numIterations = 500; mae = array2table(zeros(numIterations,3),VariableNames=["Cumulative" "Window" "Chunk"]); PoL = zeros(numIterations,numObsPerChunk); % Per observation loss values driftTimes = []; dstatus = zeros(numIterations,1); statusname = strings(numIterations,1);
Simulate a data stream with incoming chunks of 50 observations each and perform incremental drift-aware learning. At each iteration:
Simulate predictor data and labels, and update the drift generator using the helper function
hgenerate.Call
updateMetricsto compute cumulative and window metrics on the incoming chunk of data. Overwrite the previous incremental model with a new one fitted to overwrite the previous metrics.Call
lossto compute the MAD on the incoming chunk of data. Whereas the cumulative and window metrics require that custom losses return the loss for each observation,lossrequires the loss on the entire chunk. Compute the mean of the absolute deviation.Call
perObservationLossto compute the per observation regression error.Call
fitto fit the incremental model to the incoming chunk of data.Store the cumulative, window, and chunk metrics and per observation loss to see how they evolve during incremental learning.
for j = 1:numIterations % Generate data [driftGenerator,X,Y] = hgenerate(driftGenerator,numObsPerChunk); % Perform incremental fitting and store performance metrics idaMdl = updateMetrics(idaMdl,X,Y); PoL(j,:) = perObservationLoss(idaMdl,X,Y,'LossFun',@(x,y,w)(maefcn(x,y))); mae{j,1:2} = idaMdl.Metrics{"MeanAbsoluteError",:}; mae{j,3} = loss(idaMdl,X,Y,LossFun=@(x,y,w)mean(maefcn(x,y,w))); idaMdl = fit(idaMdl,X,Y); statusname(j) = string(idaMdl.DriftStatus); if idaMdl.DriftDetected driftTimes(end+1) = j; dstatus(j) = 2; elseif idaMdl.WarningDetected dstatus(j) = 1; else dstatus(j) = 0; end end
idaMdl is an incrementalDriftAwareLearner model object trained on all the data in the stream. During incremental learning and after the model is warm, updateMetrics checks the performance of the model on the incoming observations, and the fit function fits the model to those observations.
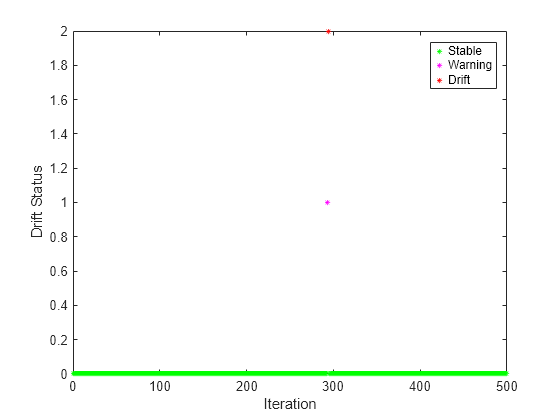
Plot the drift status.
gscatter(1:numIterations,dstatus,statusname,'gmr','*',4,'on',"Iteration","Drift Status") xlim([0 numIterations])
Plot the performance metrics to see how they evolved during incremental learning.
