addElevation
Description
elevatedSceneData = addElevation(sceneData,geoReferencedPointCloud)sceneData by using the elevation
information from the georeferenced point cloud
geoReferencedPointCloud.
Note
This function requires the Scenario Builder for Automated Driving Toolbox™ support package and the Lidar Toolbox™. You can install the Scenario Builder for Automated Driving Toolbox support package from the Add-On Explorer. For more information about installing add-ons, see Get and Manage Add-Ons.
Examples
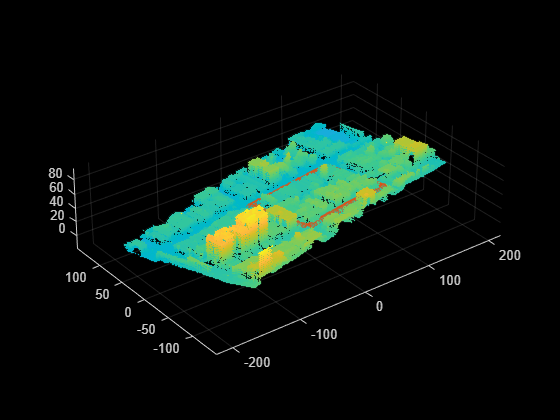
Load a roadrunnerHDMap object into the workspace.
load("addElevationData.mat","rrMap")
Read a georeferenced point cloud for an area that represents the loaded roadrunnerHDMap object.
geoReferencedPointCloud = pcread("USGS_LPC_CA_NoCAL_3DEP_Supp_Funding_2018_D18_w2276n1958_Cropped_geoReferenced.pcd");Use the point cloud to add elevation to the scene data from the roadrunnerHDMap object.
elevatedSceneData = addElevation(rrMap,geoReferencedPointCloud);
Overlay and plot the elevated scene data and georeferenced point cloud. Observe the elevation information added to the scene.
plot(elevatedSceneData) hold on pcshow(geoReferencedPointCloud) hold off
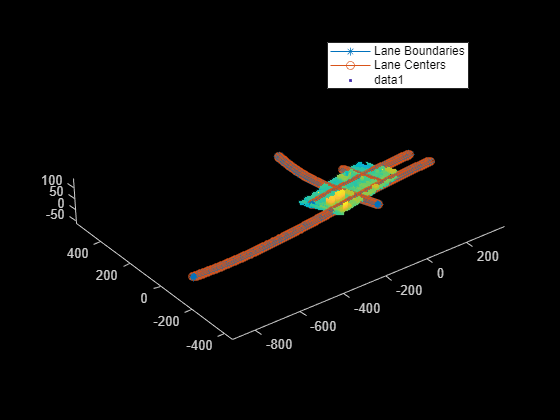
Load 2D lane boundary points into the workspace.
load("addElevationData.mat","laneBoundaryPoints")
Read a georeferenced point cloud for an area that contains the loaded 2D lane boundary points.
geoReferencedPointCloud = pcread("USGS_LPC_CA_NoCAL_3DEP_Supp_Funding_2018_D18_w2276n1958_Cropped_geoReferenced.pcd");Use the point cloud to add elevations to the 2D lane boundary points.
elevatedLanes = addElevation(laneBoundaryPoints,geoReferencedPointCloud);
Overlay and plot the elevated lanes and georeferenced point cloud. Observe the elevation information added to the lane boundary points.
pcshow(geoReferencedPointCloud) hold on scatter3(elevatedLanes(:,1),elevatedLanes(:,2),elevatedLanes(:,3)) hold off
Load static object cuboids into the workspace.
load("addElevationData.mat","statObjs")
Read a georeferenced point cloud for an area that contains the loaded static object cuboids.
geoReferencedPointCloud = pcread("USGS_LPC_CA_NoCAL_3DEP_Supp_Funding_2018_D18_w2276n1958_Cropped_geoReferenced.pcd");Add the elevation information from the point cloud to the static object cuboids, replacing the existing elevation data of the cuboids.
elevatedCuboids = addElevation(statObjs,geoReferencedPointCloud);
Overlay and plot the updated cuboids and georeferenced point cloud. Observe the elevation information added to the static object cuboids.
pcshow(geoReferencedPointCloud) hold on showShape("cuboid",elevatedCuboids) hold off

Input Arguments
Scene data to which to add elevation, specified as a roadrunnerHDMap object, N-by-2 matrix, or
M-by-9 matrix.
