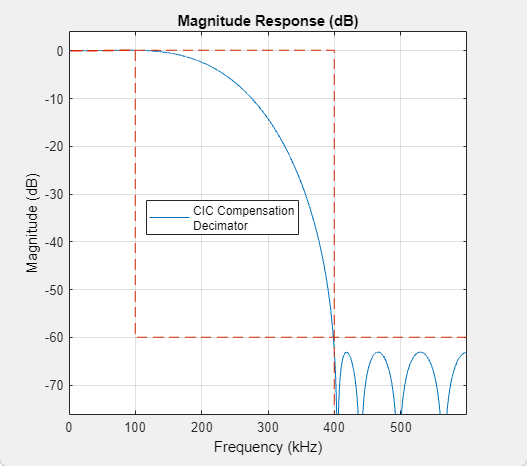
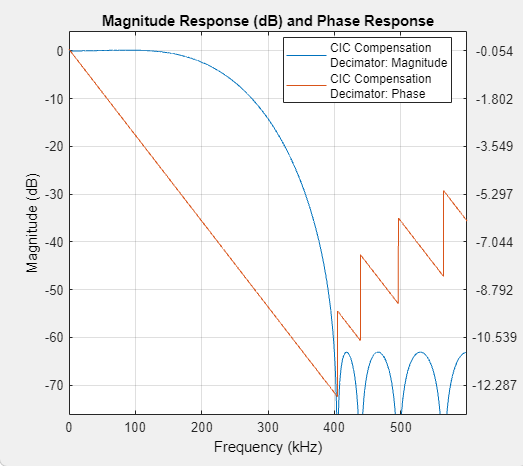
CIC Compensation Decimator
Compensate for CIC filter using FIR decimator
Libraries:
DSP System Toolbox /
Filtering /
Multirate Filters
Description
The CIC Compensation Decimator block uses an FIR polyphase decimator as the compensation filter. CIC compensation decimators are multirate FIR filters that you cascade with CIC decimators to mitigate the drawbacks of the CIC filters.
CIC decimation filters are used in areas that require high decimation. These filters are popular in ASICs and FPGAs, since they do not have any multipliers. CIC filters have two drawbacks:
CIC filters have a magnitude response that causes a droop in the passband region. This magnitude response is:
M — Differential delay
n — Number of stages
ω — Normalized angular frequency
CIC filters have a wide transition region.
The compensation decimator filters have an inverse passband response to correct for the CIC droop, and they have a narrow transition width.
This block brings the capabilities of the dsp.CICCompensationDecimator
System object™ to the Simulink® environment.
Ports
Input
Output
Parameters
Block Characteristics
Data Types |
|
Direct Feedthrough |
|
Multidimensional Signals |
|
Variable-Size Signals |
|
Zero-Crossing Detection |
|
Algorithms
The response of a CIC filter is given by:
R, D, and N are the rate change factor, the differential delay, and the number of sections in the CIC filter, respectively.
After decimation, the CIC response has the form:
The normalized version of this last response is the one that the CIC compensator needs to compensate. Hence, the passband response of the CIC compensator should take the following form:
where ωp is the passband frequency of the CIC compensation filter.
Notice that when ω/2R ≪ π, the previous equation for Hciccomp(ω) can be simplified using the fact that sin(x) ≅ x:
This previous equation is the inverse sinc approximation to the true inverse passband response of the CIC filter.