figure h = plot(mae.Variables); xlim([0 numIterations]) ylim([0 4]) ylabel("Mean Absolute Deviation") xlabel("Iteration") xline(idaMdl.MetricsWarmupPeriod/numObsPerChunk,"g-.","Warmup Period",LineWidth= 1.5) xline(idaMdl.TrainingPeriod/numObsPerChunk,"b-.","Training Period",LabelVerticalAlignment="middle",LineWidth= 1.5) xline(driftTimes,"m--","Drift",LabelVerticalAlignment="middle",LineWidth=1.5) legend(h,mae.Properties.VariableNames)
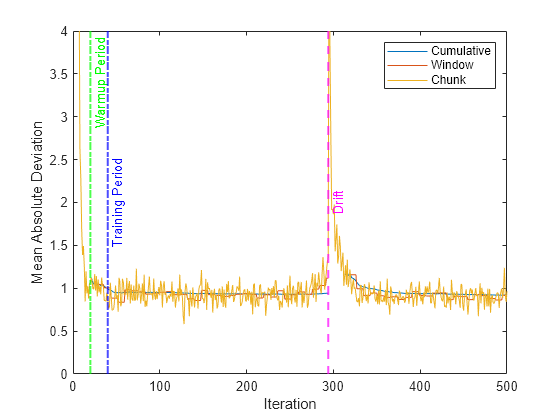
The plot suggests the following:
updateMetricscomputes the performance metrics after the metrics warm-up period only.updateMetricscomputes the cumulative metrics during each iteration.updateMetricscomputes the window metrics after processing 400 observationsBecause
idaMdlwas configured to predict observations from the beginning of incremental learning,losscan compute the MAD on each incoming chunk of data.
Plot the per observation loss.
figure()
plot(PoL,'b.');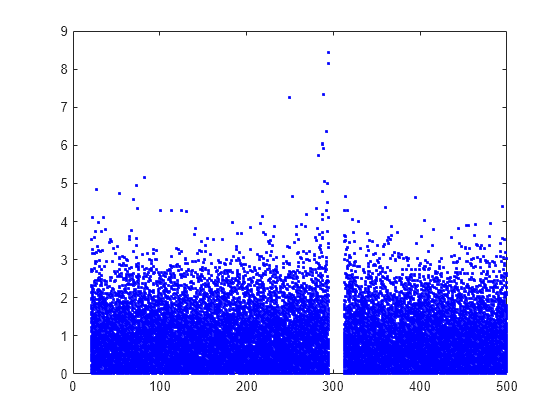
perObservationLoss computes the classification loss for each observation in the incoming chunk of data after the metrics warm-up period.
Input Arguments
Incremental drift-aware learning model fit to streaming data, specified as an incrementalDriftAwareLearner model object. You can create
Mdl using the incrementalDriftAwareLearner
function. For more details, see the object reference page.
Chunk of predictor data used to compute per observation loss, specified as a
floating-point matrix of n observations and
Mdl.BaseLearner.NumPredictors predictor variables.
When Mdl.BaseLearner accepts the
ObservationsIn name-value argument, the value of
ObservationsIn determines the orientation of the variables and
observations. The default ObservationsIn value is
"rows", which indicates that observations in the predictor data are
oriented along the rows of X.
The length of the observation responses (or labels) Y and the
number of observations in X must be equal;
Y( is the response (or label) of
observation j (row or column) in j)X.
Note
perObservationLoss supports only floating-point
input predictor data. If your input data includes categorical data, you must prepare an encoded
version of the categorical data. Use dummyvar to convert each categorical variable
to a numeric matrix of dummy variables. Then, concatenate all dummy variable matrices and any
other numeric predictors. For more details, see Dummy Variables.
Data Types: single | double
Chunk of responses or labels used to compute per observation loss, specified as one of the following.
Floating-point vector of n elements for regression models, where n is the number of rows in
X.Categorical, character, or string array, logical vector, or cell array of character vectors for classification models. If
Yis a character array, it must have one class label per row. Otherwise, it must be a vector with n elements.
The length of Y and the number of observations in
X must be equal; Y(
is the response (or label) of observation j (row or column) in
j)X.
For classification problems:
If
Ycontains a label that is not a member ofMdl.BaseLearner.ClassNames,perObservationLossissues an error.The data type of
YandMdl.BaseLearner.ClassNamesmust be the same.
Data Types: single | double | categorical | char | string | logical | cell
Name-Value Arguments
Specify optional pairs of arguments as
Name1=Value1,...,NameN=ValueN, where Name is
the argument name and Value is the corresponding value.