Specify lane boundary points as an N-by-2 matrix, where N is the number of lane boundary points. Each row represents a lane boundary point in the form [x y]. For more information, see the Add Elevations to 2D Lane Boundary Points example.
Specify cuboids of static objects as an M-by-9 matrix, where M is the number of static objects. Each row of the matrix specifies a cuboid model of a static object using the form [xctr yctr zctr xlen ylen zlen xrot yrot zrot].
xctr, yctr, and zctr specify the coordinates of the cuboid center.
xlen, ylen, and zlen specify the length of the cuboid, in meters, along the x-, y-, and z-axes, respectively, before rotation has been applied.
xrot, yrot, and zrot specify the rotation angles, in degrees, for the cuboid along the x-, y-, and z-axes, respectively. These angles are clockwise-positive when looking in the forward direction of their corresponding axes.
This figure shows how these values determine the position of a cuboid. All values are in the world coordinate system.

For more information, see the Update Elevations of Static Object Cuboids example.
Note
For locations in the sceneData argument not included in the
geoReferencedPointCloud argument, the
addElevation function extrapolates values from the input point
cloud to estimate elevation. These estimations can be imprecise. To estimate precise
elevation, ensure that all locations in sceneData are included in
geoReferencedPointCloud.
Geographically referenced point cloud data, specified as a pointCloud object. For more information on how to create a georeferenced
point cloud, see the Georeference Sequence of Point Clouds for Scene Generation and Transform Aerial Point Cloud for Scene Generation examples.
Note
The input geoReferencedPointCloud must contain point cloud
data in the east-north-up (ENU) coordinate system.
Output Arguments
Scene data with elevations added from the input
geoReferencedPointCloud, returned as a roadrunnerHDMap object, N-by-3 matrix, or an
M-by-9 matrix.
The function returns one of these outputs based on the value of
sceneData.
RoadRunner HD Map — Elevated RoadRunner HD Map, returned as a
roadrunnerHDMapobject. For more information, see the Add Elevations to RoadRunner HD Map example.Lane boundary points — Lane boundary points, returned as an N-by-3 matrix. N is the number of lane boundary points. Each returned lane boundary point is of the form [x y z]. The z-axis values represent the added elevation information. For more information, see the Add Elevations to 2D Lane Boundary Points example.
Static object cuboids — Cuboids of static objects, returned as an M-by-9 matrix. M is the number of static objects. Each row of the matrix contains a cuboid model of a static object of the form [xctr yctr zctr xlen ylen zlen xrot yrot zrot]. The zctr value represents the updated elevation information for each cuboid. For more information, see the Update Elevations of Static Object Cuboids example.
Version History
Introduced in R2024a
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.
Website auswählen
Wählen Sie eine Website aus, um übersetzte Inhalte (sofern verfügbar) sowie lokale Veranstaltungen und Angebote anzuzeigen. Auf der Grundlage Ihres Standorts empfehlen wir Ihnen die folgende Auswahl: .
Sie können auch eine Website aus der folgenden Liste auswählen:
So erhalten Sie die bestmögliche Leistung auf der Website
Wählen Sie für die bestmögliche Website-Leistung die Website für China (auf Chinesisch oder Englisch). Andere landesspezifische Websites von MathWorks sind für Besuche von Ihrem Standort aus nicht optimiert.
Amerika
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
Europa
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)