imclearborder
Suppress light structures connected to image border
Description
J = imclearborder(I)I that are lighter than
their surroundings and connected to the image border. Use this function to clear the
image border or select image borders. For grayscale images,
imclearborder tends to reduce the overall intensity level in
addition to suppressing border structures. The output image J
is grayscale or binary, depending on the input.
J = imclearborder(___,Name=Value)imclearborder(I,Borders=["left" "right"])
removes only the structures touching the left or right border of an image.
Examples
Read a binary image (a postprocessed image of microscopic quartz columnar grains [2]) into the workspace and display it.
originalBW = imread("quartz_columns.png");
imshow(originalBW)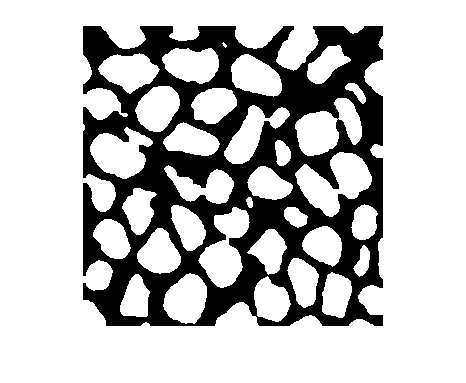
Clear all light objects in the image that are connected to the image border, and display the adjusted image.
BWclearB = imclearborder(originalBW); imshow(BWclearB)

Read a grayscale image containing an object with a dark border into the workspace, and display it.
I = imread("logo.png");
imshow(I)
Complement the image and remove the border. Display the image.
J = imcomplement(I); JNoBorder = imclearborder(J); imshow(JNoBorder)

Complement the image again to return it to the original input image contrast.
INoBorder = imcomplement(JNoBorder); imshow(INoBorder)

Read a binary image (a postprocessed image of microscopic quartz columnar grains [2]) into the workspace, and display it.
originalBW = imread("quartz_columns.png");
imshow(originalBW)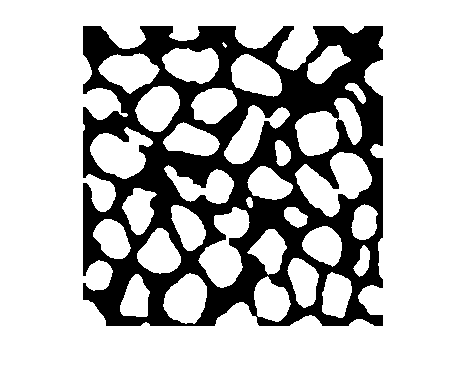
Remove only the objects which are connected to the top or bottom border of the image.
BWclear2B = imclearborder(originalBW, Borders=["top" "bottom"]); imshow(BWclear2B)

