Unit Test Generated Code with MATLAB Coder
This example shows how to test the output of generated code by using MATLAB® unit tests with MATLAB® Coder™.
To monitor for regressions in code functionality, you can write unit tests for your code. In MATLAB, you can create and run unit tests by using the MATLAB testing framework. To test MEX code and standalone code that you generate from MATLAB code, you can use the same unit tests that you use to test MATLAB code.
A MEX function includes instrumentation that helps you to detect issues before you generate production code. Running unit tests on a MEX function tests the instrumented code in MATLAB. Generated standalone code (static library or shared library) does not include the instrumentation and can include optimizations that are not present in the MEX code. To run unit tests on standalone code in a separate process outside of MATLAB, use software-in-the-loop (SIL) or processor-in-the-loop (PIL) execution. To use SIL or PIL execution, you must have Embedded Coder®.
This example shows how to:
Create MATLAB unit tests that call your MATLAB function. This example uses class-based unit tests.
Generate a MEX function from your MATLAB function.
Run the unit tests on the MEX function.
Run the unit tests on standalone code by using SIL.
Examine the Files
The example performs unit tests on the MEX function generated from the MATLAB function addOne. This function adds 1 to its input argument.
type addOne.mfunction y = addOne(x) %#codegen y = x + 1; end
The file TestAddOne.m contains a class-based unit test with two tests.
reallyAddsOneverifies that when the input is 1, the answer is 2.addsFractionverifies that when the input is pi, the answer is pi + 1.
For more information about writing class based-unit tests, see Class-Based Unit Tests.
type TestAddOne.mclassdef TestAddOne < matlab.unittest.TestCase
methods ( Test )
function reallyAddsOne( testCase )
x = 1;
y = addOne( x );
testCase.verifyEqual( y, 2 );
end
function addsFraction( testCase )
x = pi;
y = addOne( x );
testCase.verifyEqual( y, x+1 );
end
end
end
The file run_unit_tests.m calls runtests to run the tests in TestAddOne.m.
type run_unit_tests.mruntests('TestAddOne')
Run Unit Tests by Using the MATLAB Coder App
Generate Code
To open the MATLAB Coder app, on the MATLAB Toolstrip Apps tab, under Code Generation, click the MATLAB Coder app icon.
Generate MEX code for the function addOne by following these steps:
Open the Entry Points pane by clicking the Entry Points button in the MATLAB Coder toolstrip.
Type or select
addOneas an entry point function.Expand the function signature and specify that the input argument
xis a double scalar.In the MATLAB Coder toolstrip, from the Build Type list, select
MEX.In the MATLAB Coder toolstrip, click the Generate Code and Build button.
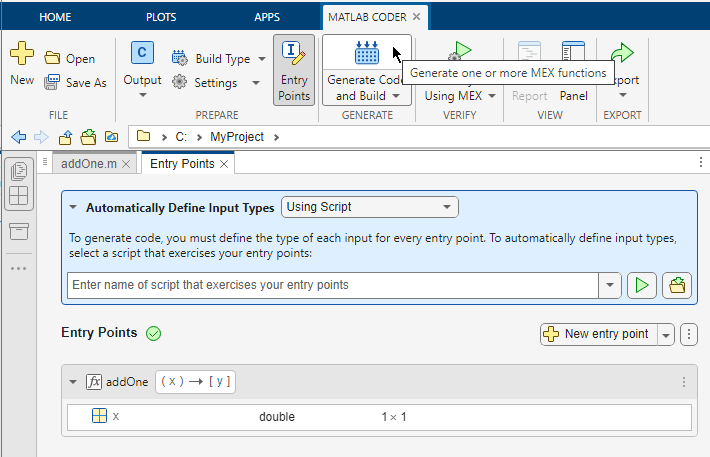
Run Unit Tests on MEX Function
To run units tests on the MEX function, click the Verify Using MEX button. Then, select the test file run_unit_tests.m.
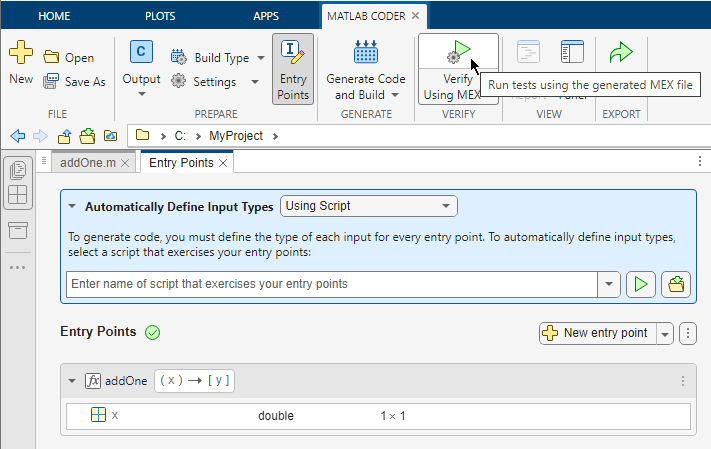
The app displays the test output in the Command Window. The unit tests pass.
To confirm that the unit tests fail when MEX function returns incorrect output, change the generated code by modifying the type of input variable x. On the Entry Points pane, specify that the input argument x is a single scalar. Rerun the unit tests by clicking the Verify Using MEX button in the MATLAB Coder toolstrip.
