Measurement Accuracy, Bias, and Resolution
Definition of Terms
Measurement accuracy and resolution are related concepts that are often confused with one another. Accuracy expresses how close a measurement is to its true value. Resolution is related to the granularity, or fineness, of a measurement. One description of resolution expresses how close together two objects can be before they cannot be distinguished as separate objects. Resolution used in this sense is sometimes referred to as the Rayleigh resolution. Resolution need not refer to two different objects. It can also be used to describe errors in an object size is or how far has an object has moved before its motion can be detected. Accuracy and resolution may apply to radar measurements such as range, azimuth and elevation, and range rate.
Resolution
Resolution is the ability to distinguish between two objects. For example, range resolution is the ability of radar system to distinguish between two or more targets in the same angular direction but at different ranges. Range resolution depends on the bandwidth of the transmitted pulse. A radar system should be able to distinguish targets separated by one-half the pulse width.
You can think of resolution as an instrumentation limitation such as signal bandwidth or antenna aperture size. Each measurement has a characteristic quantity that determines that limitation. It is further assumed that the measurement error associated with a particular parameter is independent of the errors in any of the other parameters, the accuracy is limited only by receiver noise, and that all bias errors are accounted for separately. This table lists the defining characteristic for each measured quantity.
| Radar Measurement | Characteristic Property | Resolution (Δ) |
| Range | Bandwidth | c/BW |
| Angle | Antenna or array aperture | λ/D |
| Speed (Doppler) | Coherent integration time | λ/T |
The range resolution ΔR is the minimum range between two targets that can be resolved and is inversely proportional to the rms signal bandwidth BW. A larger bandwidth provides greater range resolution:
where c is the speed of light. You can use the
RangeResolutionproperty of theradarDataGeneratorSystem object™ to specify the range resolution of the measurement.Range rate resolution Δv defines the minimum separation in range rate at which the radar can distinguish between two targets. Range-rate resolution is inversely proportional to the coherent integration time of N pulses
where Δv is the range-rate resolution, T is the pulse repetition interval (PRI), and N is the number of transmitted pulses. You can use the
RangeRateResolutionproperty to set the range rate resolution.Azimuth and elevation resolutions
are determined primarily by antenna or array aperture size, signal frequency, and array tapering. The
AzimuthResolutionandElevationResolutionproperties of theradarDataGeneratorSystem object specify the minimum angular separation in azimuth angle or elevation angle at which the radar can distinguish between two targets. The angular resolution is typically the half-power (3dB) beamwidth of the of the radar but it can also be the angular distance to the first null. The quantities that affect resolution are antenna or array aperture width, frequency, and array tapering. For a circular aperture of diameter D, the resolution is 1.22λ/D.
Accuracy
The accuracy σmeas of a radar measurement states how precisely the measurement can be made. Accuracy is defined as the root-mean square value (RMS) of the difference between an estimated value of a quantity and its true value. Generally, accuracy is inversely proportional to the square-root of the signal-to-noise ratio and therefore improves with SNR. Accuracy is also a function of resolution. A general relation between resolution and accuracy is
where χ is the received signal-to-noise ratio at the output of a matched filter
Es is the signal energy and σw2is the noise spectral density. SNR denotes detection-level SNR after all processing gains such as coherent pulse integration, pulse compression, Doppler, and beamforming have been included. 𝑘meas is a constant which depends on the type of measurement with a value typically close to one. Called the accuracy improvement factor, kmeas represents how much the accuracy of the measurements is improved over the resolution.
The equation here expresses the accuracy in terms of the kmeas, SNR, and the measurement resolution Δmeas.
