importGeometry
Import geometry from STL or STEP file
Syntax
Description
gm = importGeometry(geometryfile)
gm = importGeometry(model,geometryfile)model container.
importGeometry(
creates a geometry object from the specified STL or STEP geometry file and
includes the geometry in the model,___)model container.
___ = importGeometry(___,
creates a geometry object using one or more name-value arguments. Use this
syntax with any of the argument combinations from the previous syntaxes.Name=Value)
Examples
Input Arguments
Name-Value Arguments
Output Arguments
Limitations
importGeometrydoes not allow you to import a multidomain 2-D or 3-D geometry where subdomains have any common points. If the subdomains of the geometry have common points, the toolbox still treats these subdomains as disconnected, without any common interface between them. Each subdomain has its own mesh.Because of this limitation, you cannot import nested 3-D geometries directly. As a workaround, you can import a mesh and then create a multidomain geometry from the mesh by using the
geometryFromMeshfunction. See Multidomain Geometry Reconstructed from Mesh.
Tips
The STL format approximates the boundary of a CAD geometry by using a collection of triangles, and the
importGeometryfunction reconstructs the faces and edges from this data. Reconstruction from STL data is not precise and can result in a loss of edges and, therefore, the merging of adjacent faces. Typically, lost edges are the edges between two adjacent faces meeting at a small angle, or smooth edges bounding blend surfaces. Usually, the loss of such edges does not affect the analysis workflow.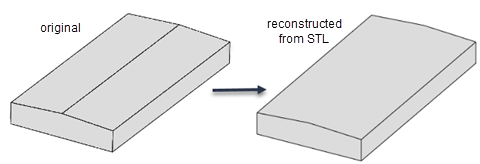
Because STL geometries are only approximations of the original CAD geometries, the areas and volumes of the STL and CAD geometries can differ.