Create a simple binary image.
BW = [0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
1 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 0
0 1 0 1 1 1 0 0 0
0 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0];Clear pixels on the border of the image using 4-connectivity. Note that imclearborder does not clear the pixel at (5,2) because, with 4-connectivity, it is not considered connected to the border pixel at (4,1).
BWc1 = imclearborder(BW,Connectivity=4)
BWc1 = 9×9
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 0
0 1 0 1 1 1 0 0 0
0 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Now clear pixels on the border of the image using 8-connectivity. imclearborder clears the pixel at (5,2) because, with 8-connectivity, it is considered connected to the border pixel (4,1).
BWc2 = imclearborder(BW,Connectivity=8)
BWc2 = 9×9
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 0
0 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 0
0 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Input Arguments
Grayscale or binary image, specified as a numeric or logical array of any dimension.
Data Types: single | double | int8 | int16 | int32 | uint8 | uint16 | uint32 | logical
Pixel connectivity, specified as one of the values in this table or a
3-by-3-by- ... -by-3 matrix of 0s and
1s. The default connectivity is 8
for 2-D images and 26 for 3-D images.
Value | Meaning | |
|---|---|---|
Two-Dimensional Connectivities | ||
| Pixels are connected if their edges touch. The neighborhood of a pixel are the adjacent pixels in the horizontal or vertical direction. |
Current pixel is shown in gray. |
| Pixels are connected if their edges or corners touch. The neighborhood of a pixel are the adjacent pixels in the horizontal, vertical, or diagonal direction. |
Current pixel is shown in gray. |
Three-Dimensional Connectivities | ||
| Pixels are connected if their faces touch. The neighborhood of a pixel are the adjacent pixels in:
|
Current pixel is shown in gray. |
| Pixels are connected if their faces or edges touch. The neighborhood of a pixel are the adjacent pixels in:
|
Current pixel is center of cube. |
| Pixels are connected if their faces, edges, or corners touch. The neighborhood of a pixel are the adjacent pixels in:
|
Current pixel is center of cube. |
For higher dimensions, imclearborder uses the default
value conndef(ndims(I),"maximal")
Connectivity can also be
defined in a more general way for any dimension by specifying a 3-by-3-by- ... -by-3 matrix of
0s and 1s. The 1-valued elements
define neighborhood locations relative to the center element of conn. Note
that conn must be symmetric about its center element. See Specifying Custom Connectivities for more information.
If you specify both the conn argument and the
Connectivity name-value argument, then
imclearborder sets the connectivity according to
Connectivity and ignores the value of
conn.
Note
A pixel on the edge of the input image might not be considered to be a
border pixel if you specify a nondefault connectivity. For example, if
conn = [0 0 0; 1 1 1; 0 0 0], elements on the
first and last row are not considered to be border pixels because,
according to that connectivity definition, they are not connected to the
region outside the image.
Data Types: double | logical
Name-Value Arguments
Specify optional pairs of arguments as
Name1=Value1,...,NameN=ValueN, where Name is
the argument name and Value is the corresponding value.
Name-value arguments must appear after other arguments, but the order of the
pairs does not matter.
Example: imclearborder(I,Borders=["left" "right"]) removes light
structures touching the left or right border of an image.
Since R2023b
Image borders to remove structures from, specified as a vector of
strings or an N-by-2 matrix of 0s
and 1s:
Vector of strings — Specifies which borders of a 2-D image to remove structures from as any combination of
"left","right","top", and"bottom". When you specifyIas a 2-D image, the default value ofBordersis["left" "right" "top" "bottom"].N-by-2 matrix of
0s and1s—Specifies which borders of an N-dimensional image to remove structures from, where the first element of each row represents the first border in the corresponding dimension and the second element represents the second border in that dimension. For example, ifBorders(k,1)is1, then structures which touch the first border in the k-th dimension are selected. IfBorders(k,2)is1, then structures which touch the second border in the k-th dimension are selected. For example, specifyingBorders = [0 0; 1 1; 0 0]is equivalent to specifyingBorders = ["left" "right"]. The default value ofBordersfor N-dimensional images isones(ndims(I),2), which specifies to remove structures touching all borders of the image.
Since R2023b
Pixel connectivity, specified as 4,
8, 6, 18,
26, or a 3-by-3-by- ... -by-3 matrix of
0s and 1s. For more
information, see conn.
Data Types: double | logical
Output Arguments
Processed grayscale or binary image, returned as numeric or logical array, depending on the input image you specify.
Algorithms
imclearborder uses morphological reconstruction
where:
The mask image is the input image.
The marker image is 0 everywhere except along the border, where it equals the mask image.
References
[1] Soille, Pierre. Morphological Image Analysis: Principles and Applications Berlin ; New York: Springer, 1999, 164–165.
[2] Molnar, Ian. "Uniform Quartz - Silver Nanoparticle Injection Experiment." Digital Rocks Portal (April 2025). Accessed August 8, 2025. https://www.doi.org/10.17612/P7Z59J.
Extended Capabilities
Usage notes and limitations:
imclearbordersupports the generation of C code (requires MATLAB® Coder™). Note that if you choose the genericMATLAB Host Computertarget platform,imclearbordergenerates code that uses a precompiled, platform-specific shared library. Use of a shared library preserves performance optimizations but limits the target platforms for which code can be generated. For more information, see Types of Code Generation Support in Image Processing Toolbox.Supports only up to 3-D inputs.
The name-value argument
Connectivitymust be a compile-time constant.If the
Bordersvalue is not in numeric matrix form, then you must specify it as a cell array.
Version History
Introduced before R2006aThe imclearborder function shows improved performance. For
example, in the code being timed below, the call to
imclearborder is about 1.7x faster than in the previous
release.
function t = imclearborderTimingTest A = imbinarize(imread("rice.png")); f = @() imclearborder(A); t = timeit(f); end
The approximate execution times are:
R2023a: 0.85 ms
R2023b: 0.51 ms
The code was timed on a macOS 12.5.1, Intel® Core i9 CPU @ 3.6 GHz test system.
Specify the borders at which to remove connected structures by using the
Borders name value argument. For example,
imclearborder(I,Borders=["left" "right"]) removes light
structures touching only the left or right image border.
See Also
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.
Website auswählen
Wählen Sie eine Website aus, um übersetzte Inhalte (sofern verfügbar) sowie lokale Veranstaltungen und Angebote anzuzeigen. Auf der Grundlage Ihres Standorts empfehlen wir Ihnen die folgende Auswahl: .
Sie können auch eine Website aus der folgenden Liste auswählen:
So erhalten Sie die bestmögliche Leistung auf der Website
Wählen Sie für die bestmögliche Website-Leistung die Website für China (auf Chinesisch oder Englisch). Andere landesspezifische Websites von MathWorks sind für Besuche von Ihrem Standort aus nicht optimiert.
Amerika
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
Europa
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)