The figure below shows the normalized accuracy of a detected object's measurement
plotted against received signal SNR. The accuracy is calculated using the Cramer-Rao bound.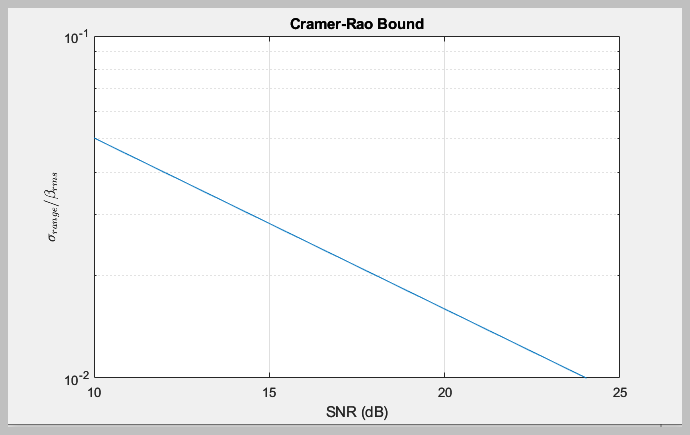
This section shows estimation accuracies of radar parameters
Range estimation accuracy is derived from the pulse time-of-arrival accuracy: which depends on the signal bandwidth (Hz) and the signal-to-noise ratio. Then inserting the equation for range resolution
you can relate σ2Ras
Range-rate estimation accuracy is given
where N is the number pulses, λ is the signal wavelength, and PRI is the pulse repetition interval.
Azimuth and elevation angle estimation accuracies are both expressed by
where φ represents azimuth or elevation. γ is a weighting term to account for the effective array length after spatial tapering is applied to control sidelobes levels and is typically on the order of unity.
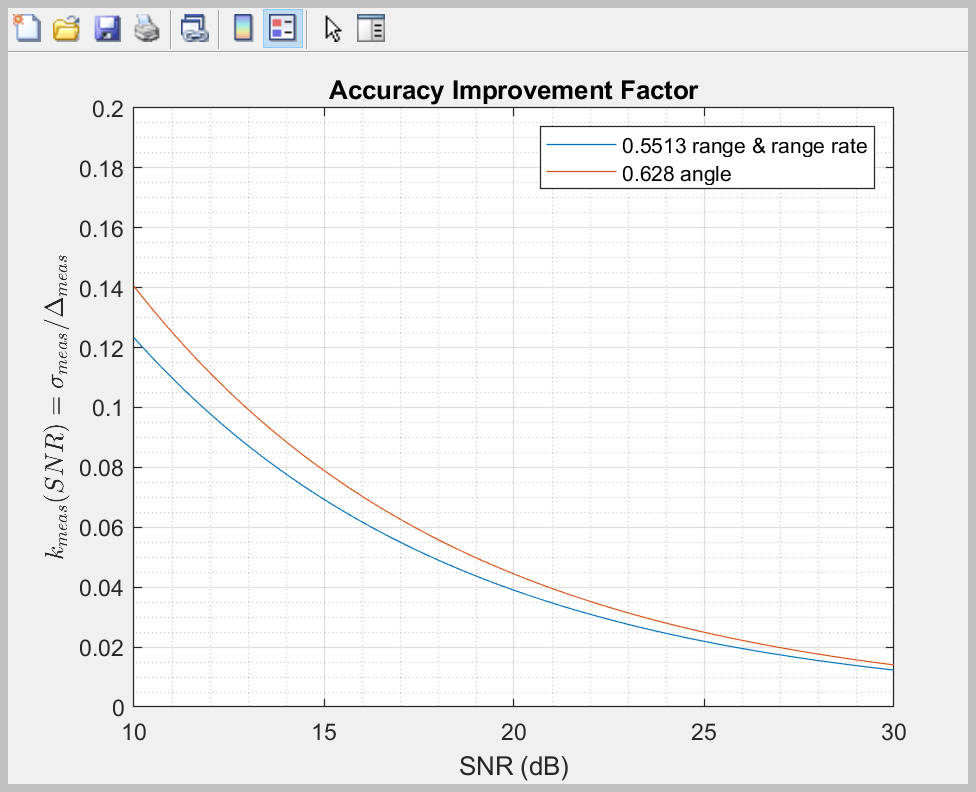
This table gives typical accuracy improvement factors for range, range rate, and angle measurements:
Measurement type | Improvement factor kmeas |
| range (derived for LFM chirp) | sqrt(3)/π ≅ 0.5513 |
| range rate | sqrt(3)/π ≅ 0.5513 |
| angle (azimuth or elevation) | 0.628 |
This figure plots the accuracy improvement factor using parameters specified in the table above for range, range rate, and angle measurements as a functions of SNR. Without biases, the accuracy approaches zero as the SNR increases.