Name-value arguments must appear after other arguments, but the order of the
pairs does not matter.
Example: ObservationsIn="columns",LossFun="hinge" specifies that the
observations are in columns and the loss function is the built-in hinge loss.
Orientation of the data in X, specified as
"rows" or "columns".
perObservationLoss supports ObservationsIn only
if Mdl.BaseLearner supports the ObservationsIn
name-value argument.
Example: ObservationsIn="columns"
Data Types: char | string
Loss function, specified as a built-in loss function name or a function handle.
The following table lists the built-in loss function names.
For Regression Models:
Name Description "squarederror"Squared error "epsiloninsensitive"Epsilon-insensitive error Default is
"squarederror"for regression models.For Classification Models:
Name Description "binodeviance"Binomial deviance "classiferror"Misclassification error rate "exponential"Exponential "hinge"Hinge "logit"Logistic "quadratic"Quadratic "mincost"Minimal expected misclassification cost (for incrementalClassificationNaiveBayesonly)Default is
"mincost"forincrementalClassificationNaiveBayesmodel object and"classiferror"for other classification objects.Note
You can only specify
"classiferror"forincrementalClassificationECOC.
To specify a custom loss function, use function handle notation. The function must have one of these forms:
For Regression Models:
lossval = lossfcn(Y,YFit)
The output argument
lossvalis a floating-point scalar.You specify the function name (
lossfcnYis a length n numeric vector of observed responses.YFitis a length n numeric vector of corresponding predicted responses.
For Classification Models:
lossval = lossfcn(C,S)
The output argument
lossvalis an n-by-1 floating-point vector, where n is the number of observations inX. The value inlossval(is the classification loss of observationj)jYou specify the function name (
lossfcnCis an n-by-K logical matrix with rows indicating the class to which the corresponding observation belongs.Kis the number of distinct classes (numel(Mdl.BaseLearner.ClassNames)), and the column order corresponds to the class order in theMdl.BaseLearner.ClassNamesproperty. CreateCby settingC(=p,q)1, if observationpqp0.Sis an n-by-K numeric matrix of predicted classification scores.Sis similar to theScoreoutput ofpredict, where rows correspond to observations in the data and the column order corresponds to the class order in theMdl.BaseLearner.ClassNamesproperty.S(is the classification score of observationp,q)pq
Example: LossFun="logit"
Example: LossFun=@lossfcn
Data Types: char | string | function_handle
References
[1] Barros, Roberto S.M. , et al. "RDDM: Reactive drift detection method." Expert Systems with Applications. vol. 90, Dec. 2017, pp. 344-55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2017.08.023.
[2] Bifet, Albert, et al. "New Ensemble Methods for Evolving Data Streams." Proceedings of the 15th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. ACM Press, 2009, p. 139. https://doi.org/10.1145/1557019.1557041.
[3] Gama, João, et al. "Learning with drift detection". Advances in Artificial Intelligence – SBIA 2004, edited by Ana L. C. Bazzan and Sofiane Labidi, vol. 3171, Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 2004, pp. 286–95. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-28645-5_29.
Version History
Introduced in R2022b
See Also
fit | incrementalDriftAwareLearner | loss | updateMetrics | updateMetricsAndFit
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.
Website auswählen
Wählen Sie eine Website aus, um übersetzte Inhalte (sofern verfügbar) sowie lokale Veranstaltungen und Angebote anzuzeigen. Auf der Grundlage Ihres Standorts empfehlen wir Ihnen die folgende Auswahl: .
Sie können auch eine Website aus der folgenden Liste auswählen:
So erhalten Sie die bestmögliche Leistung auf der Website
Wählen Sie für die bestmögliche Website-Leistung die Website für China (auf Chinesisch oder Englisch). Andere landesspezifische Websites von MathWorks sind für Besuche von Ihrem Standort aus nicht optimiert.
Amerika
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
Europa
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)