Design and Analyze Transmission Line in Shielded Enclosure
This example shows how to design and analyze a transmission line with a shielded enclosure. PCBs often experience unwanted problems such as electromagnetic interference (EMI) leading to performance degradation and failure. This might affect other sensitive electronics due to outgoing EMI. In an ideal world, a shield would completely block off these EMI and ensure that strong signals cannot escape. A microstrip enclosed in a Faraday shield is designed and analyzed using Finite Element Method (FEM). This example also examines an impact of the height of a shielding box and the added metal where a pin from a coax can sit on.
Prerequisites
The example requires the Integro-Differential Modeling Framework for MATLAB add-on. To enable the add-on:
In the Home tab Environment section, click on Add-Ons. This opens the add-on explorer. You need an active internet connection to download the add-on.
Search for Integro-Differential Modeling Framework for MATLAB and click Install
To verify if the download is successful, run
matlab.addons.installedAddonsin your MATLAB® session command line.
Create Variables
Set a designed frequency and a range of frequency.
Centerfreq = 2e9; freq = sort([linspace(1e9,3e9,20),2e9]);
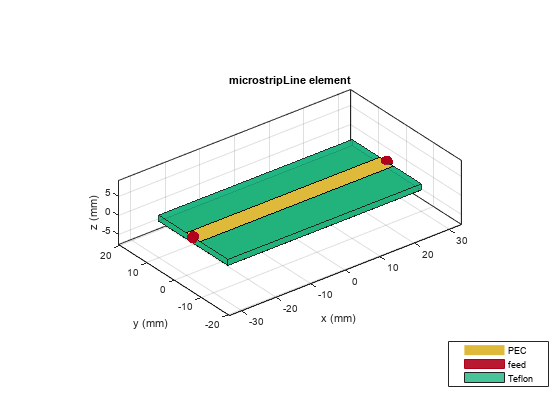
Design of Microstrip
Use the design function on the microstripLine object to create a microstrip at the desired frequency. The default substrate for a microstrip is Teflon.
mline = design(microstripLine,Centerfreq);
Visualize the microstrip.
figure show(mline)
Use the sparameters function to compute the S-parameters in the frequency range of 1 - 3 GHz.
spar1 = sparameters(mline,freq);
Plot the S-parameters of the microstrip.
figure rfplot(spar1,1);
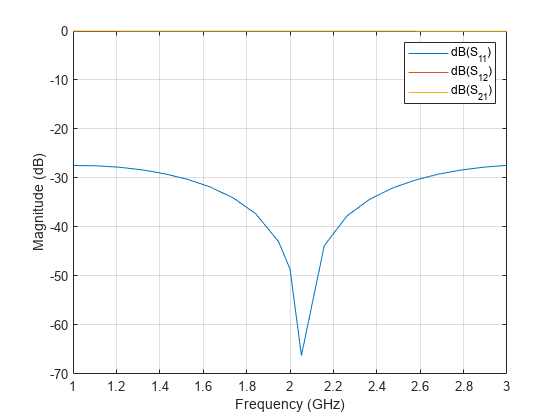
The return coefficient is below -30 dB over the frequency range of 1 - 3 GHz.
Add Metal Shield
Add a 61.8 mm-by-25.6 mm-by-10 mm PEC shielded box to the transmission line. A shield always covers all four sides of a microstrip. Move the shield in z-direction to align its bottom to the ground plane. A microstrip is excited by a coaxial wave port with a characteristic impedance of 50 ohms derived from the outer or inner diameters and the dielectric constant of waveguide region.
mline.IsShielded = true; mline.Shielding.Height = 10e-3; mline.Shielding.Center = [0 0 0.5*mline.Shielding.Height];
Visualize the microstrip.
figure show(mline)
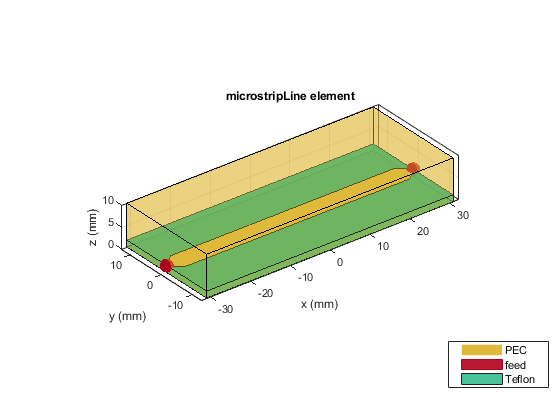
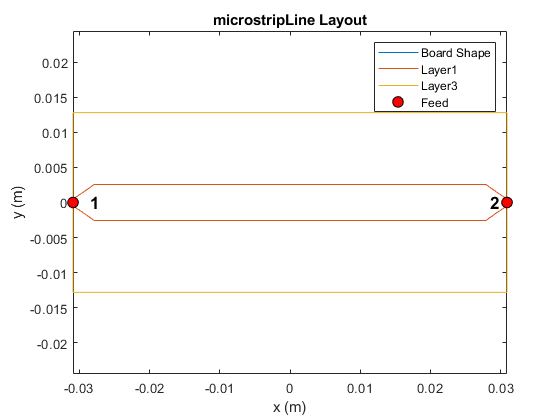
Display the layout of the microstrip. Additional metals are added tapering out from the coax wave port with a width equal to coax inner diameter to the trace of a microstrip. Use PinFootprint and PinLength properties in Connector to determine the shape and length of the added metal for placement of a coax pin . This allows to examine a match between the coax and the borad.