Bias
A measurement may also have a bias which is a constant offset to its measured value. Additional terms are added to the accuracies to account for biases in the estimates of radar parameters. Biases place a lower limit on the estimated accuracies. They may be due to, for example, instrumentation or timing errors.
Range bias, bR, can be specified as a fraction of the range resolution
RangeResolutiondefined using theRangeBiasFractionproperty.
The range rate bias, bv, can be expressed as a fraction of the range-rate resolution
RangeRateResolutionusing theRangeRateBiasFraction.The
AzimuthBiasFractionproperty sets the azimuth error bias and is expressed as a fraction of the azimuth resolutionAzimuthResolutionproperty. The bias sets a lower bound on the azimuth accuracy of the radar. TheElevationBiasFractionproperty is the elevation error bias expressed as a fraction of the elevation resolutionElevationResolutionproperty. This bias sets a lower bound on the elevation accuracy of the radar.
This figure shows the accuracy improvement factor calculated using parameter values specified in the table above for the range, range rate, and angle measurements as a functions of SNR when there are biases present in the measurements.
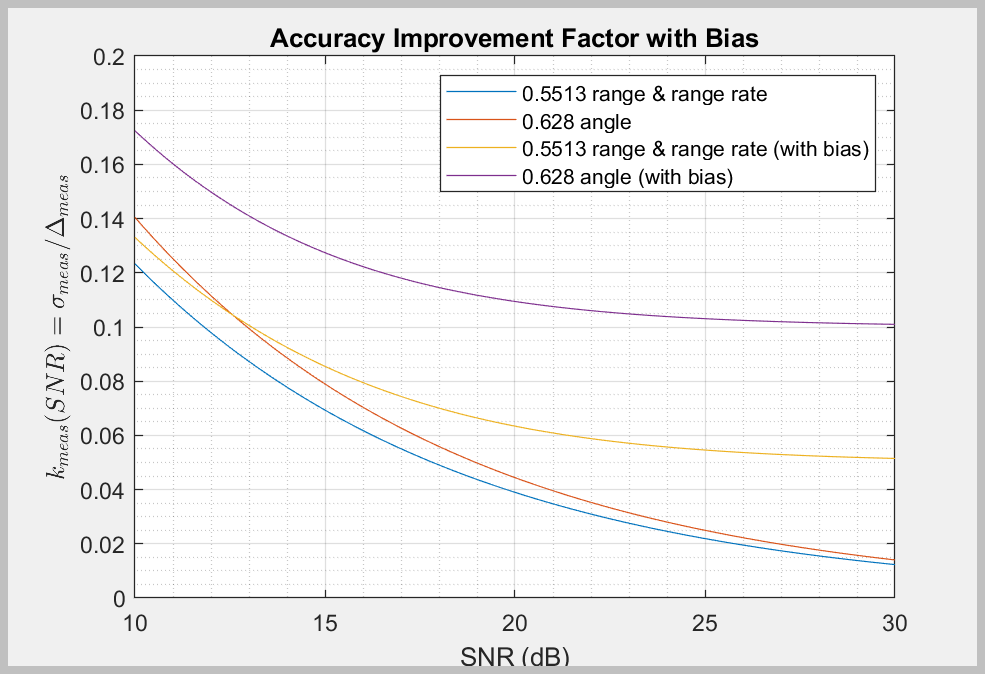
With biases present, the accuracy does not approach zero asymptotically as SNR increases.
References
[1] Richards, M. A. Fundamentals of Radar Signal Processing. Second edition, McGraw-Hill Education, 2014.
[2] Skolnik, Merrill. Radar Handbook. Third Edition, McGraw-Hill Publishing, 2008.