Measure Servo Motor Shaft Angle Using Device Driver Block in Connected I/O
This topic explains how to enable Connected I/O on a Servo Read device driver block to read the angle of a standard servo motor shaft connected to the Arduino® hardware during normal mode simulation.
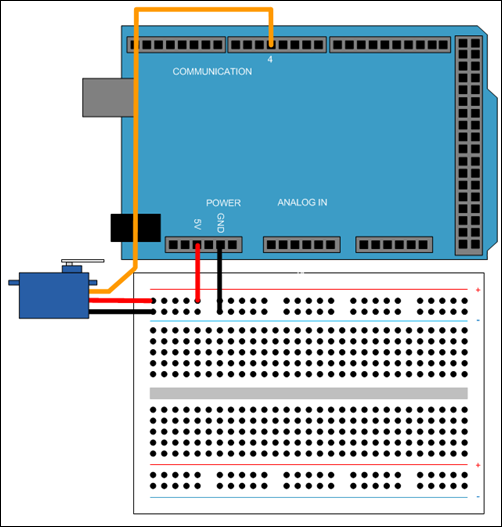
Step 1: Connect the Servo Motor to the Hardware
Connect the micro-USB end of the USB cable to the hardware and the regular USB end of the USB cable to the computer. Wait until the PWR LED on the hardware starts blinking.
Connect the power wire of the servo motor (usually red) to the 5-V pin of the hardware.
Connect the ground wire of the servo motor (usually black) to the ground pin of the hardware.
Connect the signal wire of the servo motor (usually orange) to digital pin 4 of the hardware.
Using the Hardware Setup screen, configure the Arduino hardware network.
For more information on the pins on the hardware, see Pin Mapping for Arduino Timer-Dependent Blocks.
Step 2: Create a Servo Read System Object
Click Create a Device Driver Block to create a device driver System object™. Optionally, you can use the sample Standard Servo Read block,
arduino_StandardServoRead.m, which is available in your
Arduino support package installation folder. To open the sample file, execute
this command in the MATLAB® Command
Window.
open(fullfile(matlabshared.supportpkg.getSupportPackageRoot,'toolbox','target','supportpackages','arduinobase','+codertarget','+arduinobase','+internal','arduino_StandardServoRead.m'))
Step 3: Create a Servo Read Add-On
This section shows how to read the angle of a standard servo motor shaft from the hardware to the Simulink® block and create all the necessary files in your custom library using MATLAB and C++.
Step 4: Specify the Behavior of the Servo Read Device Driver Block
These methods define initialization, output, and termination behavior of the
device driver block. Use setupImpl to initialize the hardware
peripheral. Use stepImpl to read from or write to the hardware
peripheral. Use releaseImpl to release hardware resources
used.
In the MATLAB editor, open the
arduino_StandardServoRead.mclass file.At the top of the code, define the classes the system object inherits from.
& codertarget.arduinobase.ioclient.SimulinkAddonLib
Add the
ioServoReadproperty along with the other properties listed in the file.properties (Nontunable,Hidden) ioServoRead SimulinkIOEn end
Update the
setupImplmethod with this code.function setupImpl(obj) ... elseif coder.target('MATLAB') obj.SimulinkIOEn = codertarget.arduinobase.internal.isSimulinkIoEnabled; if obj.SimulinkIOEn obj.registerAddon('ServoRead/ServoRead'); % Register the addon obj.ioServoRead = arduinoioaddons.ServoRead.ServoRead(obj); % Create an object of the m-class obj.getArduinoIOClient(); % Create IO server with the ServoRead addon end end end
Update the
stepImplmethod to call the methods defined in the class file.function stepImpl(obj,u) ... elseif coder.target('MATLAB') if obj.SimulinkIOEn angle = int32(obj.ioServoRead.read(uint8(obj.pinNumber))); end end end
Update the
releaseImplmethod to unregister the add-on and delete the IO client object.function releaseImpl(obj) if coder.target('MATLAB') if obj.SimulinkIOEn obj.unregisterAddon('ServoRead/ServoRead'); obj.deleteArduinoIOClient; end end end
Step 5: Create a Simulink Model with Servo Read System Object
To bring the ServoRead
System object into Simulink, follow the steps:
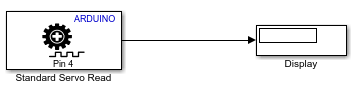
Open a new Simulink model.
Add the Standard Servo Read block to the model.
Double-click the block to specify the Pin Number parameter as
4.From the Sinks library, add the Display block to the model.
Connect the blocks as shown.
Step 6: Read the Shaft Angle in Connected I/O
In the Simulation tab of the Simulink Model Toolbar, change Simulation mode to
Normal.To open the Configuration Parameters dialog box, in the Modeling tab, click Model Settings.
On the Hardware Implementation pane, set Hardware board to match your hardware, for example,
'Arduino Due'.On the Hardware tab of the Simulink model, in the Mode section, select
Connected IOand then click Run with IO. This action will build and run the Simulink model containing your System object on the host computer.
While the model runs on the computer, the Servo Read block reads the position of the shaft once per second and displays the output in the Display block. Modify the model design and monitor the effect of the modified design before deploying the model on the hardware.