figure layout(mline)
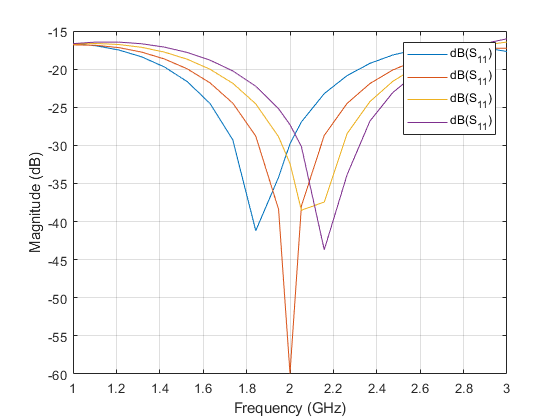
Impact of Added Metal on S-parameters
Set a range of length of added metal from 0.5 mm to 2 mm.
pinLength = (0.5:0.5:2)*1e-3;
Analyze the impact of the length of added tapered metals on the S-parameters. Use the sparameters function to calculate the S-parameters in the frequency range of 1 - 3 GHz.
for i = 1:numel(pinLength) mline.Connector.PinLength = pinLength(i); spar2(i) = sparameters(mline,freq); %#ok<SAGROW> end
Plot the S-parameters of the microstrip with the shield.
figure rfplot(spar2(1),1,1) hold on for i = 2:numel(spar2) rfplot(spar2(i),1,1); end
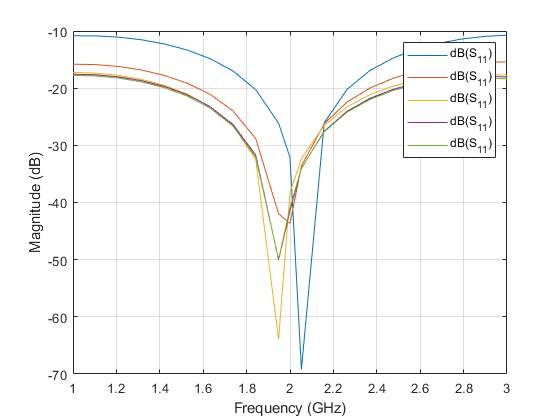
Impact of Shielding Height on S-parameters
Set the range for the shielding height from 4 mm to 20 mm.
shHeight = (4:4:20)*1e-3;
Set the length of added tapered metal to 1 mm.
mline.Connector.PinLength = 1e-3;
Analyze th impact of the shielding height on the S-parameters. Use the sparameters function to calculate the S-parameters in the frequency range of 1 - 3 GHz.
for i = 1:numel(shHeight) mline.Shielding.Height = shHeight(i); mline.Shielding.Center = [0 0 0.5*shHeight(i)]; spar3(i) = sparameters(mline,freq); %#ok<SAGROW> end
Plot the S-parameters of the microstrip with the shield.
figure rfplot(spar3(1),1,1) hold on for i = 2:numel(spar3) rfplot(spar3(i),1,1); end
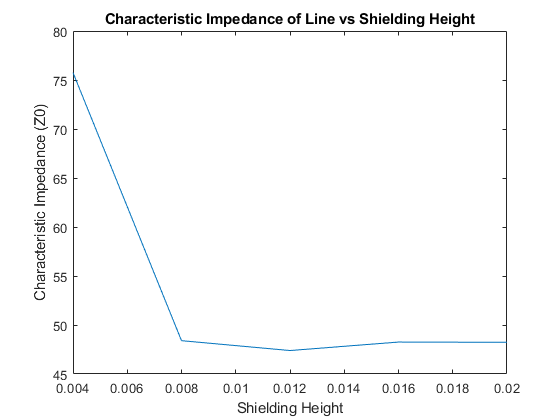
Impact of Shielding Height on Characteristics Impedance
Set the reference impedance.
fcIdx = find(freq==2e9); ZRef = 50;
Calculate the characteristic impedance of the line from the reflection and transmission coefficients.
for i = 1:numel(spar3) s11 = (rfparam(spar3(i),1,1)); s21 = (rfparam(spar3(i),2,1)); % Characteristic impedance of the line Zlin = ((1+s11(fcIdx)).^2 - s21(fcIdx).^2)./((1-s11(fcIdx)).^2 - s21(fcIdx).^2); Z0h(i) = sqrt(ZRef^2*Zlin); %#ok<SAGROW> end
Plot the characteristics impedance of the microstrip with the shield.
figure plot(shHeight,abs(Z0h)) xlabel('Shielding Height') ylabel('Characteristic Impedance (Z0)') title('Characteristic Impedance of Line vs Shielding Height')