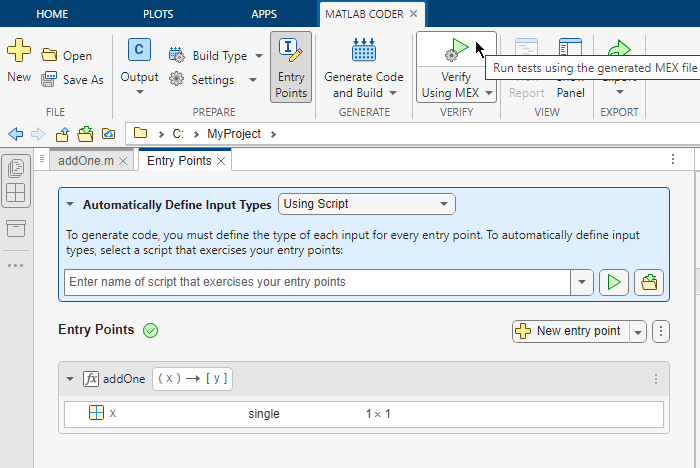
The unit tests fail.
reallyAddsOnefails because the class of the output type is single, not double.addsFractionfails because the output class and value do not match the expected class and value. The output type is single, not double. The value of the single-precision output, 4.1415930, is not the same as the value of the double-precision output, 4.141592653589793.
Run Unit Tests with Software-in-the-Loop Verification (Requires Embedded Coder)
If you have Embedded Coder®, you can run the unit tests on generated standalone code by using software-in-the-loop (SIL) verification.
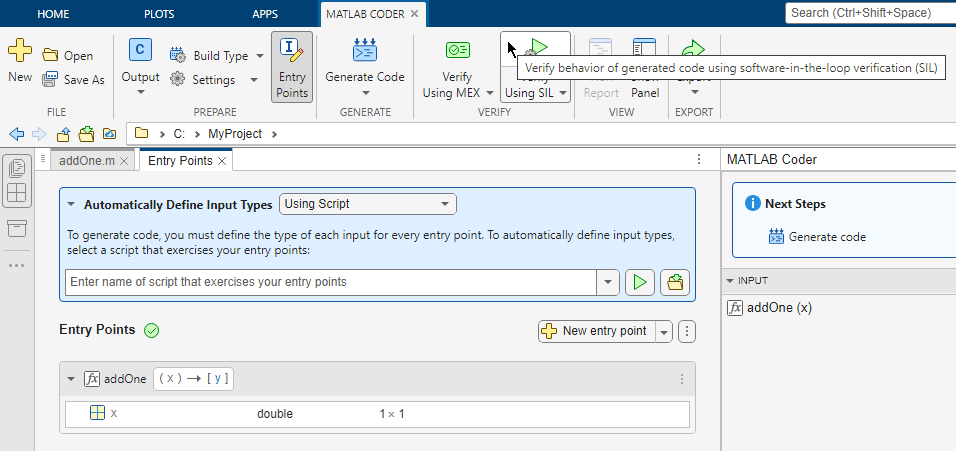
First, generate a standalone static C library for addOne by following these steps:
In the MATLAB Coder toolstrip, from the Build Type list, select
Static Library (.lib).In the MATLAB Coder toolstrip, click the Verify Using SIL button. The app uses the test file
run_unit_tests.m.
Run Unit Tests at the Command Line
Generate Code
If you use the command-line workflow to generate code, you can run unit tests on a MEX function by using coder.runTest with a test file that runs the unit tests.
Generate a MEX function for the addOne function. Specify that the input argument is a double scalar by providing a sample input value.
codegen addOne -args {2}
Code generation successful.
Run Unit Tests on MEX Function
Run the units tests on the MEX function. Specify that the test file is run_unit_tests and that the function is addOne. When coder.runTest runs the test file, it replaces calls to addOne with calls to addOne_mex. The unit tests run on the MEX function instead of the original MATLAB function. The unit tests pass.
coder.runTest("run_unit_tests","addOne");
ans =
1×2 TestResult array with properties:
Name
Passed
Failed
Incomplete
Duration
Details
Totals:
2 Passed, 0 Failed, 0 Incomplete.
0.014247 seconds testing time.
To confirm that the unit tests fail when MEX function returns incorrect output, change the generated code by modifying the type of input variable x. Regenerate the MEX function, and specify that the input argument is a single scalar.
codegen addOne -args {single(2)}
Code generation successful.
Run unit tests on the modified MEX function. The unit tests fail.
coder.runTest("run_unit_tests","addOne")
ans =
1×2 TestResult array with properties:
Name
Passed
Failed
Incomplete
Duration
Details
Totals:
0 Passed, 2 Failed (rerun), 2 Incomplete.
0.0068377 seconds testing time.
Run Unit Tests with Software-in-the-Loop Verification (Requires Embedded Coder)
If you have Embedded Coder, you can run the unit tests on generated standalone code by using software-in-the-loop (SIL) verification.
Create a coder.EmbeddedCodeConfig object for a static library, and configure the object for SIL.
cfg = coder.config("lib"); cfg.VerificationMode = "SIL";
Generate code for the MATLAB function and the SIL interface. Specify that the input argument is a double scalar.
codegen -config cfg -args {2} addOne
Code generation successful.
Run a test file that runs the unit tests with the SIL interface. The unit tests pass.
coder.runTest("run_unit_tests",['addOne_sil.',mexext])
ans =
1×2 TestResult array with properties:
Name
Passed
Failed
Incomplete
Duration
Details
Totals:
2 Passed, 0 Failed, 0 Incomplete.
0.28996 seconds testing time.
clear addOne_sil### Application stopped ### Stopping SIL execution for 'addOne'